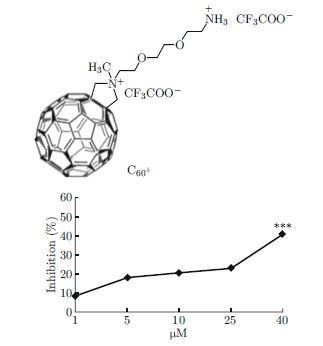
A Cationic [60] Fullerene Derivative Reduces Invasion and Migration of HT-29 CRC Cells in Vitro at Dose Free of Significant Effects on Cell Survival
Corresponding Author: Gianni Sava
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 6 No. 2 (2014), Article Number: 163-168
Abstract
Nanomaterials with unique characteristics exhibit favorable therapeutic and diagnostic properties, implying their enormous potential as biomedical candidates. C60 has been used in gene- and drug-delivery, as imaging agents, and as photosensitizers in cancer therapy. In this study, the influences of a cationic functionalized fullerene on cellular behavior of human colorectal cancer cell line (HT-29) were investigated. Results indicated that HT-29 treated with the studied compound showed a lower sensitivity but a significant impairment in migration and invasion by interfering with the activities of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and 9). The presence of fullerene also altered the capacity of adhesion-related proteins to perform their activity, thereby inducing dramatically adverse effects on the cell physiological functions such as cell adhesion. Thus, our study suggests that this compound is a new potential anti-metastatic effector and a therapeutic component for malignant colorectal cancer.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- A. Jemal, R. Siegel, J. Xu and E. Ward, “Cancer statistics, 2010”, CA Cancer J. Clin. 60(5), 277–300 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.3322/caac.20073
- J. M. Davies and R. M. Goldberg, “Treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer”, Semin. Oncol. 38(4), 552–60 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2011.05.009
- K. K. Jain, “Nanotechnology in clinical laboratory diagnostics”, Clin. Chim. Acta 358 (1–2), 37–54 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cccn.2005.03.014
- P. Chaudhuri, R. Harfouche, S. Soni, D. M. Hentschel, and S. Sengupta, “Shape effect of carbon nanovectors on angiogenesis”, ACS Nano 4(1), 574–82 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn901465h
- M. Grodzik, E. Sawosz, M. Wierzbicki, P. Orlowski, A. Hotowy, T. Niemiec, M. Szmidt, K. Mitura and A. Chwalibog, “Nanoparticles of carbon allotropes inhibit glioblastoma multiforme angiogenesis in ovo”, Int. J. Nanomed. 6, 3041–3048 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S25528
- M. Wierzbicki, E. Sawosz, M. Grodzik, M. Prasek, S. Jaworski and A. Chwalibog “Comparison of antiangiogenic properties of pristine carbon nanoparticles”, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8(1), 195 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-8-195
- S. V. Prylutska, A. P. Burlaka, Y. I. Prylutskyy, U. Ritter and P. Scharff, “Pristine C(60) fullerenes inhibit the rate of tumor growth and metastasis”, Exp Oncol 33(3), 162–164 (2011).
- C. Chen, G. Xing, J. Wang, Y. Zhao, B. Li, J. Tang, G. Jia, T. Wang, J. Sun, L. Xing, H. Yuan, Y. Gao, H. Meng, Z. Chen, F. Zhao, Z. Chai and X. Fang, “Multihydroxylated [Gd@C82(OH)22]n nanoparticles: Antineoplastic activity of high efficiency and low toxi-city”, Nano Lett. 5(10), 2050–2057 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nl051624b
- M. Lucafò, S. Pacor, C. Fabbro, T. Da Ros, S. Zorzet, M. Prato and G. Sava, “Study of a potential drug delivery system based on carbon nanoparticles: Effects of fullerene derivatives in MCF7 mammary carcinoma cells”, J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1–13 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0830-8
- M. Lucafò, M. Gerdol, A. Pallavicini, S. Pacor, S. Zorzet, T. Da Ros, M. Prato and G. Sava, “Profiling the molecular mechanism of fullerene cytotoxicity on tumorcells by RNA-seq”, Toxicology 314(1), 183–192 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2013.10.001
- K. Kordatos, T. Da Ros, S. Bosi, E. Vazquez, M. Bergamin, C. Cusan, F. Pellarini, V. Tomberli, B. Baiti, D. Pantarotto, V. Georgakilas, G. Spalluto and M. Prato, “Novel versatile fullerene synthons”, J. Org. Chem. 66, 4915–4920 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jo015608k
- A. Albini, Y. Iwamoto, H. K. Kleinman, G. R. Martin, S. A. Aaronson, J. M. Kozlowski and R. N. McEwan, “A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells”, Cancer Res. 47(12), 3239–45 (1987).
- P. Provenzano and P. J. Keely, “Mechanical signaling through the cytoskeleton regulates cell proliferation by coordinated focal adhesion and Rho GTPase signalling”, J. Cell Sci. 124 (Pt8), 1195–1205 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.067009
- F. G. Giancotti and E. Ruoslahti, “Integrin signaling”, Science 285(5430), 1028–1032 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5430.1028
- J. D. Hood and D. A. Cheresh, “Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration”, Nature Rev. Cancer 2(2), 91–100 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc727
- F. Aoudjit and K. Vuori, “Integrin signaling in cancer cell survival and chemoresistance”, Chemother. Res. Pract. 1-16 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/283181
- M. Millard, S. Odde and N. Neamati, “Integrin targeted therapeutics”, Theranostics 1, 154–188 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.7150/thno/v01p0154
- S. Hernandez-Barrantes, M. Bernardo, M. Toth, and R. Fridman, “Regulation of membrane type-matrix metalloproteinases”, Semin. Cancer Biol. 12(2), 131–138 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/scbi.2001.0421
- H. Sato, T. Takino, Y. Okada, J. Cao, A. Shinagawa, E. Yamamoto, and M. Seiki, “A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells”, Nature 370(6484), 61–65 (1994). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/370061a0
- A. Y. Strongin, B. L. Marmer, G. A. Grant and G. I. Goldberg “Plasma membrane-dependent activation of the 72-kDa type IV collagenase is prevented by complex formation with TIMP-2”, J. Biol. Chem. 268(19), 14033–14039 (1993).
- Q. Nguyen, F. Willenbrock, M. I. Cockett, M. O’Shea, A. J. Docherty and G. Murphy, “Different domain interactions are involved in the binding of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases to stromelysin-1 and gelatinase A”, Biochem. 33(8), 2089–2095 (1994). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi00174a015
- M. Bernardo and R. Fridman, “TIMP-2 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2) regulates MMP-2 (matrix metalloproteinase-2) activity in the extracellular environment after pro-MMP-2 activation by MT1 (membrane type 1)-MMP”, Biochem. J. 374 (Pt3), 739–745 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BJ20030557
- P. Vempati, E. D. Karagiannis and A. S. Popel “A Biochemical Model of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Activation and Inhibition”, J. Biol. Chem. 282(52), 37585–37596 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M611500200
- H. Kolkenbrock, D. Orgel, A. Hecker-Kia, W Noack, N. Ulbrich “The complex between a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP-2) and 72-kDa progelatinase is a metalloproteinase inhibitor”, Eur. J. Biochem. 198(3), 775–781 (1991). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16080.x
- N. Fujimoto, R. V. Ward, T. Shinya, K. Iwata, Y. Yamashita and T. Hayakawa, “Interaction between tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 and progelatinase A: immunoreactivity analyses”, Biochem. J. 313 (Pt3), 827–833 (1996).
References
A. Jemal, R. Siegel, J. Xu and E. Ward, “Cancer statistics, 2010”, CA Cancer J. Clin. 60(5), 277–300 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.3322/caac.20073
J. M. Davies and R. M. Goldberg, “Treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer”, Semin. Oncol. 38(4), 552–60 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2011.05.009
K. K. Jain, “Nanotechnology in clinical laboratory diagnostics”, Clin. Chim. Acta 358 (1–2), 37–54 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cccn.2005.03.014
P. Chaudhuri, R. Harfouche, S. Soni, D. M. Hentschel, and S. Sengupta, “Shape effect of carbon nanovectors on angiogenesis”, ACS Nano 4(1), 574–82 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn901465h
M. Grodzik, E. Sawosz, M. Wierzbicki, P. Orlowski, A. Hotowy, T. Niemiec, M. Szmidt, K. Mitura and A. Chwalibog, “Nanoparticles of carbon allotropes inhibit glioblastoma multiforme angiogenesis in ovo”, Int. J. Nanomed. 6, 3041–3048 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S25528
M. Wierzbicki, E. Sawosz, M. Grodzik, M. Prasek, S. Jaworski and A. Chwalibog “Comparison of antiangiogenic properties of pristine carbon nanoparticles”, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8(1), 195 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-8-195
S. V. Prylutska, A. P. Burlaka, Y. I. Prylutskyy, U. Ritter and P. Scharff, “Pristine C(60) fullerenes inhibit the rate of tumor growth and metastasis”, Exp Oncol 33(3), 162–164 (2011).
C. Chen, G. Xing, J. Wang, Y. Zhao, B. Li, J. Tang, G. Jia, T. Wang, J. Sun, L. Xing, H. Yuan, Y. Gao, H. Meng, Z. Chen, F. Zhao, Z. Chai and X. Fang, “Multihydroxylated [Gd@C82(OH)22]n nanoparticles: Antineoplastic activity of high efficiency and low toxi-city”, Nano Lett. 5(10), 2050–2057 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nl051624b
M. Lucafò, S. Pacor, C. Fabbro, T. Da Ros, S. Zorzet, M. Prato and G. Sava, “Study of a potential drug delivery system based on carbon nanoparticles: Effects of fullerene derivatives in MCF7 mammary carcinoma cells”, J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1–13 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0830-8
M. Lucafò, M. Gerdol, A. Pallavicini, S. Pacor, S. Zorzet, T. Da Ros, M. Prato and G. Sava, “Profiling the molecular mechanism of fullerene cytotoxicity on tumorcells by RNA-seq”, Toxicology 314(1), 183–192 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2013.10.001
K. Kordatos, T. Da Ros, S. Bosi, E. Vazquez, M. Bergamin, C. Cusan, F. Pellarini, V. Tomberli, B. Baiti, D. Pantarotto, V. Georgakilas, G. Spalluto and M. Prato, “Novel versatile fullerene synthons”, J. Org. Chem. 66, 4915–4920 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jo015608k
A. Albini, Y. Iwamoto, H. K. Kleinman, G. R. Martin, S. A. Aaronson, J. M. Kozlowski and R. N. McEwan, “A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells”, Cancer Res. 47(12), 3239–45 (1987).
P. Provenzano and P. J. Keely, “Mechanical signaling through the cytoskeleton regulates cell proliferation by coordinated focal adhesion and Rho GTPase signalling”, J. Cell Sci. 124 (Pt8), 1195–1205 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.067009
F. G. Giancotti and E. Ruoslahti, “Integrin signaling”, Science 285(5430), 1028–1032 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5430.1028
J. D. Hood and D. A. Cheresh, “Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration”, Nature Rev. Cancer 2(2), 91–100 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc727
F. Aoudjit and K. Vuori, “Integrin signaling in cancer cell survival and chemoresistance”, Chemother. Res. Pract. 1-16 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/283181
M. Millard, S. Odde and N. Neamati, “Integrin targeted therapeutics”, Theranostics 1, 154–188 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.7150/thno/v01p0154
S. Hernandez-Barrantes, M. Bernardo, M. Toth, and R. Fridman, “Regulation of membrane type-matrix metalloproteinases”, Semin. Cancer Biol. 12(2), 131–138 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/scbi.2001.0421
H. Sato, T. Takino, Y. Okada, J. Cao, A. Shinagawa, E. Yamamoto, and M. Seiki, “A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells”, Nature 370(6484), 61–65 (1994). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/370061a0
A. Y. Strongin, B. L. Marmer, G. A. Grant and G. I. Goldberg “Plasma membrane-dependent activation of the 72-kDa type IV collagenase is prevented by complex formation with TIMP-2”, J. Biol. Chem. 268(19), 14033–14039 (1993).
Q. Nguyen, F. Willenbrock, M. I. Cockett, M. O’Shea, A. J. Docherty and G. Murphy, “Different domain interactions are involved in the binding of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases to stromelysin-1 and gelatinase A”, Biochem. 33(8), 2089–2095 (1994). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi00174a015
M. Bernardo and R. Fridman, “TIMP-2 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2) regulates MMP-2 (matrix metalloproteinase-2) activity in the extracellular environment after pro-MMP-2 activation by MT1 (membrane type 1)-MMP”, Biochem. J. 374 (Pt3), 739–745 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BJ20030557
P. Vempati, E. D. Karagiannis and A. S. Popel “A Biochemical Model of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Activation and Inhibition”, J. Biol. Chem. 282(52), 37585–37596 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M611500200
H. Kolkenbrock, D. Orgel, A. Hecker-Kia, W Noack, N. Ulbrich “The complex between a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP-2) and 72-kDa progelatinase is a metalloproteinase inhibitor”, Eur. J. Biochem. 198(3), 775–781 (1991). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16080.x
N. Fujimoto, R. V. Ward, T. Shinya, K. Iwata, Y. Yamashita and T. Hayakawa, “Interaction between tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 and progelatinase A: immunoreactivity analyses”, Biochem. J. 313 (Pt3), 827–833 (1996).