Impact of Morphology of Conductive Agent and Anode Material on Lithium Storage Properties
Corresponding Author: Kezheng Chen
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 7 No. 4 (2015), Article Number: 360-367
Abstract
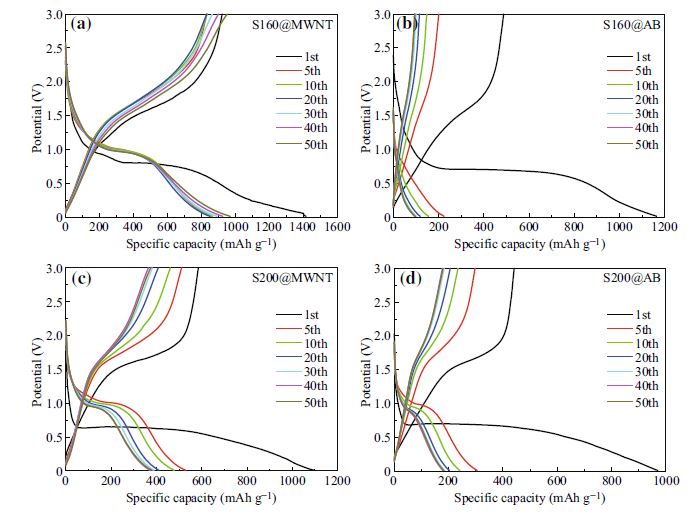
In this study, the impact of morphology of conductive agent and anode material (Fe3O4) on lithium storage properties was throughly investigated. Granular and belt-like Fe3O4 active materials were separately blended with two kinds of conductive agents (i.e., granular acetylene black and multi-walled carbon nanotube) as anodes in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), respectively. It was found that the morphology of conductive agent is of utmost importance in determining LIBs storage properties. In contrast, not as the way we anticipated, the morphology of anode material merely plays a subordinate role in their electrochemical performances. Further, the morphology-matching principle of electrode materials was discussed so as to render their utilization more rational and effective in LIBs.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- L.G. Lu, X.B. Han, J.Q. Li, J.F. Hua, M.G. Ouyang, A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 226, 272–288 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.10.060
- L. Zhang, H.B. Wu, X.W. Lou, Iron-oxide-based advanced anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 4(4), 1300958 (2014). doi:10.1002/aenm.201300958
- Y. Tang, Y. Zhang, J. Deng, J. Wei, H.L. Tam, B.K. Chandran, Z. Dong, Z. Chen, X.D. Chen, Mechanical force-driven growth of elongated bending TiO2-based nanotubular materials for ultrafast rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 26(35), 6111–6118 (2014). doi:10.1002/adma.201402000
- S. Chandrashekar, N.M. Trease, H.J. Chang, L.S. Du, C.P. Grey, A. Jerschow, Li MRI of Li batteries reveals location of microstructural lithium. Nat. Mater. 11, 311–315 (2012). doi:10.1038/nmat3246
- R. Teki, K.D. Moni, R. Krishnan, C.P. Thomas, T.M. Lu, N.K. Prashant, N. Koratkar, Nanostructured silicon anodes for lithium ion rechargeable batteries. Small 5(20), 2236–2242 (2009). doi:10.1002/smll.200900382
- Y.L. Ding, Y. Wen, C.C. Chen, P.A. Aken, J. Maier, Y. Yu, Nanosheets of earth-abundant jarosite as novel anodes for high-rate and long-life lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(19), 10518–10524 (2015). doi:10.1021/acsami.5b01992
- M. Madian, L. Giebeler, M. Klose, T. Jaumann, M. Uhlemann, A. Gebert, S. Oswald, N. Ismail, A. Eychmüller, J. Eckert, Self-organized TiO2/CoO nanotubes as potential anode materials for lithium ion batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 3(5), 909–919 (2015). doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00026
- J.K. Hwang, C. Jo, M.G. Kim, J. Chun, E. Lim, S. Kim, S. Jeong, Y. Kim, J. Lee, Mesoporous Ge/GeO2/carbon lithium-ion battery anodes with high capacity and high reversibility. ACS Nano 9(5), 5299–5309 (2015). doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b00817
- J.M.D. Coey, A.E. Berkowitz, L. Balcells, F.F. Putris, F.T. Parker, Magnetoresistance of magnetite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 734 (1998). doi:10.1063/1.120859
- P.L. Taberna, S. Mitra, P. Poizot, P. Simon, J.M. Tarascon, High rate capabilities Fe3O4-based Cu nano-architectured electrodes for lithium-ion battery applications. Nat. Mater. 5, 567–573 (2006). doi:10.1038/nmat1672
- B. Wang, H.B. Wu, L. Zhang, X.W. Lou, Self-Supported construction of uniform Fe3O4 hollow microspheres from nanoplate building blocks. Angew. Chem. 52(15), 4165–4168 (2013). doi:10.1002/anie.201300190
- Q.Q. Xiong, J.P. Tu, Y. Lu, J. Chen, Y.X. Yu, Y.Q. Qiao, X.L. Wang, C.D. Gu, Synthesis of hierarchical hollow-structured single-crystalline magnetite (Fe3O4) microspheres: the highly powerful storage versus lithium as an anode for lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(10), 6495–6502 (2012). doi:10.1021/jp3002178
- Y. Shi, M. Shi, Y. Qiao, J. Tu, H. Chen, Fe3O4 nanobelts: one-pot and template-free synthesis, magnetic property, and application for lithium storage. Nanotechnology 23(39), 395601 (2012). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/23/39/395601
- T. Zhu, J.S. Chen, X.W. Lou, Glucose-assisted one-pot synthesis of FeOOH nanorods and their transformation to Fe3O4@Carbon nanorods for application in lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(19), 9814–9820 (2011). doi:10.1021/jp2013754
- L. Wang, Y. Yu, P.C. Chen, D.W. Zhang, C.H. Chen, Electrospinning synthesis of C/Fe3O4 composite nanofibers and their application for high performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 183(2), 717–723 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.05.079
- M. Nishizawa, K. Mukai, S. Kuwabata, C.R. Martin, H. Yoneyama, Template synthesis of polypyrrole-coated spinel LiMn2O4 nanotubules and their properties as cathode active materials for lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 144(6), 1923–1927 (1997). doi:10.1149/1.1837722
- B. Wang, J.S. Chen, H.B. Wu, Z. Wang, X.W. Lou, Quasiemulsion-templated formation of α-Fe2O3 hollow spheres with enhanced lithium storage properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(43), 17146–17148 (2011). doi:10.1021/ja208346s
- Y.M. Lin, P.R. Abel, A. Heller, C.B. Mullins, α-Fe2O3 nanorods as anode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2(22), 2885–2891 (2011). doi:10.1021/jz201363j
- M.V. Reddy, T. Yu, C.H. Sow, Z.X. Shen, C.T. Lim, G.V.S. Rao, B.V.R. Chowdari, α-Fe2O3 nanoflakes as an anode material for Li-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17(15), 2792–2799 (2007). doi:10.1002/adfm.200601186
- H. Wang, H.S. Casalongue, Y. Liang, H. Dai, Ni(OH)2 nanoplates grown on graphene as advanced electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(21), 7472–7477 (2010). doi:10.1021/ja102267j
- J. Liu, Y. Li, R. Ding, J. Jiang, Y. Hu, X. Ji, Q. Chi, Z. Zhu, X. Huang, Carbon/ZnO nanorod array electrode with significantly improved lithium storage capability. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(13), 5336–5339 (2009). doi:10.1021/jp900427c
- J.Z. Wang, C. Zhong, D. Wexler, N.H. Idris, Z.X. Wang, L.Q. Chen, H.K. Liu, Graphene-encapsulated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with 3D laminated structure as superior anode in lithium ion batteries. Chem. Eur. J. 17(2), 661–667 (2011). doi:10.1002/chem.201001348
- G.M. Zhou, D.W. Wang, F. Li, L.L. Zhang, N. Li, Z.S. Wu, L. Wen, G.Q. Lu, H.M. Cheng, Graphene-wrapped Fe3O4 anode material with improved reversible capacity and cyclic stability for lithium ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 22(18), 5306–5313 (2010). doi:10.1021/cm101532x
- Y. He, L. Huang, J.S. Cai, X.M. Zheng, S.G. Sun, Structure and electrochemical performance of nanostructured Fe3O4/carbon nanotube composites as anodes for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 55(3), 1140–1144 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.10.014
- T.Q. Wang, X.L. Wang, Y. Lu, Q.Q. Xiong, X.Y. Zhao, J.B. Cai, S. Huang, C.D. Gu, J.P. Tu, Self-assembly of hierarchical Fe3O4 microsphere/graphene nanosheet composite: towards a promising high-performance anode for Li-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 4, 322–330 (2014). doi:10.1039/C3RA45268A
- Q.M. Su, D. Xie, J. Zhang, G.H. Du, B.S. Xu, In situ transmission electron microscopy observation of the conversion mechanism of Fe2O3/graphene anode during lithiation-delithiation processes. ACS Nano 7(10), 9115–9121 (2013). doi:10.1021/nn403720p
- P. Poizot, S. Laruelle, S. Grugeon, L. Dupont, J.M. Tarascon, Nano-sized transition-metal oxides as negative-electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Nature 407, 496–499 (2000). doi:10.1038/35035045
- L.W. Ji, Z. Lin, M. Alcoutlabi, X.W. Zhang, Recent developments in nanostructured anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 2682–2699 (2011). doi:10.1039/c0ee00699h
- J. Cabana, L. Monconduit, D. Larcher, M.R. Palacin, Beyond intercalation-based Li-ion batteries: the state of the art and challenges of electrode materials reacting through conversion reactions. Adv. Mater. 22(35), E170–E192 (2010). doi:10.1002/adma.201000717
- P.G. Bruce, B. Scrosati, J.M. Tarascon, Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47(16), 2930–2946 (2008). doi:10.1002/anie.200702505
- W.M. Zhang, X.L. Wu, J.S. Hu, Y.G. Guo, L.J. Wan, Carbon coated Fe3O4 nanospindles as a superior anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18(24), 3941–3946 (2008). doi:10.1002/adfm.200801386
- J.S. Chen, X.W. Lou, SnO2 and TiO2 nanosheets for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Today 15(6), 246–254 (2012). doi:10.1016/S1369-7021(12)70115-3
- J.S. Chen, L.A. Archer, X.W. Lou, SnO2 hollow structures and TiO2 nanosheets for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 9912–9924 (2011). doi:10.1039/c0jm04163g
References
L.G. Lu, X.B. Han, J.Q. Li, J.F. Hua, M.G. Ouyang, A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 226, 272–288 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.10.060
L. Zhang, H.B. Wu, X.W. Lou, Iron-oxide-based advanced anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 4(4), 1300958 (2014). doi:10.1002/aenm.201300958
Y. Tang, Y. Zhang, J. Deng, J. Wei, H.L. Tam, B.K. Chandran, Z. Dong, Z. Chen, X.D. Chen, Mechanical force-driven growth of elongated bending TiO2-based nanotubular materials for ultrafast rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 26(35), 6111–6118 (2014). doi:10.1002/adma.201402000
S. Chandrashekar, N.M. Trease, H.J. Chang, L.S. Du, C.P. Grey, A. Jerschow, Li MRI of Li batteries reveals location of microstructural lithium. Nat. Mater. 11, 311–315 (2012). doi:10.1038/nmat3246
R. Teki, K.D. Moni, R. Krishnan, C.P. Thomas, T.M. Lu, N.K. Prashant, N. Koratkar, Nanostructured silicon anodes for lithium ion rechargeable batteries. Small 5(20), 2236–2242 (2009). doi:10.1002/smll.200900382
Y.L. Ding, Y. Wen, C.C. Chen, P.A. Aken, J. Maier, Y. Yu, Nanosheets of earth-abundant jarosite as novel anodes for high-rate and long-life lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(19), 10518–10524 (2015). doi:10.1021/acsami.5b01992
M. Madian, L. Giebeler, M. Klose, T. Jaumann, M. Uhlemann, A. Gebert, S. Oswald, N. Ismail, A. Eychmüller, J. Eckert, Self-organized TiO2/CoO nanotubes as potential anode materials for lithium ion batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 3(5), 909–919 (2015). doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00026
J.K. Hwang, C. Jo, M.G. Kim, J. Chun, E. Lim, S. Kim, S. Jeong, Y. Kim, J. Lee, Mesoporous Ge/GeO2/carbon lithium-ion battery anodes with high capacity and high reversibility. ACS Nano 9(5), 5299–5309 (2015). doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b00817
J.M.D. Coey, A.E. Berkowitz, L. Balcells, F.F. Putris, F.T. Parker, Magnetoresistance of magnetite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 734 (1998). doi:10.1063/1.120859
P.L. Taberna, S. Mitra, P. Poizot, P. Simon, J.M. Tarascon, High rate capabilities Fe3O4-based Cu nano-architectured electrodes for lithium-ion battery applications. Nat. Mater. 5, 567–573 (2006). doi:10.1038/nmat1672
B. Wang, H.B. Wu, L. Zhang, X.W. Lou, Self-Supported construction of uniform Fe3O4 hollow microspheres from nanoplate building blocks. Angew. Chem. 52(15), 4165–4168 (2013). doi:10.1002/anie.201300190
Q.Q. Xiong, J.P. Tu, Y. Lu, J. Chen, Y.X. Yu, Y.Q. Qiao, X.L. Wang, C.D. Gu, Synthesis of hierarchical hollow-structured single-crystalline magnetite (Fe3O4) microspheres: the highly powerful storage versus lithium as an anode for lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(10), 6495–6502 (2012). doi:10.1021/jp3002178
Y. Shi, M. Shi, Y. Qiao, J. Tu, H. Chen, Fe3O4 nanobelts: one-pot and template-free synthesis, magnetic property, and application for lithium storage. Nanotechnology 23(39), 395601 (2012). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/23/39/395601
T. Zhu, J.S. Chen, X.W. Lou, Glucose-assisted one-pot synthesis of FeOOH nanorods and their transformation to Fe3O4@Carbon nanorods for application in lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(19), 9814–9820 (2011). doi:10.1021/jp2013754
L. Wang, Y. Yu, P.C. Chen, D.W. Zhang, C.H. Chen, Electrospinning synthesis of C/Fe3O4 composite nanofibers and their application for high performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 183(2), 717–723 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.05.079
M. Nishizawa, K. Mukai, S. Kuwabata, C.R. Martin, H. Yoneyama, Template synthesis of polypyrrole-coated spinel LiMn2O4 nanotubules and their properties as cathode active materials for lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 144(6), 1923–1927 (1997). doi:10.1149/1.1837722
B. Wang, J.S. Chen, H.B. Wu, Z. Wang, X.W. Lou, Quasiemulsion-templated formation of α-Fe2O3 hollow spheres with enhanced lithium storage properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(43), 17146–17148 (2011). doi:10.1021/ja208346s
Y.M. Lin, P.R. Abel, A. Heller, C.B. Mullins, α-Fe2O3 nanorods as anode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2(22), 2885–2891 (2011). doi:10.1021/jz201363j
M.V. Reddy, T. Yu, C.H. Sow, Z.X. Shen, C.T. Lim, G.V.S. Rao, B.V.R. Chowdari, α-Fe2O3 nanoflakes as an anode material for Li-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17(15), 2792–2799 (2007). doi:10.1002/adfm.200601186
H. Wang, H.S. Casalongue, Y. Liang, H. Dai, Ni(OH)2 nanoplates grown on graphene as advanced electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(21), 7472–7477 (2010). doi:10.1021/ja102267j
J. Liu, Y. Li, R. Ding, J. Jiang, Y. Hu, X. Ji, Q. Chi, Z. Zhu, X. Huang, Carbon/ZnO nanorod array electrode with significantly improved lithium storage capability. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(13), 5336–5339 (2009). doi:10.1021/jp900427c
J.Z. Wang, C. Zhong, D. Wexler, N.H. Idris, Z.X. Wang, L.Q. Chen, H.K. Liu, Graphene-encapsulated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with 3D laminated structure as superior anode in lithium ion batteries. Chem. Eur. J. 17(2), 661–667 (2011). doi:10.1002/chem.201001348
G.M. Zhou, D.W. Wang, F. Li, L.L. Zhang, N. Li, Z.S. Wu, L. Wen, G.Q. Lu, H.M. Cheng, Graphene-wrapped Fe3O4 anode material with improved reversible capacity and cyclic stability for lithium ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 22(18), 5306–5313 (2010). doi:10.1021/cm101532x
Y. He, L. Huang, J.S. Cai, X.M. Zheng, S.G. Sun, Structure and electrochemical performance of nanostructured Fe3O4/carbon nanotube composites as anodes for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 55(3), 1140–1144 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.10.014
T.Q. Wang, X.L. Wang, Y. Lu, Q.Q. Xiong, X.Y. Zhao, J.B. Cai, S. Huang, C.D. Gu, J.P. Tu, Self-assembly of hierarchical Fe3O4 microsphere/graphene nanosheet composite: towards a promising high-performance anode for Li-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 4, 322–330 (2014). doi:10.1039/C3RA45268A
Q.M. Su, D. Xie, J. Zhang, G.H. Du, B.S. Xu, In situ transmission electron microscopy observation of the conversion mechanism of Fe2O3/graphene anode during lithiation-delithiation processes. ACS Nano 7(10), 9115–9121 (2013). doi:10.1021/nn403720p
P. Poizot, S. Laruelle, S. Grugeon, L. Dupont, J.M. Tarascon, Nano-sized transition-metal oxides as negative-electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Nature 407, 496–499 (2000). doi:10.1038/35035045
L.W. Ji, Z. Lin, M. Alcoutlabi, X.W. Zhang, Recent developments in nanostructured anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 2682–2699 (2011). doi:10.1039/c0ee00699h
J. Cabana, L. Monconduit, D. Larcher, M.R. Palacin, Beyond intercalation-based Li-ion batteries: the state of the art and challenges of electrode materials reacting through conversion reactions. Adv. Mater. 22(35), E170–E192 (2010). doi:10.1002/adma.201000717
P.G. Bruce, B. Scrosati, J.M. Tarascon, Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47(16), 2930–2946 (2008). doi:10.1002/anie.200702505
W.M. Zhang, X.L. Wu, J.S. Hu, Y.G. Guo, L.J. Wan, Carbon coated Fe3O4 nanospindles as a superior anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18(24), 3941–3946 (2008). doi:10.1002/adfm.200801386
J.S. Chen, X.W. Lou, SnO2 and TiO2 nanosheets for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Today 15(6), 246–254 (2012). doi:10.1016/S1369-7021(12)70115-3
J.S. Chen, L.A. Archer, X.W. Lou, SnO2 hollow structures and TiO2 nanosheets for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 9912–9924 (2011). doi:10.1039/c0jm04163g