Position-resolved Surface Characterization and Nanofabrication Using an Optical Microscope Combined with a Nanopipette/Quartz Tuning Fork Atomic Force Microscope
Corresponding Author: Wonho Jhe
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 6 No. 1 (2014), Article Number: 70-79
Abstract
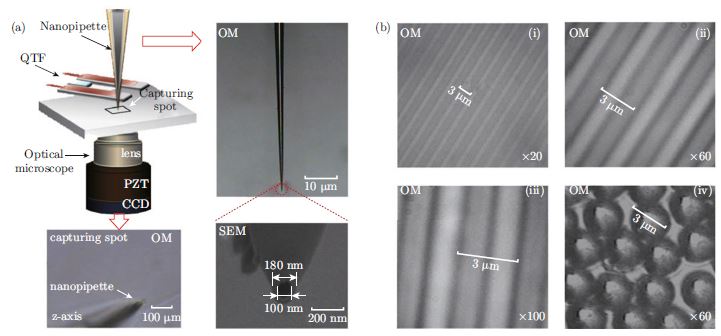
In this work, we introduce position-resolved surface characterization and nanofabrication using an optical microscope (OM) combined with a nanopipette-based quartz tuning fork atomic force microscope (nanopipette/QTF-AFM) system. This system is used to accurately determine substrate position and nanoscale phenomena under ambient conditions. Solutions consisting of 5 nm Au nanoparticles, nanowires, and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) are deposited onto the substrate through the nano/microaperture of a pulled pipette. Nano/microscale patterning is performed using a nanopipette/QTF-AFM, while position is resolved by monitoring the substrate with a custom OM. With this tool, one can perform surface characterization (force spectroscopy/microscopy) using the quartz tuning fork (QTF) sensor. Nanofabrication is achieved by accurately positioning target materials on the surface, and on-demand delivery and patterning of various solutions for molecular architecture.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- D. Cyranoski, “Science education: Reading, writing and nanofabrication”, Nature 460, 171–172 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/460171a
- B. D. Gates, Q. Xu, M. Stewart, D. Ryan, C. G. Willson and G. M. Whitesides, “New Approaches to Nanofabrication: Molding, Printing, and Other Techniques”, Chem. Rev. 105(4), 1171–1196 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cr030076o
- S. Y. Chou, P. R. Krauss and P. J. Renstrom, “Imprint lithography with 25-nanometer resolution”, Science 272(5258), 85–87 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5258.85
- D. R. S. Cumming, S. Thoms, S. P. Beaumont and J. M. R. Weaver, “Fabrication of 3 nm wires using 100 keV electron beam lithography and poly(methyl methacrylate) resist”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 68(3), 322–324 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.116073
- M. Remeika and A. Bezryadin, “Sub-10 nanometre fabrication: molecular templating, electron-beam sculpting and crystallization of metallic nanowires”, Nanotechnology 16(8), 1172–1176 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/8/032
- R. D. Piner, J. Zhu, F. Xu, S. Hong and C. A. Mirkin, “Dip-pen nanolithography”, Science 283(5402), 661–663 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.283.5402.661
- S. Hong, J. Zhu and C. A. Mirkin, “Multiple ink nanolithography: toward a multiple-pen nano-plotter”, Science 286(5439), 523–525 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5439.523
- M. Hong, J. Bae, K. Kim and W. Jhe, “Scanning nanolithography using a material-filled nanopipette”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77(16), 2604–2606 (2000). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1319181
- A. Bruckbauer, L. Ying, A. M. Rothery, D. Zhou, A. I. Shevchuk, C. Abell, Y. E. Korchev and D. Klenerman, “Writing with DNA and protein using a nanopipet for controlled delivery”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124(30), 8810–8811 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja026816c
- F. Iwata, S. Nagami, Y. Sumiya and A. Sasaki, “Nanometre-scale deposition of colloidal Au particles using electrophoresis in a nanopipette probe”, Nanotechnology 18(10), 105301 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/10/105301
- A. Meister, M. Liley, J. Brugger, R. Pugin and H. Heinzelmann, “Nanodispenser for attoliter volume deposition using atomic force microscopy probes modified by focused-ion-beam milling”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(25), 6260–6262 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1842352
- S. Deladi, N. R. Tas, J. W. Berenschot, G. J. M. Krijnen, M. J. de Boer, J. H. de Boer, M. Peter and M. C. Elwenspoek, “Micromachined fountain pen for atomic force microscope-based nanopatterning”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(22), 5361–5363 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1823040
- A. Fang, E. Dujardin and T. Ondarcuhu, “Control of droplet size in liquid nanodispensing”, Nano Lett. 6(10), 2368–2374 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nl061694y
- B. M. Kim, T. Murray and H. H. Bau, “The fabrication of integrated carbon pipes with sub micron diameters”, Nanotechnology 16(8), 1317–1320 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/8/056
- M. Schrlau and H. H. Bau, “Carbon-based Nanoprobes for cell biology”, Micro Nano Fluid 7(4), 439–450 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0458-x
- J. A. Thompson and H. H. Bau, “Microfluidic beadbased assay: theory and experiments”, J.Chrom. B. 878(2), 228–236 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.08.050
- J. Thompson, X. Du, J. M. Grogan, M. Schrlau and H. H. Bau, “Polymeric microbead arrays for microfluidic applications”, J.Micromech. Microeng. 20(11), 115017 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/20/11/115017
- S. Ito and F. Iwata, “Nanometer-scale deposition of metal plating using a nanopipette probe in liquid condition”, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 50, 08LB15 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.50.08LB15
- A. Lewis, Y. Kheifetz, E. Shambrodt, A. Radko, C. Sukenik and E. Khatchatryan, “Fountain pen nanochemistry: atomic force control of chrome etching”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75(17), 2689–2691 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.125120
- R. R. Gruter, J. Voros and T. Zambelli, “FluidFM as a lithography tool in liquid: spatially controlled deposition offluorescent nanoparticles”, Nanoscale 5(3), 1097 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C2NR33214K
- F. J. Giessibl, “Atomic resolution of the silicon (111)-(7x7) surface by atomic force microscopy”, Science 267(5194), 68–71 (1995). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.267.5194.68
- F. J. Giessibl, “Advances in atomic force microscopy”, Rev. Mod. Phys. 75(3), 949 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.75.949
- M. Lee, B. Sung, N. Hashemi and W. Jhe, “Study of a nanoscale water cluster by atomic force microscopy”, Faraday Discuss. 141, 415–421 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/B807740C
- H. Choe, M.-H. Hong, Y. Seo, K. Lee, G. Kim, Y. Cho, J. Ihm and W. Jhe, “Formation, manipulation, and elasticity measurement of a nanometric column of water molecules”, Phys. Rev.Lett. 95(18), 187801 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.187801
- M. Lee and W. Jhe, “General theory of amplitude-modulation atomic force microscopy”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97(3), 036104 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.036104
- S. An, J. Kim, K. Lee, B. Kim, M. Lee and W. Jhe, “Mechanical properties of the nanoscale molecular cluster of water meniscus by high-precision frequency modulation atomic force spectroscopy”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 101(5), 053114 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4740083
- M. Lee, J. Jahng, K. Kim and W. Jhe, “Quantitative atomic force measurement with a quartz tuning fork”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(2), 023117 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2756125
- S. An, M. Hong, J. Kim, S. Kwon, K. Lee, M. Lee and W. Jhe, “Quartz tuning fork-based frequency modulation atomic force spectroscopy and microscopy with all digital phase-locked loop”, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83(11), 113705 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4765702
- S. An, C. Stambaugh, G. Kim, M. Lee, Y. Kim, K. Lee and W. Jhe, “Low-volume liquid delivery and nanolithography using a nanopipette combined with a quartz tuning fork-atomic force microscope”, Nanoscale 4(20), 6493–6500 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C2NR30972F
- J. K. Hwang, S. Cho, J. M. Dang, E. B. Kwak, K. Song, J. Moon and M. M. Sung, “Direct nanoprinting by liquid-bridge-mediated nanotransfer moulding”, Nat. Nanotech. 5, 742–748 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2010.175
- J. Park, M. Hardy, J. Kang, K. Barton, K. Adair, D. K. Mukhopadhyay, C. Lee, M. S. Strano, A. G. Alleyne, J. G. Georgiadis, P. M. Ferreira and J. A. Rogers, “High-resolution electrohydrodynamic jet printing”, Nat. Mater. 6, 782–789 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmat1974
- R. S. Wagner and W. C. Ellis, “Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of single crystal growth”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 4(5), 89–90 (1964). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1753975
- M. Liu, Y. Chen, Q. Guo, R. Li, X. Sun and J. Yang, “Controllable positioning and alignment of silver nanowires by tunable hydrodynamic focusing”, Nanotechnology 22(12), 125302 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/22/12/125302
- A. W. Maijenburg, M. G. Maas, E. J. B. Rodijk, W. Ahmed, E. S. Kooij, E. T. Carlen, D. H. A. Blank and J. E. ten Elshof, “Dielectrophoretic alignment of metal and metal oxide nanowires and nanotubes: a universal set of parameters for bridging pre-patterned microelectrodes”, J. Col. Inter. Sci. 355(2), 486–493 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.12.011
- A. A. S. Bhagat, P. Jothimuthu and I. Papautsky, “Photodefinable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) for rapid lab-on-a-chip prototyping”, Lab Chip 7(9), 1192–1197 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/B704946C
- T. Scharnweber, R. Truckenmller, A. M. Schneider, A. Welle, M. Reinhardt and S. Giselbrecht, “Rapid prototyping of microstructures in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) by direct UV-lithography”, Lab Chip 11(7), 1368–1371 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C0LC00567C
- K. J. Regehr, M. Domenech, J. T. Koepsel, K. C. Carver, S. J. Ellison-Zelski, W. L. Murphy, L. A. Schuler, E. T. Alarid and D. J. Beebe, “Biological implications of polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic cell culture”, Lab Chip 9(15), 2132–2139 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/B903043C
- L. Engel, J. Shklovsky, D. Schrieber, S. Krylov and Y. Shacham-Diamand, “Freestanding smooth micron-scale polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membranes by thermal imprinting”, J. Micromech.Microeng. 22(4), 045003 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/22/4/045003
References
D. Cyranoski, “Science education: Reading, writing and nanofabrication”, Nature 460, 171–172 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/460171a
B. D. Gates, Q. Xu, M. Stewart, D. Ryan, C. G. Willson and G. M. Whitesides, “New Approaches to Nanofabrication: Molding, Printing, and Other Techniques”, Chem. Rev. 105(4), 1171–1196 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cr030076o
S. Y. Chou, P. R. Krauss and P. J. Renstrom, “Imprint lithography with 25-nanometer resolution”, Science 272(5258), 85–87 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5258.85
D. R. S. Cumming, S. Thoms, S. P. Beaumont and J. M. R. Weaver, “Fabrication of 3 nm wires using 100 keV electron beam lithography and poly(methyl methacrylate) resist”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 68(3), 322–324 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.116073
M. Remeika and A. Bezryadin, “Sub-10 nanometre fabrication: molecular templating, electron-beam sculpting and crystallization of metallic nanowires”, Nanotechnology 16(8), 1172–1176 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/8/032
R. D. Piner, J. Zhu, F. Xu, S. Hong and C. A. Mirkin, “Dip-pen nanolithography”, Science 283(5402), 661–663 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.283.5402.661
S. Hong, J. Zhu and C. A. Mirkin, “Multiple ink nanolithography: toward a multiple-pen nano-plotter”, Science 286(5439), 523–525 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5439.523
M. Hong, J. Bae, K. Kim and W. Jhe, “Scanning nanolithography using a material-filled nanopipette”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77(16), 2604–2606 (2000). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1319181
A. Bruckbauer, L. Ying, A. M. Rothery, D. Zhou, A. I. Shevchuk, C. Abell, Y. E. Korchev and D. Klenerman, “Writing with DNA and protein using a nanopipet for controlled delivery”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124(30), 8810–8811 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja026816c
F. Iwata, S. Nagami, Y. Sumiya and A. Sasaki, “Nanometre-scale deposition of colloidal Au particles using electrophoresis in a nanopipette probe”, Nanotechnology 18(10), 105301 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/10/105301
A. Meister, M. Liley, J. Brugger, R. Pugin and H. Heinzelmann, “Nanodispenser for attoliter volume deposition using atomic force microscopy probes modified by focused-ion-beam milling”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(25), 6260–6262 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1842352
S. Deladi, N. R. Tas, J. W. Berenschot, G. J. M. Krijnen, M. J. de Boer, J. H. de Boer, M. Peter and M. C. Elwenspoek, “Micromachined fountain pen for atomic force microscope-based nanopatterning”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(22), 5361–5363 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1823040
A. Fang, E. Dujardin and T. Ondarcuhu, “Control of droplet size in liquid nanodispensing”, Nano Lett. 6(10), 2368–2374 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nl061694y
B. M. Kim, T. Murray and H. H. Bau, “The fabrication of integrated carbon pipes with sub micron diameters”, Nanotechnology 16(8), 1317–1320 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/8/056
M. Schrlau and H. H. Bau, “Carbon-based Nanoprobes for cell biology”, Micro Nano Fluid 7(4), 439–450 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0458-x
J. A. Thompson and H. H. Bau, “Microfluidic beadbased assay: theory and experiments”, J.Chrom. B. 878(2), 228–236 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.08.050
J. Thompson, X. Du, J. M. Grogan, M. Schrlau and H. H. Bau, “Polymeric microbead arrays for microfluidic applications”, J.Micromech. Microeng. 20(11), 115017 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/20/11/115017
S. Ito and F. Iwata, “Nanometer-scale deposition of metal plating using a nanopipette probe in liquid condition”, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 50, 08LB15 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.50.08LB15
A. Lewis, Y. Kheifetz, E. Shambrodt, A. Radko, C. Sukenik and E. Khatchatryan, “Fountain pen nanochemistry: atomic force control of chrome etching”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75(17), 2689–2691 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.125120
R. R. Gruter, J. Voros and T. Zambelli, “FluidFM as a lithography tool in liquid: spatially controlled deposition offluorescent nanoparticles”, Nanoscale 5(3), 1097 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C2NR33214K
F. J. Giessibl, “Atomic resolution of the silicon (111)-(7x7) surface by atomic force microscopy”, Science 267(5194), 68–71 (1995). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.267.5194.68
F. J. Giessibl, “Advances in atomic force microscopy”, Rev. Mod. Phys. 75(3), 949 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.75.949
M. Lee, B. Sung, N. Hashemi and W. Jhe, “Study of a nanoscale water cluster by atomic force microscopy”, Faraday Discuss. 141, 415–421 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/B807740C
H. Choe, M.-H. Hong, Y. Seo, K. Lee, G. Kim, Y. Cho, J. Ihm and W. Jhe, “Formation, manipulation, and elasticity measurement of a nanometric column of water molecules”, Phys. Rev.Lett. 95(18), 187801 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.187801
M. Lee and W. Jhe, “General theory of amplitude-modulation atomic force microscopy”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97(3), 036104 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.036104
S. An, J. Kim, K. Lee, B. Kim, M. Lee and W. Jhe, “Mechanical properties of the nanoscale molecular cluster of water meniscus by high-precision frequency modulation atomic force spectroscopy”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 101(5), 053114 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4740083
M. Lee, J. Jahng, K. Kim and W. Jhe, “Quantitative atomic force measurement with a quartz tuning fork”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(2), 023117 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2756125
S. An, M. Hong, J. Kim, S. Kwon, K. Lee, M. Lee and W. Jhe, “Quartz tuning fork-based frequency modulation atomic force spectroscopy and microscopy with all digital phase-locked loop”, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83(11), 113705 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4765702
S. An, C. Stambaugh, G. Kim, M. Lee, Y. Kim, K. Lee and W. Jhe, “Low-volume liquid delivery and nanolithography using a nanopipette combined with a quartz tuning fork-atomic force microscope”, Nanoscale 4(20), 6493–6500 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C2NR30972F
J. K. Hwang, S. Cho, J. M. Dang, E. B. Kwak, K. Song, J. Moon and M. M. Sung, “Direct nanoprinting by liquid-bridge-mediated nanotransfer moulding”, Nat. Nanotech. 5, 742–748 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2010.175
J. Park, M. Hardy, J. Kang, K. Barton, K. Adair, D. K. Mukhopadhyay, C. Lee, M. S. Strano, A. G. Alleyne, J. G. Georgiadis, P. M. Ferreira and J. A. Rogers, “High-resolution electrohydrodynamic jet printing”, Nat. Mater. 6, 782–789 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmat1974
R. S. Wagner and W. C. Ellis, “Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of single crystal growth”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 4(5), 89–90 (1964). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1753975
M. Liu, Y. Chen, Q. Guo, R. Li, X. Sun and J. Yang, “Controllable positioning and alignment of silver nanowires by tunable hydrodynamic focusing”, Nanotechnology 22(12), 125302 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/22/12/125302
A. W. Maijenburg, M. G. Maas, E. J. B. Rodijk, W. Ahmed, E. S. Kooij, E. T. Carlen, D. H. A. Blank and J. E. ten Elshof, “Dielectrophoretic alignment of metal and metal oxide nanowires and nanotubes: a universal set of parameters for bridging pre-patterned microelectrodes”, J. Col. Inter. Sci. 355(2), 486–493 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.12.011
A. A. S. Bhagat, P. Jothimuthu and I. Papautsky, “Photodefinable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) for rapid lab-on-a-chip prototyping”, Lab Chip 7(9), 1192–1197 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/B704946C
T. Scharnweber, R. Truckenmller, A. M. Schneider, A. Welle, M. Reinhardt and S. Giselbrecht, “Rapid prototyping of microstructures in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) by direct UV-lithography”, Lab Chip 11(7), 1368–1371 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C0LC00567C
K. J. Regehr, M. Domenech, J. T. Koepsel, K. C. Carver, S. J. Ellison-Zelski, W. L. Murphy, L. A. Schuler, E. T. Alarid and D. J. Beebe, “Biological implications of polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic cell culture”, Lab Chip 9(15), 2132–2139 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/B903043C
L. Engel, J. Shklovsky, D. Schrieber, S. Krylov and Y. Shacham-Diamand, “Freestanding smooth micron-scale polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membranes by thermal imprinting”, J. Micromech.Microeng. 22(4), 045003 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/22/4/045003