Ultra-thin Glass Film Coated with Graphene: A New Material for Spontaneous Emission Enhancement of Quantum Emitter
Corresponding Author: Chun Jiang
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 7 No. 3 (2015), Article Number: 261-267
Abstract
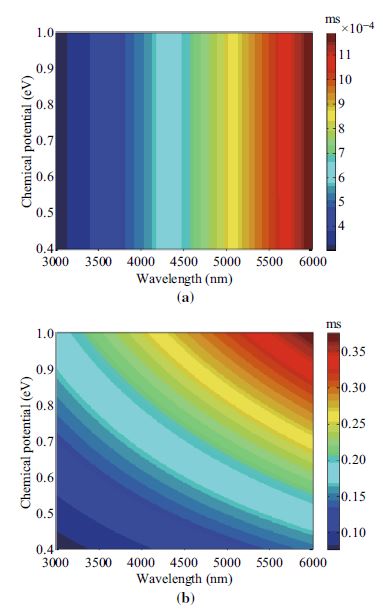
We propose an ultra-thin glass film coated with graphene as a new kind of surrounding material which can greatly enhance spontaneous emission rate (SER) of dipole emitter embedded in it. With properly designed parameters, numerical results show that SER-enhanced factors as high as 1.286 × 106 can be achieved. The influences of glass film thickness and chemical potential/doping level of graphene on spontaneous emission enhancement are also studied in this paper. A comparison is made between graphene and other coating materials such as gold and silver to see their performances in SER enhancement.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- E.M. Purcell, Spontaneous emission probabilities at radio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 69, 681 (1946). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.69.674.2
- V.S.C.M. Rao, S. Hughes, Numerical study of exact Purcell factors in finite-size planar photonic crystal waveguides. Opt. Lett. 33(14), 1587–1589 (2008). doi:10.1364/OL.33.001587
- M. Kuttge, F.J.G. de Abajo, A. Polman, Ultrasmall mode volume plasmonic nanodisk resonators. Nano Lett. 10(5), 1537–1541 (2010). doi:10.1021/nl902546r
- P. Kristensen, C.V. Vlack, S. Hughes, Generalized effective mode volume for leaky optical cavities. Opt. Lett. 37(10), 1649–1651 (2012). doi:10.1364/OL.37.001649
- H. Iwase, D. Enlund, J. Vučković, Analysis of the Purcell effect in photonic and plasmonic crystals with losses. Opt. Express 18(16), 16546–16560 (2010). doi:10.1364/OE.18.016546
- A.K. Geim, K.S. Novoselov, The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007). doi:10.1038/nmat1849
- M. Jablan, H. Buljan, M. Soljačić, Plasmonics in graphene at infrared frequencies. Phys. Rev. B 80, 245435 (2009). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.80.245435
- F.H.L. Koppens, D.E. Chang, F.J.G. de Abajo, Graphene plasmonics: a platform for strong light-matter interactions. Nano Lett. 11(8), 3370–3377 (2011). doi:10.1021/nl201771h
- G.W. Hanson, E. Forati, W. Linz, A.B. Yakovlev, Excitation of terahertz surface plasmons on graphene surfaces by an elementary dipole and quantum emitter: strong electrodynamic effect of dielectric support. Phys. Rev. B 86, 235440 (2012). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.86.235440
- P.A. Huidobro, AYu. Nikitin, C. González-Ballestero, L. Martín-Moreno, F.J. García-Vidal, Superradiance mediated by graphene surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. B 85, 155438 (2012). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.85.155438
- AYu. Nikitin, F. Guinea, F.J. García-Vidal, L. Martín-Moreno, Fields radiated by a nanoemitter in a graphene sheet. Phys. Rev. B 84, 195446 (2011). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.84.195446
- L. Sun, B. Tang, C. Jiang, Enhanced spontaneous emission of mid-infrared dipole emitter in double-layer graphene waveguide. Opt. Express 22(22), 26487–26497 (2014). doi:10.1364/OE.22.026487
- R.A. Soref, S.J. Emelett, W.R. Buchwald, Silicon waveguided components for the long-wave infrared region. J. Opt. A 8, 840–848 (2006). doi:10.1088/1464-4258/8/10/004
- V. Raghunathan, D. Borlaug, R. Rice, B. Jalali, Demonstration of a mid-infrared silicon Raman amplifier. Opt. Express 15, 14355–14362 (2007). doi:10.1364/OE.15.014355
- P. Meystre, M. Sargent, Elements of Quantum Optics, 4th edn. (Springer, New York, 2007), pp. 299–349. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-03877-2
- L. Novotny, B. Hecht, Principles of Nano-optics, 2nd edn. (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2012), pp. 250–303. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511794193
- A. Reina, H. Son, L. Jiao, B. Fan, M.S. Dresselhaus, Z. Liu, J. Kong, Transferring and identification of single- and few-layer graphene on arbitrary substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 17741–17744 (2008). doi:10.1021/jp807380s
- L.A. Falkovsky, Optical properties of graphene. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 129(1), 012004 (2008). doi:10.1088/1742-6596/129/1/012004
- M.I. Katsnelson, Graphene: Carbon in Two Dimensions (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2012), pp. 161–184. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139031080
- L. Gao, J. Shu, C. Qiu, Q. Xu, Excitation of plasmonic waves in graphene by guided-mode resonances. ACS Nano 6(9), 7806–7813 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn301888e
- A. Vakil, N. Engheta, Transformation optics using graphene. Science 332(6035), 1291–1294 (2011). doi:10.1126/science.1202691
- S.A. Mikhailov, K. Ziegler, New electromagnetic mode in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 016803 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.016803
- D.B. Farmer, H.-Y. Chiu, Y.-M. Lin, K.A. Jenkins, F. Xia, P. Avouris, Utilization of a buffered dielectric to achieve high field-effect carrier mobility in graphene transistors. Nano Lett. 9(12), 4474–4478 (2009). doi:10.1021/nl902788u
- T. Fang, A. Konar, H. Xing, D. Jena, Mobility in semiconducting graphene nanoribbons: phonon, impurity, and edge roughness scattering. Phys. Rev. B 78, 205403 (2008). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.78.205403
- I. Gontijo, M. Boroditsky, E. Yablonovitch, S. Keller, U.K. Mishra, S.P. DenBaars, Coupling of InGaN quantum-well photoluminescence to silver surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. B 60(16), 11564–11567 (1999). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.60.11564
References
E.M. Purcell, Spontaneous emission probabilities at radio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 69, 681 (1946). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.69.674.2
V.S.C.M. Rao, S. Hughes, Numerical study of exact Purcell factors in finite-size planar photonic crystal waveguides. Opt. Lett. 33(14), 1587–1589 (2008). doi:10.1364/OL.33.001587
M. Kuttge, F.J.G. de Abajo, A. Polman, Ultrasmall mode volume plasmonic nanodisk resonators. Nano Lett. 10(5), 1537–1541 (2010). doi:10.1021/nl902546r
P. Kristensen, C.V. Vlack, S. Hughes, Generalized effective mode volume for leaky optical cavities. Opt. Lett. 37(10), 1649–1651 (2012). doi:10.1364/OL.37.001649
H. Iwase, D. Enlund, J. Vučković, Analysis of the Purcell effect in photonic and plasmonic crystals with losses. Opt. Express 18(16), 16546–16560 (2010). doi:10.1364/OE.18.016546
A.K. Geim, K.S. Novoselov, The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007). doi:10.1038/nmat1849
M. Jablan, H. Buljan, M. Soljačić, Plasmonics in graphene at infrared frequencies. Phys. Rev. B 80, 245435 (2009). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.80.245435
F.H.L. Koppens, D.E. Chang, F.J.G. de Abajo, Graphene plasmonics: a platform for strong light-matter interactions. Nano Lett. 11(8), 3370–3377 (2011). doi:10.1021/nl201771h
G.W. Hanson, E. Forati, W. Linz, A.B. Yakovlev, Excitation of terahertz surface plasmons on graphene surfaces by an elementary dipole and quantum emitter: strong electrodynamic effect of dielectric support. Phys. Rev. B 86, 235440 (2012). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.86.235440
P.A. Huidobro, AYu. Nikitin, C. González-Ballestero, L. Martín-Moreno, F.J. García-Vidal, Superradiance mediated by graphene surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. B 85, 155438 (2012). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.85.155438
AYu. Nikitin, F. Guinea, F.J. García-Vidal, L. Martín-Moreno, Fields radiated by a nanoemitter in a graphene sheet. Phys. Rev. B 84, 195446 (2011). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.84.195446
L. Sun, B. Tang, C. Jiang, Enhanced spontaneous emission of mid-infrared dipole emitter in double-layer graphene waveguide. Opt. Express 22(22), 26487–26497 (2014). doi:10.1364/OE.22.026487
R.A. Soref, S.J. Emelett, W.R. Buchwald, Silicon waveguided components for the long-wave infrared region. J. Opt. A 8, 840–848 (2006). doi:10.1088/1464-4258/8/10/004
V. Raghunathan, D. Borlaug, R. Rice, B. Jalali, Demonstration of a mid-infrared silicon Raman amplifier. Opt. Express 15, 14355–14362 (2007). doi:10.1364/OE.15.014355
P. Meystre, M. Sargent, Elements of Quantum Optics, 4th edn. (Springer, New York, 2007), pp. 299–349. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-03877-2
L. Novotny, B. Hecht, Principles of Nano-optics, 2nd edn. (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2012), pp. 250–303. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511794193
A. Reina, H. Son, L. Jiao, B. Fan, M.S. Dresselhaus, Z. Liu, J. Kong, Transferring and identification of single- and few-layer graphene on arbitrary substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 17741–17744 (2008). doi:10.1021/jp807380s
L.A. Falkovsky, Optical properties of graphene. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 129(1), 012004 (2008). doi:10.1088/1742-6596/129/1/012004
M.I. Katsnelson, Graphene: Carbon in Two Dimensions (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2012), pp. 161–184. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139031080
L. Gao, J. Shu, C. Qiu, Q. Xu, Excitation of plasmonic waves in graphene by guided-mode resonances. ACS Nano 6(9), 7806–7813 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn301888e
A. Vakil, N. Engheta, Transformation optics using graphene. Science 332(6035), 1291–1294 (2011). doi:10.1126/science.1202691
S.A. Mikhailov, K. Ziegler, New electromagnetic mode in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 016803 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.016803
D.B. Farmer, H.-Y. Chiu, Y.-M. Lin, K.A. Jenkins, F. Xia, P. Avouris, Utilization of a buffered dielectric to achieve high field-effect carrier mobility in graphene transistors. Nano Lett. 9(12), 4474–4478 (2009). doi:10.1021/nl902788u
T. Fang, A. Konar, H. Xing, D. Jena, Mobility in semiconducting graphene nanoribbons: phonon, impurity, and edge roughness scattering. Phys. Rev. B 78, 205403 (2008). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.78.205403
I. Gontijo, M. Boroditsky, E. Yablonovitch, S. Keller, U.K. Mishra, S.P. DenBaars, Coupling of InGaN quantum-well photoluminescence to silver surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. B 60(16), 11564–11567 (1999). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.60.11564