Observation of Resistive Switching Memory by Reducing Device Size in a New Cr/CrO x /TiO x /TiN Structure
Corresponding Author: Siddheswar Maikap
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 7 No. 4 (2015), Article Number: 392-399
Abstract
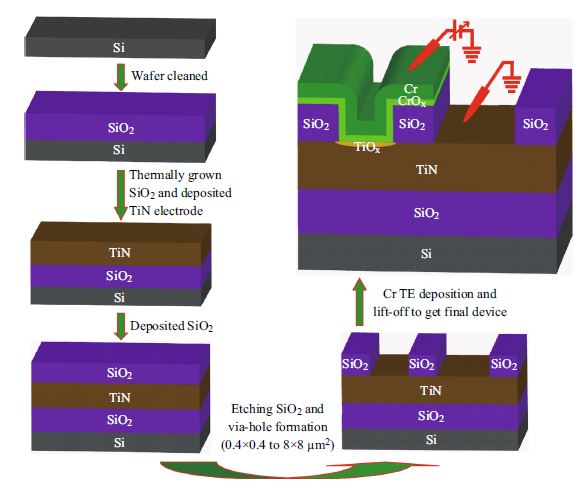
The resistive switching memory characteristics of 100 randomly measured devices were observed by reducing device size in a Cr/CrO x /TiO x /TiN structure for the first time. Transmission electron microscope image confirmed a via-hole size of 0.4 µm. A 3-nm-thick amorphous TiO x with 4-nm-thick polycrystalline CrO x layer was observed. A small 0.4-µm device shows reversible resistive switching at a current compliance of 300 µA as compared to other larger size devices (1–8 µm) owing to reduction of leakage current through the TiO x layer. Good device-to-device uniformity with a yield of >85 % has been clarified by weibull distribution owing to higher slope/shape factor. The switching mechanism is based on oxygen vacancy migration from the CrO x layer and filament formation/rupture in the TiO x layer. Long read pulse endurance of >105 cycles, good data retention of 6 h, and a program/erase speed of 1 µs pulse width have been obtained.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- F. Pan, S. Gao, C. Chen, S. Song, F. Zeng, Recent progress in resistive random access memories: materials, switching mechanisms, and performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 83, 1–59 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.mser.2014.06.002
- K. Terabe, T. Hasegawa, T. Nakayama, M. Aono, Quantized conductance atomic switch. Nature 433, 47–50 (2005). doi:10.1038/nature03190
- R. Waser, M. Aono, Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories. Nat. Mater. 6, 833–840 (2007). doi:10.1038/nmat2023
- B. Govoreanu, G.S. Kar, Y-Y. Chen, V. Paraschiv, S. Kubicek, et al., 10 × 10 nm2 Hf/HfO x crossbar resistive RAM with excellent performance, reliability and low-energy operation. Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 31.6.1–31.6.4. (2011). doi:10.1109/IEDM.2011.6131652
- M.-J. Lee, C.B. Lee, D. Lee, S.R. Lee, M. Chang et al., A fast, high-endurance and scalable non-volatile memory device made from asymmetric Ta2O5−x /TaO2−x bilayer structures. Nat. Mater. 10, 625–630 (2011). doi:10.1038/nmat3070
- A. Prakash, D. Jana, S. Maikap, TaOx–based resistive switching memories: prospective and challenges. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 418 (2013). doi:10.1186/1556-276X-8-418
- B.J. Choi, D.S. Jeong, S.K. Kim, C. Rohde, S. Choi et al., Resistive switching mechanism of TiO2 thin films grown by atomic-layer deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 033715 (2005). doi:10.1063/1.2001146
- J.J. Yang, M.D. Pickett, X. Li, D.A.A. Ohlberg, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 429–433 (2008). doi:10.1038/nnano.2008.160
- C. Hermes, R. Bruchhaus, R. Waser, Forming-free TiO2-based resistive switching devices on CMOS-compatible W-plugs. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 32(11), 1588–1590 (2011). doi:10.1109/LED.2011.2166371
- L. Qingjiang, A. Khiat, L. Salaoru, C. Papavassiliou, X. Hui, T. Prodomakis, Memory impedance in TiO2 based metal-insulator-metal devices. Sci. Rep.-UK 4, 4522 (2014). doi:10.1038/srep04522
- L. Li, Y. Zhang, Z. Chew, A Cu/ZnO nanowire/Cu resistive switching device. Nano-Micro Lett. 5(3), 159–162 (2013). doi:10.1007/BF03353745
- B. Sun, Y. Liu, W. Zhao, J. Wu, P. Chen, Hydrothermal preparation and white-light controlled resistive switching behavior of BaWO4 nanospheres. Nano-Micro Lett. 7(1), 80–85 (2014). doi:10.1007/s40820-014-0021-5
- B. Prasai, B. Sai, M.K. Underwood, J.P. Lewis, D.A. Drabold, Properties of amorphous and crystalline titanium dioxide from first principles. J. Mater. Sci. 47(21), 7515–7521 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6439-6
- D.-H. Kwon, K.M. Kim, J.H. Jang, J.M. Jeon, M.H. Lee et al., Atomic structure of conducting nanofilaments in TiO2 resistive switching memory. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 148–153 (2010). doi:10.1038/nnano.2009.456
- H.Y. Jeong, J.Y. Lee, S.Y. Choi, Interface-engineered amorphous TiO2-based resistive memory devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 3912–3917 (2010). doi:10.1002/adfm.201001254
- J. Park, M. Jo, S. Jung, J. Lee, W. Lee, S. Kim, S. Park, J. Shin, H. Hwang, New set/reset scheme for excellent uniformity in bipolar resistive memory. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 32(3), 228–230 (2011). doi:10.1109/LED.2010.2094599
- E. Goren, M. Ungureanu, R. Zazpe, M. Rozenberg, L.E. Hueso, P. Stoliar, Y. Tsur, F. Casanova, Resistive switching phenomena in TiO x nanoparticle layers for memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 143506 (2014). doi:10.1063/1.4897142
- B. Zeng, D. Xu, M. Tang, Y. Xiao, Y. Zhou, R. Xiong, Z. Li, Y. Zhou, Improvement of resistive switching performance via an amorphous ZrO2 layer formation in TiO2-based forming-free resistive random access memory. J. Appl. Phys. 116, 124514 (2014). doi:10.1063/1.4896402
- J.P. Strachan, M.D. Pickett, J.J. Yang, S. Aloni, A.L.D. Kilcoyne, G.M. Ribeiro, R.S. Williams, Direct identification of the conducting channels in a functioning memristive device. Adv. Mater. 22, 3573–3577 (2010). doi:10.1002/adma.201000186
- W.Y. Chang, H.W. Huang, W.T. Wang, C.H. Hou, Y.L. Chueh, J.R. He, High uniformity of resistive switching characteristics in a Cr/ZnO/Pt device. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159, G29–G32 (2012). doi:10.1149/2.092203jes
- N.R. Mann, R.E. Schafer, N.D. Singpurwalla, Methods for Statistical Analysis of Reliability and Life Data (Wiley publishers, New York, 1974)
- K. Kamiya, M.Y. Yang, S.G. Park, B.M. Kope, Y. Nishi, M. Niwa, K. Shiraishi, ON–OFF switching mechanism of resistive-random-access-memories based on the formation and disruption of oxygen conducting channels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 073502 (2012). doi:10.1063/1.3685222
- S. Roy, S. Maikap, G. Sreekanth, M. Dutta, D. Jana, Y.Y. Chen, J.R. Yang, Improved resistive switching phenomena and mechanism using Cu–Al alloy in a new Cu:AlO x /TaO x /TiN structure. J. Alloy. Compd. 637, 517–523 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.02.168
- H.H. Pham, L.W. Wang, Oxygen vacancy and hole conduction in amorphous TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 541 (2015). doi:10.1039/C4CP04209C
- W. Shen, R. Dittmann, U. Breuer, R. Waser, Improved endurance behavior of resistive switching in (Ba, Sr)TiO3 thin films with W top electrode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 222102 (2008). doi:10.1063/1.3039809
References
F. Pan, S. Gao, C. Chen, S. Song, F. Zeng, Recent progress in resistive random access memories: materials, switching mechanisms, and performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 83, 1–59 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.mser.2014.06.002
K. Terabe, T. Hasegawa, T. Nakayama, M. Aono, Quantized conductance atomic switch. Nature 433, 47–50 (2005). doi:10.1038/nature03190
R. Waser, M. Aono, Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories. Nat. Mater. 6, 833–840 (2007). doi:10.1038/nmat2023
B. Govoreanu, G.S. Kar, Y-Y. Chen, V. Paraschiv, S. Kubicek, et al., 10 × 10 nm2 Hf/HfO x crossbar resistive RAM with excellent performance, reliability and low-energy operation. Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 31.6.1–31.6.4. (2011). doi:10.1109/IEDM.2011.6131652
M.-J. Lee, C.B. Lee, D. Lee, S.R. Lee, M. Chang et al., A fast, high-endurance and scalable non-volatile memory device made from asymmetric Ta2O5−x /TaO2−x bilayer structures. Nat. Mater. 10, 625–630 (2011). doi:10.1038/nmat3070
A. Prakash, D. Jana, S. Maikap, TaOx–based resistive switching memories: prospective and challenges. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 418 (2013). doi:10.1186/1556-276X-8-418
B.J. Choi, D.S. Jeong, S.K. Kim, C. Rohde, S. Choi et al., Resistive switching mechanism of TiO2 thin films grown by atomic-layer deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 033715 (2005). doi:10.1063/1.2001146
J.J. Yang, M.D. Pickett, X. Li, D.A.A. Ohlberg, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 429–433 (2008). doi:10.1038/nnano.2008.160
C. Hermes, R. Bruchhaus, R. Waser, Forming-free TiO2-based resistive switching devices on CMOS-compatible W-plugs. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 32(11), 1588–1590 (2011). doi:10.1109/LED.2011.2166371
L. Qingjiang, A. Khiat, L. Salaoru, C. Papavassiliou, X. Hui, T. Prodomakis, Memory impedance in TiO2 based metal-insulator-metal devices. Sci. Rep.-UK 4, 4522 (2014). doi:10.1038/srep04522
L. Li, Y. Zhang, Z. Chew, A Cu/ZnO nanowire/Cu resistive switching device. Nano-Micro Lett. 5(3), 159–162 (2013). doi:10.1007/BF03353745
B. Sun, Y. Liu, W. Zhao, J. Wu, P. Chen, Hydrothermal preparation and white-light controlled resistive switching behavior of BaWO4 nanospheres. Nano-Micro Lett. 7(1), 80–85 (2014). doi:10.1007/s40820-014-0021-5
B. Prasai, B. Sai, M.K. Underwood, J.P. Lewis, D.A. Drabold, Properties of amorphous and crystalline titanium dioxide from first principles. J. Mater. Sci. 47(21), 7515–7521 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6439-6
D.-H. Kwon, K.M. Kim, J.H. Jang, J.M. Jeon, M.H. Lee et al., Atomic structure of conducting nanofilaments in TiO2 resistive switching memory. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 148–153 (2010). doi:10.1038/nnano.2009.456
H.Y. Jeong, J.Y. Lee, S.Y. Choi, Interface-engineered amorphous TiO2-based resistive memory devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 3912–3917 (2010). doi:10.1002/adfm.201001254
J. Park, M. Jo, S. Jung, J. Lee, W. Lee, S. Kim, S. Park, J. Shin, H. Hwang, New set/reset scheme for excellent uniformity in bipolar resistive memory. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 32(3), 228–230 (2011). doi:10.1109/LED.2010.2094599
E. Goren, M. Ungureanu, R. Zazpe, M. Rozenberg, L.E. Hueso, P. Stoliar, Y. Tsur, F. Casanova, Resistive switching phenomena in TiO x nanoparticle layers for memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 143506 (2014). doi:10.1063/1.4897142
B. Zeng, D. Xu, M. Tang, Y. Xiao, Y. Zhou, R. Xiong, Z. Li, Y. Zhou, Improvement of resistive switching performance via an amorphous ZrO2 layer formation in TiO2-based forming-free resistive random access memory. J. Appl. Phys. 116, 124514 (2014). doi:10.1063/1.4896402
J.P. Strachan, M.D. Pickett, J.J. Yang, S. Aloni, A.L.D. Kilcoyne, G.M. Ribeiro, R.S. Williams, Direct identification of the conducting channels in a functioning memristive device. Adv. Mater. 22, 3573–3577 (2010). doi:10.1002/adma.201000186
W.Y. Chang, H.W. Huang, W.T. Wang, C.H. Hou, Y.L. Chueh, J.R. He, High uniformity of resistive switching characteristics in a Cr/ZnO/Pt device. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159, G29–G32 (2012). doi:10.1149/2.092203jes
N.R. Mann, R.E. Schafer, N.D. Singpurwalla, Methods for Statistical Analysis of Reliability and Life Data (Wiley publishers, New York, 1974)
K. Kamiya, M.Y. Yang, S.G. Park, B.M. Kope, Y. Nishi, M. Niwa, K. Shiraishi, ON–OFF switching mechanism of resistive-random-access-memories based on the formation and disruption of oxygen conducting channels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 073502 (2012). doi:10.1063/1.3685222
S. Roy, S. Maikap, G. Sreekanth, M. Dutta, D. Jana, Y.Y. Chen, J.R. Yang, Improved resistive switching phenomena and mechanism using Cu–Al alloy in a new Cu:AlO x /TaO x /TiN structure. J. Alloy. Compd. 637, 517–523 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.02.168
H.H. Pham, L.W. Wang, Oxygen vacancy and hole conduction in amorphous TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 541 (2015). doi:10.1039/C4CP04209C
W. Shen, R. Dittmann, U. Breuer, R. Waser, Improved endurance behavior of resistive switching in (Ba, Sr)TiO3 thin films with W top electrode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 222102 (2008). doi:10.1063/1.3039809