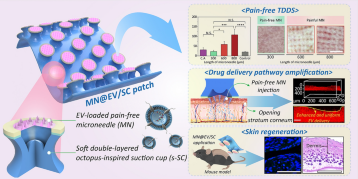
A Hierarchical Short Microneedle-Cupping Dual-Amplified Patch Enables Accelerated, Uniform, Pain-Free Transdermal Delivery of Extracellular Vesicles
Corresponding Author: Changhyun Pang
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 18 (2026), Article Number: 11
Abstract
Microneedles (MNs) have been extensively investigated for transdermal delivery of large-sized drugs, including proteins, nucleic acids, and even extracellular vesicles (EVs). However, for their sufficient skin penetration, conventional MNs employ long needles (≥ 600 μm), leading to pain and skin irritation. Moreover, it is critical to stably apply MNs against complex skin surfaces for uniform nanoscale drug delivery. Herein, a dually amplified transdermal patch (MN@EV/SC) is developed as the stem cell-derived EV delivery platform by hierarchically integrating an octopus-inspired suction cup (SC) with short MNs (≤ 300 μm). While leveraging the suction effect to induce nanoscale deformation of the stratum corneum, MN@EV/SC minimizes skin damage and enhances the adhesion of MNs, allowing EV to penetrate deeper into the dermis. When MNs of various lengths are applied to mouse skin, the short MNs can elicit comparable corticosterone release to chemical adhesives, whereas long MNs induce a prompt stress response. MN@EV/SC can achieve a remarkable penetration depth (290 µm) for EV, compared to that of MN alone (111 µm). Consequently, MN@EV/SC facilitates the revitalization of fibroblasts and enhances collagen synthesis in middle-aged mice. Overall, MN@EV/SC exhibits the potential for skin regeneration by modulating the dermal microenvironment and ensuring patient comfort.
Highlights:
1 A bio-inspired dual-amplified patch (MN@EV/SC) was fabricated by integrating extracellular vesicle-loaded microneedles with a soft suction chamber for effective transdermal delivery.
2 The MN@EV/SC system achieved an exceptional penetration depth of 290 μm, while minimizing plasma corticosterone levels with short microneedles, ensuring patient comfort through pain-free application.
3 This system showed the potential for dermatological application by revitalizing dermal fibroblasts, and enhancing collagen synthesis through effective delivery of extracellular vesicles while preserving their biological functionality.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- B. Berner, V.A. John, Pharmacokinetic characterisation of transdermal delivery systems. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 26(2), 121–134 (1994). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199426020-00005
- F. Benaouda, R. Inacio, C.H. Lim, H. Park, T. Pitcher et al., Needleless administration of advanced therapies into the skin via the appendages using a hypobaric patch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119(18), e2120340119 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2120340119
- W.F. Wong, K.P. Ang, G. Sethi, C.Y. Looi, Recent advancement of medical patch for transdermal drug delivery. Medicina 59(4), 778 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040778
- M.R. Prausnitz, S. Mitragotri, R. Langer, Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3(2), 115–124 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1304
- R.A. Briggaman, C.E. Wheeler, The epidermal-dermal junction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 65(1), 71–84 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1111/1523-1747.ep12598050
- M.K. Kim, S.J. Chung, M.H. Lee, A.R. Cho, C.K. Shim, Targeted and sustained delivery of hydrocortisone to normal and stratum corneum-removed skin without enhanced skin absorption using a liposome gel. J. Control. Release 46(3), 243–251 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(96)01604-5
- S. Fathi-Karkan, M. Heidarzadeh, M.T. Narmi, N. Mardi, H. Amini et al., Exosome-loaded microneedle patches: promising factor delivery route. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 243, 125232 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125232
- J.D. Bos, M.M.H.M. Meinardi, The 500 Dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs. Exp. Dermatol. 9(3), 165–169 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0625.2000.009003165.x
- Y. Han, X. Qin, W. Lin, C. Wang, X. Yin et al., Microneedle-based approaches for skin disease treatment. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 132 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-025-01662-y
- J.D. Byrne, M.R.N. Jajja, A.T. O’Neill, L.R. Bickford, A.W. Keeler et al., Local iontophoretic administration of cytotoxic therapies to solid tumors. Sci. Transl. Med. 7(273), 273ra14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3009951
- E.O. Lallow, N.C. Jhumur, I. Ahmed, S.B. Kudchodkar, C.C. Roberts et al., Novel suction-based in vivo cutaneous DNA transfection platform. Sci. Adv. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abj0611
- Q. Bao, X. Zhang, Z. Hao, Q. Li, F. Wu et al., Advances in polysaccharide-based microneedle systems for the treatment of ocular diseases. Nano-Micro Lett. 16(1), 268 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01477-3
- Y. Xiang, K. Shi, Y. Li, J. Xue, Z. Tong et al., Active micro-nano-collaborative bioelectronic device for advanced electrophysiological recording. Nano-Micro Lett. 16(1), 132 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01336-1
- L. Lin, Y. Wang, M. Cai, X. Jiang, Y. Hu et al., Multimicrochannel microneedle microporation platform for enhanced intracellular drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32(21), 2109187 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202109187
- S.H. Joo, J. Kim, J. Hong, S. Fakhraei Lahiji, Y.H. Kim, Dissolvable self-locking microneedle patches integrated with immunomodulators for cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 35(10), e2209966 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202209966
- R.F. Donnelly, M.J. Garland, A.Z. Alkilani, Microneedle-iontophoresis combinations for enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Methods Mol. Biol. 1141, 121–132 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0363-4_7
- M.T. Clementoni, M.B. Roscher, G.S. Munavalli, Photodynamic photorejuvenation of the face with a combination of microneedling, red light, and broadband pulsed light. Lasers Surg. Med. 42(2), 150–159 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20905
- G. Kang, M. Kim, H. Yang, J. Shin, J. Sim et al., Latch applicator for efficient delivery of dissolving microneedles based on rapid release of elastic strain energy by thumb force. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(11), 2210805 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202210805
- L. Fan, X. Zhang, L. Wang, Y. Song, K. Yi et al., Bio-inspired porous microneedles dwelled stem cells for diabetic wound treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(28), 2316742 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202316742
- Y. Sun, W. He, C. Jiang, J. Li, J. Liu et al., Wearable biodevices based on two-dimensional materials: from flexible sensors to smart integrated systems. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 109 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01597-w
- D.-H. Kim, N. Lu, R. Ma, Y.-S. Kim, R.-H. Kim et al., Epidermal electronics. Science 333(6044), 838–843 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1206157
- D.W. Kim, S. Baik, H. Min, S. Chun, H.J. Lee et al., Highly permeable skin patch with conductive hierarchical architectures inspired by amphibians and octopi for omnidirectionally enhanced wet adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(13), 1807614 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201807614
- A. Generotti, R. Contreras, B. Zounes, E. Schade, A. Kemme et al., Intradermal DNA vaccine delivery using vacuum-controlled, needle-free electroporation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 34, 102070 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102070
- J. Wu, Y. Feng, X. Guo, M. Meng, H. Li et al., A versatile nanovaccine enhancement strategy based on suction-inspired physical therapy. ACS Nano 18(6), 4957–4971 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c10623
- Y. Wu, X. Li, H. Tian, D. Wang, J. Zhang et al., Microtemplated electrowetting for fabrication of shape-controllable microdomes in extruded microsucker arrays toward Octopus-inspired dry/wet adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(7), 2210562 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202210562
- J. Lee, G.W. Hwang, B.S. Lee, N.J. Park, S.N. Kim et al., Artificial Octopus-limb-like adhesive patches for cupping-driven transdermal delivery with nanoscale control of stratum corneum. ACS Nano 18(7), 5311–5321 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c09304
- W. Li, Y. Yu, R. Huang, X. Wang, P. Lai et al., Multi-bioinspired functional conductive hydrogel patches for wound healing management. Adv. Sci. 10(25), e2301479 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202301479
- S. Shin, H. Ko, C.H. Kim, B.K. Yoon, S. Son et al., Curvature-sensing peptide inhibits tumour-derived exosomes for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Mater. 22(5), 656–665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-023-01515-2
- S.P. Davis, B.J. Landis, Z.H. Adams, M.G. Allen, M.R. Prausnitz, Insertion of microneedles into skin: measurement and prediction of insertion force and needle fracture force. J. Biomech. 37(8), 1155–1163 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2003.12.010
- Y.A. Gomaa, D.I.J. Morrow, M.J. Garland, R.F. Donnelly, L.K. El-Khordagui et al., Effects of microneedle length, density, insertion time and multiple applications on human skin barrier function: Assessments by transepidermal water loss. Toxicol. Vitro 24(7), 1971–1978 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2010.08.012
- M. Nohara, A. Tohei, T. Sato, H. Amao, Evaluation of response to restraint stress by salivary corticosterone levels in adult male mice. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 78(5), 775–780 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.15-0610
- M. Benedetti, R. Merino, R. Kusuda, M.I. Ravanelli, F. Cadetti et al., Plasma corticosterone levels in mouse models of pain. Eur. J. Pain 16(6), 803–815 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532-2149.2011.00066.x
- Y. Wang, T. Gao, B. Wang, Application of mesenchymal stem cells for anti-senescence and clinical challenges. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14(1), 260 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-023-03497-z
- K. Zhang, K. Cheng, Stem cell-derived exosome versus stem cell therapy. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 1(9), 608–609 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-023-00064-2
- A. Waseem, Saudamini, R. Haque, M. Janowski, S.S. Raza, Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: shaping the next era of stroke treatment. Neuroprotection 1(2), 99–116 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/nep3.30
- X. Zhang, T. Liu, X. Hou, Z. Zhou, F. Zhang et al., Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells delay brain aging by upregulating SIRT1 expression. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 13213 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-40543-5
- J. Wang, L. Cai, N. Li, Z. Luo, H. Ren et al., Developing mRNA nanomedicines with advanced targeting functions. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 155 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-025-01665-9
- J.H. Lee, Y.J. Won, H. Kim, M. Choi, E. Lee et al., Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote wound healing and tissue regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(13), 10434 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310434
- I.K. Herrmann, M.J.A. Wood, G. Fuhrmann, Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16(7), 748–759 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00931-2
- Y.K. Kim, J. Lee, H.Y. Kim, S.H. Kim, J.H. Hwang et al., Key factors to establish the ovalbumin-induced atopic dermatitis minipig model: age and body weight. Lab. Anim. Res. 38(1), 32 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42826-022-00141-4
- R. Sanz, A.C. Calpena, M. Mallandrich, B. Clares, Enhancing topical analgesic administration: review and prospect for transdermal and transbuccal drug delivery systems. Curr. Pharm. Des. 21(20), 2867–2882 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612821666150428145627
- S. Hu, Z. Li, J. Cores, K. Huang, T. Su et al., Needle-free injection of exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblast spheroids ameliorates skin photoaging. ACS Nano 13(10), 11273–11282 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b04384
- K. Justyna, Ś Patrycja, M. Krzysztof, W. Rafał, Dissolving microneedles fabricated from 3D-printed master molds for application in veterinary medicine. Sci. Rep. 15(1), 14102 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-98984-z
- X.P. Zhang, B.L. Zhang, B.Z. Chen, Z.Q. Zhao, W.M. Fei et al., Dissolving microneedle rollers for rapid transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 12(2), 459–471 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-01048-8
- D. Ando, M. Miyatsuji, H. Sakoda, E. Yamamoto, T. Miyazaki et al., Mechanical characterization of dissolving microneedles: factors affecting physical strength of needles. Pharmaceutics 16(2), 200 (2024). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020200
- J. H. Park, J. An, S. Kwon, (Sungkyunkwan Univ.) Korean Patent KR1027891080000B1, 2025.
- A.C. Franco, C. Aveleira, C. Cavadas, Skin senescence: mechanisms and impact on whole-body aging. Trends Mol. Med. 28(2), 97–109 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2021.12.003
- M.A. Farage, K.W. Miller, P. Elsner, H.I. Maibach, Characteristics of the aging skin. Adv. Wound Care 2(1), 5–10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2011.0356
- J. Krutmann, A. Bouloc, G. Sore, B.A. Bernard, T. Passeron, The skin aging exposome. J. Dermatol. Sci. 85(3), 152–161 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.09.015
- M. Toutfaire, E. Bauwens, F. Debacq-Chainiaux, The impact of cellular senescence in skin ageing: a notion of mosaic and therapeutic strategies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 142, 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.011
- F. Rodier, J. Campisi, Four faces of cellular senescence. J. Cell Biol. 192(4), 547–556 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201009094
- Z. Qin, R.M. Balimunkwe, T. Quan, Age-related reduction of dermal fibroblast size upregulates multiple matrix metalloproteinases as observed in aged human skin in vivo. Br. J. Dermatol. 177(5), 1337–1348 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.15379
- A. Calcinotto, J. Kohli, E. Zagato, L. Pellegrini, M. Demaria et al., Cellular senescence: aging, cancer, and injury. Physiol. Rev. 99(2), 1047–1078 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00020.2018
- K. Chatsirisupachai, D. Palmer, S. Ferreira, J.P. de Magalhães, A human tissue-specific transcriptomic analysis reveals a complex relationship between aging, cancer, and cellular senescence. Aging Cell 18(6), e13041 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13041
- A. Zorina, V. Zorin, A. Isaev, D. Kudlay, M. Vasileva et al., Dermal fibroblasts as the main target for skin anti-age correction using a combination of regenerative medicine methods. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 45(5), 3829–3847 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45050247
- M. Kou, L. Huang, J. Yang, Z. Chiang, S. Chen et al., Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: a next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 13(7), 580 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05034-x
- A. Sivanantham, Y. Jin, Impact of storage conditions on EV integrity/surface markers and cargos. Life 12(5), 697 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050697
- S. Uxa, P. Castillo-Binder, R. Kohler, K. Stangner, G.A. Müller et al., Ki-67 gene expression. Cell Death Differ. 28(12), 3357–3370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00823-x
- S. Zdanov, J. Remacle, O. Toussaint, Establishment of H2O2-induced premature senescence in human fibroblasts concomitant with increased cellular production of H2O2. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1067(1), 210–216 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1354.025
- T. Wang, Z. Jian, A. Baskys, J. Yang, J. Li et al., MSC-derived exosomes protect against oxidative stress-induced skin injury via adaptive regulation of the NRF2 defense system. Biomaterials 257, 120264 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120264
- L. Peterle, S. Sanfilippo, F. Borgia, N. Cicero, S. Gangemi, Alopecia areata: a review of the role of oxidative stress, possible biomarkers, and potential novel therapeutic approaches. Antioxidants 12(1), 135 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010135
- J.-P. Coppé, P.-Y. Desprez, A. Krtolica, J. Campisi, The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: the dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 5, 99–118 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102144
- H. Shoji, K. Takao, S. Hattori, T. Miyakawa, Age-related changes in behavior in C57BL/6J mice from young adulthood to middle age. Mol. Brain 9, 11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-016-0191-9
- M. Terao, M. Tani, S. Itoi, T. Yoshimura, T. Hamasaki et al., 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 specific inhibitor increased dermal collagen content and promotes fibroblast proliferation. PLoS ONE 9(3), e93051 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093051
- J.P. Alameda, Á. Ramírez, R.A. García-Fernández, M. Navarro, A. Page et al., Premature aging and cancer development in transgenic mice lacking functional CYLD. Aging 11(1), 127–159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101732
- S. Zhang, S.J. Chuah, R.C. Lai, J.H.P. Hui, S.K. Lim et al., MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials 156, 16–27 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.11.028
- L. Yu, H. Wen, C. Liu, C. Wang, H. Yu et al., Embryonic stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles rejuvenate senescent cells and antagonize aging in mice. Bioact. Mater. 29, 85–97 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.06.011
- H. Zhang, X. Xiao, L. Wang, X. Shi, N. Fu et al., Human adipose and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mitigate photoaging via TIMP1/Notch1. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9(1), 294 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01993-z
- J. Zhang, J. Guan, X. Niu, G. Hu, S. Guo et al., Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J. Transl. Med. 13, 49 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-015-0417-0
- R. Li, H. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Yang, K. Zhong et al., MSC-EVs and UCB-EVs promote skin wound healing and spatial transcriptome analysis. Sci. Rep. 15, 4006 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-87592-6
- T.P. Lozito, W.M. Jackson, L.J. Nesti, R.S. Tuan, Human mesenchymal stem cells generate a distinct pericellular zone of MMP activities via binding of MMPs and secretion of high levels of TIMPs. Matrix Biol. 34, 132–143 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2013.10.003
- J. Salazar, T. Carmona, F.C. Zacconi, D. Venegas-Yazigi, C. Cabello-Verrugio et al., The human dermis as a target of nanops for treating skin conditions. Pharmaceutics 15(1), 10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010010
- Y. Wang, C. Liu, C. Fang, Q. Peng, W. Qin et al., Engineered cancer nanovaccines: a new frontier in cancer therapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 30 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01533-y
- F. Zhang, H. Zhang, S. Wang, M. Gao, K. Du et al., A dynamically phase-adaptive regulating hydrogel promotes ultrafast anti-fibrotic wound healing. Nat. Commun. 16(1), 3738 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58987-w
- J. Hu, R. Chen, Z. Li, F. Wu, Y. Yang et al., Polyphenol-coordinated supramolecular hydrogel as a promising “one-stop-shop” strategy for acute infected wound treatment. Appl. Mater. Today 29, 101586 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101586
References
B. Berner, V.A. John, Pharmacokinetic characterisation of transdermal delivery systems. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 26(2), 121–134 (1994). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199426020-00005
F. Benaouda, R. Inacio, C.H. Lim, H. Park, T. Pitcher et al., Needleless administration of advanced therapies into the skin via the appendages using a hypobaric patch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119(18), e2120340119 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2120340119
W.F. Wong, K.P. Ang, G. Sethi, C.Y. Looi, Recent advancement of medical patch for transdermal drug delivery. Medicina 59(4), 778 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040778
M.R. Prausnitz, S. Mitragotri, R. Langer, Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3(2), 115–124 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1304
R.A. Briggaman, C.E. Wheeler, The epidermal-dermal junction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 65(1), 71–84 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1111/1523-1747.ep12598050
M.K. Kim, S.J. Chung, M.H. Lee, A.R. Cho, C.K. Shim, Targeted and sustained delivery of hydrocortisone to normal and stratum corneum-removed skin without enhanced skin absorption using a liposome gel. J. Control. Release 46(3), 243–251 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(96)01604-5
S. Fathi-Karkan, M. Heidarzadeh, M.T. Narmi, N. Mardi, H. Amini et al., Exosome-loaded microneedle patches: promising factor delivery route. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 243, 125232 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125232
J.D. Bos, M.M.H.M. Meinardi, The 500 Dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs. Exp. Dermatol. 9(3), 165–169 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0625.2000.009003165.x
Y. Han, X. Qin, W. Lin, C. Wang, X. Yin et al., Microneedle-based approaches for skin disease treatment. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 132 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-025-01662-y
J.D. Byrne, M.R.N. Jajja, A.T. O’Neill, L.R. Bickford, A.W. Keeler et al., Local iontophoretic administration of cytotoxic therapies to solid tumors. Sci. Transl. Med. 7(273), 273ra14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3009951
E.O. Lallow, N.C. Jhumur, I. Ahmed, S.B. Kudchodkar, C.C. Roberts et al., Novel suction-based in vivo cutaneous DNA transfection platform. Sci. Adv. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abj0611
Q. Bao, X. Zhang, Z. Hao, Q. Li, F. Wu et al., Advances in polysaccharide-based microneedle systems for the treatment of ocular diseases. Nano-Micro Lett. 16(1), 268 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01477-3
Y. Xiang, K. Shi, Y. Li, J. Xue, Z. Tong et al., Active micro-nano-collaborative bioelectronic device for advanced electrophysiological recording. Nano-Micro Lett. 16(1), 132 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01336-1
L. Lin, Y. Wang, M. Cai, X. Jiang, Y. Hu et al., Multimicrochannel microneedle microporation platform for enhanced intracellular drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32(21), 2109187 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202109187
S.H. Joo, J. Kim, J. Hong, S. Fakhraei Lahiji, Y.H. Kim, Dissolvable self-locking microneedle patches integrated with immunomodulators for cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 35(10), e2209966 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202209966
R.F. Donnelly, M.J. Garland, A.Z. Alkilani, Microneedle-iontophoresis combinations for enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Methods Mol. Biol. 1141, 121–132 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0363-4_7
M.T. Clementoni, M.B. Roscher, G.S. Munavalli, Photodynamic photorejuvenation of the face with a combination of microneedling, red light, and broadband pulsed light. Lasers Surg. Med. 42(2), 150–159 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20905
G. Kang, M. Kim, H. Yang, J. Shin, J. Sim et al., Latch applicator for efficient delivery of dissolving microneedles based on rapid release of elastic strain energy by thumb force. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(11), 2210805 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202210805
L. Fan, X. Zhang, L. Wang, Y. Song, K. Yi et al., Bio-inspired porous microneedles dwelled stem cells for diabetic wound treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(28), 2316742 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202316742
Y. Sun, W. He, C. Jiang, J. Li, J. Liu et al., Wearable biodevices based on two-dimensional materials: from flexible sensors to smart integrated systems. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 109 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01597-w
D.-H. Kim, N. Lu, R. Ma, Y.-S. Kim, R.-H. Kim et al., Epidermal electronics. Science 333(6044), 838–843 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1206157
D.W. Kim, S. Baik, H. Min, S. Chun, H.J. Lee et al., Highly permeable skin patch with conductive hierarchical architectures inspired by amphibians and octopi for omnidirectionally enhanced wet adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(13), 1807614 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201807614
A. Generotti, R. Contreras, B. Zounes, E. Schade, A. Kemme et al., Intradermal DNA vaccine delivery using vacuum-controlled, needle-free electroporation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 34, 102070 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102070
J. Wu, Y. Feng, X. Guo, M. Meng, H. Li et al., A versatile nanovaccine enhancement strategy based on suction-inspired physical therapy. ACS Nano 18(6), 4957–4971 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c10623
Y. Wu, X. Li, H. Tian, D. Wang, J. Zhang et al., Microtemplated electrowetting for fabrication of shape-controllable microdomes in extruded microsucker arrays toward Octopus-inspired dry/wet adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(7), 2210562 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202210562
J. Lee, G.W. Hwang, B.S. Lee, N.J. Park, S.N. Kim et al., Artificial Octopus-limb-like adhesive patches for cupping-driven transdermal delivery with nanoscale control of stratum corneum. ACS Nano 18(7), 5311–5321 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c09304
W. Li, Y. Yu, R. Huang, X. Wang, P. Lai et al., Multi-bioinspired functional conductive hydrogel patches for wound healing management. Adv. Sci. 10(25), e2301479 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202301479
S. Shin, H. Ko, C.H. Kim, B.K. Yoon, S. Son et al., Curvature-sensing peptide inhibits tumour-derived exosomes for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Mater. 22(5), 656–665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-023-01515-2
S.P. Davis, B.J. Landis, Z.H. Adams, M.G. Allen, M.R. Prausnitz, Insertion of microneedles into skin: measurement and prediction of insertion force and needle fracture force. J. Biomech. 37(8), 1155–1163 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2003.12.010
Y.A. Gomaa, D.I.J. Morrow, M.J. Garland, R.F. Donnelly, L.K. El-Khordagui et al., Effects of microneedle length, density, insertion time and multiple applications on human skin barrier function: Assessments by transepidermal water loss. Toxicol. Vitro 24(7), 1971–1978 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2010.08.012
M. Nohara, A. Tohei, T. Sato, H. Amao, Evaluation of response to restraint stress by salivary corticosterone levels in adult male mice. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 78(5), 775–780 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.15-0610
M. Benedetti, R. Merino, R. Kusuda, M.I. Ravanelli, F. Cadetti et al., Plasma corticosterone levels in mouse models of pain. Eur. J. Pain 16(6), 803–815 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532-2149.2011.00066.x
Y. Wang, T. Gao, B. Wang, Application of mesenchymal stem cells for anti-senescence and clinical challenges. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14(1), 260 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-023-03497-z
K. Zhang, K. Cheng, Stem cell-derived exosome versus stem cell therapy. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 1(9), 608–609 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-023-00064-2
A. Waseem, Saudamini, R. Haque, M. Janowski, S.S. Raza, Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: shaping the next era of stroke treatment. Neuroprotection 1(2), 99–116 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/nep3.30
X. Zhang, T. Liu, X. Hou, Z. Zhou, F. Zhang et al., Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells delay brain aging by upregulating SIRT1 expression. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 13213 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-40543-5
J. Wang, L. Cai, N. Li, Z. Luo, H. Ren et al., Developing mRNA nanomedicines with advanced targeting functions. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 155 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-025-01665-9
J.H. Lee, Y.J. Won, H. Kim, M. Choi, E. Lee et al., Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote wound healing and tissue regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(13), 10434 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310434
I.K. Herrmann, M.J.A. Wood, G. Fuhrmann, Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16(7), 748–759 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00931-2
Y.K. Kim, J. Lee, H.Y. Kim, S.H. Kim, J.H. Hwang et al., Key factors to establish the ovalbumin-induced atopic dermatitis minipig model: age and body weight. Lab. Anim. Res. 38(1), 32 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42826-022-00141-4
R. Sanz, A.C. Calpena, M. Mallandrich, B. Clares, Enhancing topical analgesic administration: review and prospect for transdermal and transbuccal drug delivery systems. Curr. Pharm. Des. 21(20), 2867–2882 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612821666150428145627
S. Hu, Z. Li, J. Cores, K. Huang, T. Su et al., Needle-free injection of exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblast spheroids ameliorates skin photoaging. ACS Nano 13(10), 11273–11282 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b04384
K. Justyna, Ś Patrycja, M. Krzysztof, W. Rafał, Dissolving microneedles fabricated from 3D-printed master molds for application in veterinary medicine. Sci. Rep. 15(1), 14102 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-98984-z
X.P. Zhang, B.L. Zhang, B.Z. Chen, Z.Q. Zhao, W.M. Fei et al., Dissolving microneedle rollers for rapid transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 12(2), 459–471 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-01048-8
D. Ando, M. Miyatsuji, H. Sakoda, E. Yamamoto, T. Miyazaki et al., Mechanical characterization of dissolving microneedles: factors affecting physical strength of needles. Pharmaceutics 16(2), 200 (2024). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020200
J. H. Park, J. An, S. Kwon, (Sungkyunkwan Univ.) Korean Patent KR1027891080000B1, 2025.
A.C. Franco, C. Aveleira, C. Cavadas, Skin senescence: mechanisms and impact on whole-body aging. Trends Mol. Med. 28(2), 97–109 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2021.12.003
M.A. Farage, K.W. Miller, P. Elsner, H.I. Maibach, Characteristics of the aging skin. Adv. Wound Care 2(1), 5–10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2011.0356
J. Krutmann, A. Bouloc, G. Sore, B.A. Bernard, T. Passeron, The skin aging exposome. J. Dermatol. Sci. 85(3), 152–161 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.09.015
M. Toutfaire, E. Bauwens, F. Debacq-Chainiaux, The impact of cellular senescence in skin ageing: a notion of mosaic and therapeutic strategies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 142, 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.011
F. Rodier, J. Campisi, Four faces of cellular senescence. J. Cell Biol. 192(4), 547–556 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201009094
Z. Qin, R.M. Balimunkwe, T. Quan, Age-related reduction of dermal fibroblast size upregulates multiple matrix metalloproteinases as observed in aged human skin in vivo. Br. J. Dermatol. 177(5), 1337–1348 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.15379
A. Calcinotto, J. Kohli, E. Zagato, L. Pellegrini, M. Demaria et al., Cellular senescence: aging, cancer, and injury. Physiol. Rev. 99(2), 1047–1078 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00020.2018
K. Chatsirisupachai, D. Palmer, S. Ferreira, J.P. de Magalhães, A human tissue-specific transcriptomic analysis reveals a complex relationship between aging, cancer, and cellular senescence. Aging Cell 18(6), e13041 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13041
A. Zorina, V. Zorin, A. Isaev, D. Kudlay, M. Vasileva et al., Dermal fibroblasts as the main target for skin anti-age correction using a combination of regenerative medicine methods. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 45(5), 3829–3847 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45050247
M. Kou, L. Huang, J. Yang, Z. Chiang, S. Chen et al., Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: a next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 13(7), 580 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05034-x
A. Sivanantham, Y. Jin, Impact of storage conditions on EV integrity/surface markers and cargos. Life 12(5), 697 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050697
S. Uxa, P. Castillo-Binder, R. Kohler, K. Stangner, G.A. Müller et al., Ki-67 gene expression. Cell Death Differ. 28(12), 3357–3370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00823-x
S. Zdanov, J. Remacle, O. Toussaint, Establishment of H2O2-induced premature senescence in human fibroblasts concomitant with increased cellular production of H2O2. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1067(1), 210–216 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1354.025
T. Wang, Z. Jian, A. Baskys, J. Yang, J. Li et al., MSC-derived exosomes protect against oxidative stress-induced skin injury via adaptive regulation of the NRF2 defense system. Biomaterials 257, 120264 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120264
L. Peterle, S. Sanfilippo, F. Borgia, N. Cicero, S. Gangemi, Alopecia areata: a review of the role of oxidative stress, possible biomarkers, and potential novel therapeutic approaches. Antioxidants 12(1), 135 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010135
J.-P. Coppé, P.-Y. Desprez, A. Krtolica, J. Campisi, The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: the dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 5, 99–118 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102144
H. Shoji, K. Takao, S. Hattori, T. Miyakawa, Age-related changes in behavior in C57BL/6J mice from young adulthood to middle age. Mol. Brain 9, 11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-016-0191-9
M. Terao, M. Tani, S. Itoi, T. Yoshimura, T. Hamasaki et al., 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 specific inhibitor increased dermal collagen content and promotes fibroblast proliferation. PLoS ONE 9(3), e93051 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093051
J.P. Alameda, Á. Ramírez, R.A. García-Fernández, M. Navarro, A. Page et al., Premature aging and cancer development in transgenic mice lacking functional CYLD. Aging 11(1), 127–159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101732
S. Zhang, S.J. Chuah, R.C. Lai, J.H.P. Hui, S.K. Lim et al., MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials 156, 16–27 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.11.028
L. Yu, H. Wen, C. Liu, C. Wang, H. Yu et al., Embryonic stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles rejuvenate senescent cells and antagonize aging in mice. Bioact. Mater. 29, 85–97 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.06.011
H. Zhang, X. Xiao, L. Wang, X. Shi, N. Fu et al., Human adipose and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mitigate photoaging via TIMP1/Notch1. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9(1), 294 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01993-z
J. Zhang, J. Guan, X. Niu, G. Hu, S. Guo et al., Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J. Transl. Med. 13, 49 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-015-0417-0
R. Li, H. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Yang, K. Zhong et al., MSC-EVs and UCB-EVs promote skin wound healing and spatial transcriptome analysis. Sci. Rep. 15, 4006 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-87592-6
T.P. Lozito, W.M. Jackson, L.J. Nesti, R.S. Tuan, Human mesenchymal stem cells generate a distinct pericellular zone of MMP activities via binding of MMPs and secretion of high levels of TIMPs. Matrix Biol. 34, 132–143 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2013.10.003
J. Salazar, T. Carmona, F.C. Zacconi, D. Venegas-Yazigi, C. Cabello-Verrugio et al., The human dermis as a target of nanops for treating skin conditions. Pharmaceutics 15(1), 10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010010
Y. Wang, C. Liu, C. Fang, Q. Peng, W. Qin et al., Engineered cancer nanovaccines: a new frontier in cancer therapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 30 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01533-y
F. Zhang, H. Zhang, S. Wang, M. Gao, K. Du et al., A dynamically phase-adaptive regulating hydrogel promotes ultrafast anti-fibrotic wound healing. Nat. Commun. 16(1), 3738 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58987-w
J. Hu, R. Chen, Z. Li, F. Wu, Y. Yang et al., Polyphenol-coordinated supramolecular hydrogel as a promising “one-stop-shop” strategy for acute infected wound treatment. Appl. Mater. Today 29, 101586 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101586