Size-Dependent Gold Nanoparticle Interaction at Nano–Micro Interface Using Both Monolayer and Multilayer (Tissue-Like) Cell Models
Corresponding Author: Devika B. Chithrani
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 8 No. 1 (2016), Article Number: 44-53
Abstract
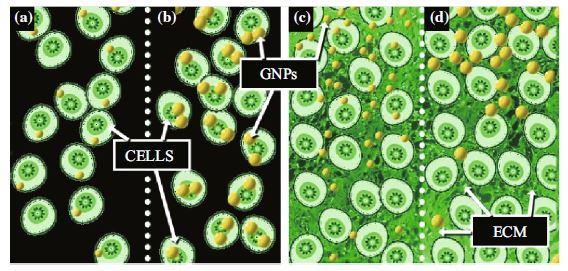
Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) are emerging as a novel tool to improve existing cancer therapeutics. GNPs are being used as radiation dose enhancers in radiation therapy as well as anticancer drugs carriers in chemotherapy. However, the success of GNP-based therapeutics depends on their ability to penetrate tumor tissue. GNPs of 20 and 50 nm diameters were used to elucidate the effects of size on the GNP interaction with tumor cells at monolayer and multilayer level. At monolayer cell level, smaller NPs had a lower uptake compared to larger NPs at monolayer cell level. However, the order was reversed at tissue-like multilayer level. The smaller NPs penetrated better compared to larger NPs in tissue-like materials. Based on our study using tissue-like materials, we can predict that the smaller NPs are better for future therapeutics due to their greater penetration in tumor tissue once leaving the leaky blood vessels. In this study, tissue-like multilayer cellular structures (MLCs) were grown to model the post-vascular tumor environment. The MLCs exhibited a much more extensive extracellular matrix than monolayer cell cultures. The MLC model can be used to optimize the nano–micro interface at tissue level before moving into animal models. This would accelerate the use of NPs in future cancer therapeutics.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- D. Yohan, B.D. Chithrani, Applications of nanoparticles in nanomedicine. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 10(9), 2371–2392 (2014). doi:10.1166/jbn.2014.2015
- S. Shrivastava, D. Dash, Label-free colorimetric estimation of proteins using nanoparticles of silver. Nano Micro Lett. 2(3), 164–168 (2010). doi:10.5101/nml.v2i3.p164-168
- B.D. Chithrani, W.C.W. Chan, Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett. 7(6), 1542–1550 (2007). doi:10.1021/nl070363y
- B.D. Chithrani, A.A. Ghazani, W.C.W. Chan, Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 6(4), 662–668 (2006). doi:10.1021/nl052396o
- R. Chouikrat, A. Seve, R. Vanderesse, H. Benachour, M. Barberi-Heyob, S. Richeter, L. Raehm, J.O. Durand, M. Verelst, C. Frochot, Non polymeric nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy applications: recent developments. Curr. Med. Chem. 19(6), 781–792 (2012). doi:10.2174/092986712799034897
- A.M. Alkilany, C.J. Murphy, Toxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles: what we have learned so far? J. Nanopart. Res. 12(7), 2313–2333 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11051-010-9911-8
- L.A. Liotta, Tumor invasion and metastases—role of the extracellular matrix: Rhoads memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 46(1), 1–7 (1986)
- P.A. Netti, D.A. Berk, M.A. Swartz, A.J. Grodzinsky, R.K. Jain, Role of extracellular matrix assembly in interstitial transport in solid tumors. Cancer Res. 60(9), 2497–2503 (2000)
- T.T. Goodman, P.L. Olive, S.H. Pun, Increased nanoparticle penetration in collagenase-treated multicellular spheroids. Int. J. Nanomed. 2(2), 265–274 (2007)
- D. Yohan, C. Cruje, X. Lu, B.D. Chithrani, Elucidating the uptake and distribution of nanoparticles in solid tumors via a multilayered cell culture model. Nano Micro Lett. 7(2), 127–137 (2015). doi:10.1007/s40820-014-0025-1
- R. Grantab, S. Sivananthan, I.F. Tannock, The penetration of anticancer drugs through tumor tissue as a function of cellular adhesion and packing density of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 66(2), 1033–1039 (2006). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-214
- R.K. Jain, Delivery of molecular and cellular medicine to solid tumors. J. Control. Rel. 53(1–3), 49–67 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0168-3659(97)00237-X
- P.K.J. Kuppen, M.M. van der Eb, L.E. Jonges, M. Hagenaars, M.E. Hokland, U. Nannmark et al., Tumor structure and extracellular matrix as a possible barrier for therapeutic approaches using immune cells or adenoviruses in colorectal cancer. Histochem. Cell Biol. 115(1), 67–72 (2001). doi:10.1007/s004180000224
- M.F. Flessner, J. Choi, K. Credit, R. Deverkadra, K. Henderson, Resistance of tumor interstitial pressure to the penetration of intraperitoneally delivered antibodies into metastatic ovarian tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 11(8), 3117–3125 (2005). doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2332
- R.M. Phillips, P.M. Loadman, B.P. Cronin, Evaluation of a novel in vitro assay for assessing drug penetration into avascular regions of tumours. Br. J. Cancer 77(12), 2112–2119 (1998). doi:10.1038/bjc.1998.355
- A.I. Minchinton, I.F. Tannock, Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6(8), 583–592 (2006). doi:10.1038/nrc1893
- A.I. Minchinton, K.R. Wendt, K.A. Clow, K.H. Fryer, Multilayers of cells growing on a permeable support. An in vitro tumour model. Acta Oncol. 36(1), 13–16 (1997). doi:10.3109/02841869709100724
- R.H. Thomlinson, L.H. Gray, The histological structure of some human lung cancers and the possible implications for radiotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 9(4), 539–549 (1955). doi:10.1038/bjc.1955.55
- R.K. Jain, Transport of molecules, particles, and cells in solid tumors. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1, 241–263 (1999). doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.1.1.241
- S. Ramanujan, A. Pluen, T.D. McKee, E.B. Brown, Y. Boucher, R.K. Jain, Diffusion and convection in collagen gels: implications for transport in the tumor interstitium. Biophys. J. 83(3), 1650–1660 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(02)73933-7
- T. Stylianopoulos, M.Z. Poh, N. Insin, M.G. Bawendi, D. Fukumura, L.L. Munn, R.K. Jain, Diffusion of particles in the extracellular matrix: the effect of repulsive electrostatic interactions. Biophys. J. 99, 1342–1349 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.016
- T. Betancourt, B. Brown, L. Brannon-Peppas, Doxorubicin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation: preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Nanomedicine 2(2), 219–232 (2007). doi:10.2217/17435889.2.2.219
- H. Lee, S. Park, J.B. Kim, J. Kim, H. Kim, Entrapped doxorubicin nanoparticles for the treatment of metastatic anoikis-resistant cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 332(1), 110–119 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.01.021
- U. Benbow, M.P. Schoenermark, K.A. Orndorff, A.L. Givan, C.E. Brinckerhoff, Human breast cancer cells activate procollagenase-1 and invade type I collagen: invasion is inhibited by all-trans retinoic acid. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 17(3), 231–238 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1006639214618
- J.Y. Pille, C. Denoyelle, J. Varet, J.R. Bertrand, J. Soria et al., Anti-rhoa and anti-rhoc sirnas inhibit the proliferation and invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 11(2), 267–274 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.08.029
- W. Bursch, A. Ellinger, H. Kienzl, L. Török, S. Pandey, M. Sikorska, R. Walker, R.S. Hermann, Active cell death induced by the anti-estrogens tamoxifen and ICI 164 384 in human mammary carcinoma cells (MCF-7) in culture: the role of autophagy. Carcinogenesis 17(8), 1595–1607 (1996). doi:10.1093/carcin/17.8.1595
- C.Y. Hsieh, R.C. Santell, S.Z. Haslam, W.G. Helferich, Estrogenic effects of genistein on the growth of estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 58(17), 3833–3838 (1998)
- T.T. Wang, J.M. Phang, Effects of estrogen on apoptotic pathways in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Cancer Res. 55(12), 2487–2489 (1995)
- G. Frens, Controlled nucleation for the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nature 241, 20–22 (1973). doi:10.1038/physci241020a0
- D.S. Cowan, K.O. Hicks, W.R. Wilson, Multicellular membranes as an in vitro model for extravascular diffusion in tumours. Br. J. Cancer Suppl. 27(2), 28–31 (1996)
- I.F. Tannock, C.M. Lee, J.K. Tunggal, D.S. Cowan, M.J. Egorin, Limited penetration of anticancer drugs through tumor tissue: a potential cause of resistance of solid tumors to chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 8(3), 878–884 (2002)
- K.O. Hicks, Y. Fleming, B.G. Siim, C.J. Koch, W.R. Wilson, Extravascular diffusion of tirapazamine: effect of metabolic consumption assessed using the multicellular layer model. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 42(3), 641–649 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(98)00268-5
- W.R. Wilson, K.O. Hicks, Measurement of extravascular drug diffusion in multicellular layers. Br. J. Cancer 79(9–10), 1623–1626 (1999)
- M. Neshatian, S. Chung, D. Yohan, C. Yang, D.B. Chithrani, Uptake of gold nanoparticles in breathless (hypoxic) cancer cells. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 11(7), 1162–1172 (2015). doi:10.1166/jbn.2015.2067
- Y. Aoyama, T. Kanamori, T. Nakai, T. Sasaki, S. Horiuchi, S. Sando, T. Niidome, Artificial viruses and their application to gene delivery. size-controlled gene coating with glycocluster nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(12), 3455–3457 (2003). doi:10.1021/ja029608t
- S.-H. Wang, C.-W. Lee, A. Chiou, P.-K. Wei, Size-dependent endocytosis of gold nanoparticles studied by three-dimensional mapping of plasmonic scattering images. J. Nanobiotechnol. 8(33), 1–13 (2010). doi:10.1186/1477-3155-8-33
- H. Gao, W. Shi, L.B. Freund, Mechanics of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102(27), 9469–9474 (2005). doi:10.1073/pnas.0503879102
- S. Zhang, J. Li, G. Lykotrafitis, G. Bao, S. Suresh, Size-dependent endocytosis of nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 21(4), 419–424 (2009). doi:10.1002/adma.200801393
- W. Chen, D.P. Cormode, Y. Vengrenyuk, B. Herranz, J.E. Feig, A. Klink, W.J. Mulder, E.A. Fisher, Z.A. Fayad, Collagen-specific peptide conjugated HDL nanoparticles as MRI contrast agent to evaluate compositional changes in atherosclerotic plaque regression. JACC. Cardiovasc. Imaging 6(3), 373–384 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2012.06.016
References
D. Yohan, B.D. Chithrani, Applications of nanoparticles in nanomedicine. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 10(9), 2371–2392 (2014). doi:10.1166/jbn.2014.2015
S. Shrivastava, D. Dash, Label-free colorimetric estimation of proteins using nanoparticles of silver. Nano Micro Lett. 2(3), 164–168 (2010). doi:10.5101/nml.v2i3.p164-168
B.D. Chithrani, W.C.W. Chan, Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett. 7(6), 1542–1550 (2007). doi:10.1021/nl070363y
B.D. Chithrani, A.A. Ghazani, W.C.W. Chan, Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 6(4), 662–668 (2006). doi:10.1021/nl052396o
R. Chouikrat, A. Seve, R. Vanderesse, H. Benachour, M. Barberi-Heyob, S. Richeter, L. Raehm, J.O. Durand, M. Verelst, C. Frochot, Non polymeric nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy applications: recent developments. Curr. Med. Chem. 19(6), 781–792 (2012). doi:10.2174/092986712799034897
A.M. Alkilany, C.J. Murphy, Toxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles: what we have learned so far? J. Nanopart. Res. 12(7), 2313–2333 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11051-010-9911-8
L.A. Liotta, Tumor invasion and metastases—role of the extracellular matrix: Rhoads memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 46(1), 1–7 (1986)
P.A. Netti, D.A. Berk, M.A. Swartz, A.J. Grodzinsky, R.K. Jain, Role of extracellular matrix assembly in interstitial transport in solid tumors. Cancer Res. 60(9), 2497–2503 (2000)
T.T. Goodman, P.L. Olive, S.H. Pun, Increased nanoparticle penetration in collagenase-treated multicellular spheroids. Int. J. Nanomed. 2(2), 265–274 (2007)
D. Yohan, C. Cruje, X. Lu, B.D. Chithrani, Elucidating the uptake and distribution of nanoparticles in solid tumors via a multilayered cell culture model. Nano Micro Lett. 7(2), 127–137 (2015). doi:10.1007/s40820-014-0025-1
R. Grantab, S. Sivananthan, I.F. Tannock, The penetration of anticancer drugs through tumor tissue as a function of cellular adhesion and packing density of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 66(2), 1033–1039 (2006). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-214
R.K. Jain, Delivery of molecular and cellular medicine to solid tumors. J. Control. Rel. 53(1–3), 49–67 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0168-3659(97)00237-X
P.K.J. Kuppen, M.M. van der Eb, L.E. Jonges, M. Hagenaars, M.E. Hokland, U. Nannmark et al., Tumor structure and extracellular matrix as a possible barrier for therapeutic approaches using immune cells or adenoviruses in colorectal cancer. Histochem. Cell Biol. 115(1), 67–72 (2001). doi:10.1007/s004180000224
M.F. Flessner, J. Choi, K. Credit, R. Deverkadra, K. Henderson, Resistance of tumor interstitial pressure to the penetration of intraperitoneally delivered antibodies into metastatic ovarian tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 11(8), 3117–3125 (2005). doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2332
R.M. Phillips, P.M. Loadman, B.P. Cronin, Evaluation of a novel in vitro assay for assessing drug penetration into avascular regions of tumours. Br. J. Cancer 77(12), 2112–2119 (1998). doi:10.1038/bjc.1998.355
A.I. Minchinton, I.F. Tannock, Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6(8), 583–592 (2006). doi:10.1038/nrc1893
A.I. Minchinton, K.R. Wendt, K.A. Clow, K.H. Fryer, Multilayers of cells growing on a permeable support. An in vitro tumour model. Acta Oncol. 36(1), 13–16 (1997). doi:10.3109/02841869709100724
R.H. Thomlinson, L.H. Gray, The histological structure of some human lung cancers and the possible implications for radiotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 9(4), 539–549 (1955). doi:10.1038/bjc.1955.55
R.K. Jain, Transport of molecules, particles, and cells in solid tumors. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1, 241–263 (1999). doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.1.1.241
S. Ramanujan, A. Pluen, T.D. McKee, E.B. Brown, Y. Boucher, R.K. Jain, Diffusion and convection in collagen gels: implications for transport in the tumor interstitium. Biophys. J. 83(3), 1650–1660 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(02)73933-7
T. Stylianopoulos, M.Z. Poh, N. Insin, M.G. Bawendi, D. Fukumura, L.L. Munn, R.K. Jain, Diffusion of particles in the extracellular matrix: the effect of repulsive electrostatic interactions. Biophys. J. 99, 1342–1349 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.016
T. Betancourt, B. Brown, L. Brannon-Peppas, Doxorubicin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation: preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Nanomedicine 2(2), 219–232 (2007). doi:10.2217/17435889.2.2.219
H. Lee, S. Park, J.B. Kim, J. Kim, H. Kim, Entrapped doxorubicin nanoparticles for the treatment of metastatic anoikis-resistant cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 332(1), 110–119 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.01.021
U. Benbow, M.P. Schoenermark, K.A. Orndorff, A.L. Givan, C.E. Brinckerhoff, Human breast cancer cells activate procollagenase-1 and invade type I collagen: invasion is inhibited by all-trans retinoic acid. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 17(3), 231–238 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1006639214618
J.Y. Pille, C. Denoyelle, J. Varet, J.R. Bertrand, J. Soria et al., Anti-rhoa and anti-rhoc sirnas inhibit the proliferation and invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 11(2), 267–274 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.08.029
W. Bursch, A. Ellinger, H. Kienzl, L. Török, S. Pandey, M. Sikorska, R. Walker, R.S. Hermann, Active cell death induced by the anti-estrogens tamoxifen and ICI 164 384 in human mammary carcinoma cells (MCF-7) in culture: the role of autophagy. Carcinogenesis 17(8), 1595–1607 (1996). doi:10.1093/carcin/17.8.1595
C.Y. Hsieh, R.C. Santell, S.Z. Haslam, W.G. Helferich, Estrogenic effects of genistein on the growth of estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 58(17), 3833–3838 (1998)
T.T. Wang, J.M. Phang, Effects of estrogen on apoptotic pathways in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Cancer Res. 55(12), 2487–2489 (1995)
G. Frens, Controlled nucleation for the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nature 241, 20–22 (1973). doi:10.1038/physci241020a0
D.S. Cowan, K.O. Hicks, W.R. Wilson, Multicellular membranes as an in vitro model for extravascular diffusion in tumours. Br. J. Cancer Suppl. 27(2), 28–31 (1996)
I.F. Tannock, C.M. Lee, J.K. Tunggal, D.S. Cowan, M.J. Egorin, Limited penetration of anticancer drugs through tumor tissue: a potential cause of resistance of solid tumors to chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 8(3), 878–884 (2002)
K.O. Hicks, Y. Fleming, B.G. Siim, C.J. Koch, W.R. Wilson, Extravascular diffusion of tirapazamine: effect of metabolic consumption assessed using the multicellular layer model. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 42(3), 641–649 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(98)00268-5
W.R. Wilson, K.O. Hicks, Measurement of extravascular drug diffusion in multicellular layers. Br. J. Cancer 79(9–10), 1623–1626 (1999)
M. Neshatian, S. Chung, D. Yohan, C. Yang, D.B. Chithrani, Uptake of gold nanoparticles in breathless (hypoxic) cancer cells. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 11(7), 1162–1172 (2015). doi:10.1166/jbn.2015.2067
Y. Aoyama, T. Kanamori, T. Nakai, T. Sasaki, S. Horiuchi, S. Sando, T. Niidome, Artificial viruses and their application to gene delivery. size-controlled gene coating with glycocluster nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(12), 3455–3457 (2003). doi:10.1021/ja029608t
S.-H. Wang, C.-W. Lee, A. Chiou, P.-K. Wei, Size-dependent endocytosis of gold nanoparticles studied by three-dimensional mapping of plasmonic scattering images. J. Nanobiotechnol. 8(33), 1–13 (2010). doi:10.1186/1477-3155-8-33
H. Gao, W. Shi, L.B. Freund, Mechanics of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102(27), 9469–9474 (2005). doi:10.1073/pnas.0503879102
S. Zhang, J. Li, G. Lykotrafitis, G. Bao, S. Suresh, Size-dependent endocytosis of nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 21(4), 419–424 (2009). doi:10.1002/adma.200801393
W. Chen, D.P. Cormode, Y. Vengrenyuk, B. Herranz, J.E. Feig, A. Klink, W.J. Mulder, E.A. Fisher, Z.A. Fayad, Collagen-specific peptide conjugated HDL nanoparticles as MRI contrast agent to evaluate compositional changes in atherosclerotic plaque regression. JACC. Cardiovasc. Imaging 6(3), 373–384 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2012.06.016