Fabrication and Evaluation of Low-cost Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 Counter Electrodes for Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
Corresponding Author: Sumei Huang
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 5 No. 4 (2013), Article Number: 281-288
Abstract
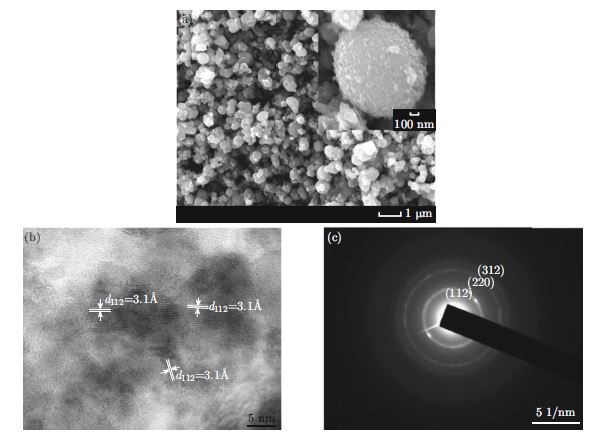
We explore a simple and eco-friendly approach for preparing CZTS powders and a screen-printing process for Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 (CZTSSe) counter electrodes (CEs) in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs). Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) nanoparticles have been synthesized via a hydrazine-free solvothermal approach without the assistance of organic ligands. CZTS has been prepared by directly drop-casting the CZTS ink on the cleaned FTO glass, while CZTSSe CEs have been fabricated by screen-printing CZTS pastes, followed by post selenization using Se vapor obtained from elemental Se pellets. The crystal structure, composition and morphology of the as-deposited CZTS nanoparticles and CZTSSe electrodes are characterized by X-ray diffractometer, energy dispersive spectrometer, field emission scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of CZTS, CZTSSe and Pt CE based DSCs are examined and analyzed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The prepared CZTS and CZTSSe CEs exhibit a cellular structure with high porosity. DSCs fabricated with CZTSSe CEs achieve a power conversion efficiency of 5.75% under AM 1.5 G illumination with an intensity of 100 mW/cm2, which is higher than that (3.22%) of the cell using the CZTS CE. The results demonstrate that the CZTSSe CE possesses good electrocatalytic activity for the reduction of charge carriers in electrolyte. The comprehensive CZTSSe CE process is cheap and scalable. It can make large-scale electro-catalytic film fabrication cost competitive for both energy harvesting and storage applications.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- B. O’Regan and M. Grfitzeli, “A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films”, nature 353(6346), 737–740 (1991). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/353737a0
- M. Nazeeruddin, A. Kay, I. Rodicio, R. Humphry-Baker, E. Mueller, P. Liska, N. Vlachopoulos and M. Graetzel, “Conversion of light to electricity by cis-X2bis (2, 2′-bipyridyl-4, 4′-dicarboxylate) ruthenium (II) charge-transfer sensitizers (X= Cl-, Br-, I-, CN-, and SCN-) on nanocrystalline titanium dioxide electrodes”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115(14), 6382–6390 (1993). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja00067a063
- M. Malekshahi Byranvand, Ali Nemati Kharat and Mohammad Hossein Bazargan, “Titania nanostructures for Dye-sensitized solar cells”, Nano-Micro Lett. 4(4), 253–266 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.3786/nml.v4n4.p253-266
- Yafei Zhang, Huijuan Geng, Zhihua Zhou, Jiang Wu, Zhiming Wang, Yaozhong Zhang, Zhongli Li, Liying Zhang, Zhi Yang and Hueyliang Hwang, “Development of inorganic solar cells by nanotechnology”, Nano-Micro Lett. 4(2), 124–134 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.3786/nml.v4i2.p124-134
- T. Ma, X. Fang, M. Akiyama, K. Inoue, H. Noma and E. Abe, “Properties of several types of novel counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Electroanal. Chem. 574(1), 77–83 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2004.08.002
- P. Li, J. Wu, J. Lin, M. Huang, Z. Lan and Q. Li, “Improvement of performance of dye-sensitized solar cells based on electrodeposited-platinum counter electrode”, Electrochim. Acta 53(12), 4161–4166 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.12.073
- G. Calogero, P. Calandra, A. Irrera, A. Sinopoli, I. Citro and G. Di Marco, “A new type of transparent and low cost counter-electrode based on platinum nanoparticles for dye-sensitized solar cells”, Energy Environ. Sci. 4(5), 1838–1844 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c0ee00463d
- A. Kay and M. Grätzel, “Low cost photovoltaic modules based on dye sensitized nanocrystalline titanium dioxide and carbon powder”, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 44(1), 99–117 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0927-0248(96)00063-3
- J. Roy-Mayhew, D. Bozym, C. Punckt and I. Aksay, “Functionalized graphene as a catalytic counter electrode in dye-sensitized solar cells”, ACS Nano 4(10), 6203–6211 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn1016428
- Q. Tai, B. Chen, F. Guo, S. Xu, H. Hu, B. Sebo and X. Z. Zhao, “In situ prepared transparent polyaniline electrode and its application in bifacial dye-sensitized solar cells”, ACS Nano 5(5), 3795–3799 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn200133g
- K. M. Lee, C. Y. Hsu, P. Y. Chen, M. Ikegami, T. Miyasaka and K. C. Ho, “Highly porous PProDOT-Et2 film as counter electrode for plastic dye-sensitized solar cells”, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11(18), 3375–3379 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b823011k
- D. Zhang, X. Li, H. Li, S. Chen, Z. Sun, X. Yin and S. Huang, “Graphene-based counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells”, Carbon 49(15), 5382–5388 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2011.08.005
- Q. Jiang, G. Li, S. Liu and X. Gao, “Surface-nitrided nickel with bifunctional structure as low-cost counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Phys. Chem. C 114(31), 13397–13401 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp1035184
- M. Wang, A. M. Anghel, B. Marsan, N. L. Cevey Ha, N. Pootrakulchote, S. M. Zakeeruddin and M. Grätzel, “CoS supersedes Pt as efficient electrocatalyst for triiodide reduction in dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(44), 15976–15977 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja905970y
- H. Sun, D. Qin, S. Huang, X. Guo, D. Li, Y. Luo and Q. Meng, “Dye-sensitized solar cells with NiS counter electrodes electrodeposited by a potential reversal technique”, Energy Environ. Sci. 4(8), 2630–2637 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c0ee00791a
- M. Wu, X. Lin, A. Hagfeldt and T. Ma, “Low-cost molybdenum carbide and tungsten carbide counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50(15), 3520–3524 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201006635
- H. Katagiri, K. Jimbo, W. S. Maw, K. Oishi, M. Yamazaki, H. Araki and A. Takeuchi, “Development of CZTS-based thin film solar cells”, Thin Solid Films 517(7), 2455–2460 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2008.11.002
- G. Zoppi, I. Forbes, R. Miles, P. J. Dale, J. J. Scragg and L. M. Peter, “Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin film solar cells produced by selenisation of magnetron sputtered precursors”, Prog. Photovoltaics 17(5), 315–319 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pip.886
- T. K. Todorov, K. B. Reuter and D. B. Mitzi, “High-efficiency solar cell with earth-abundant liquid-processed absorber”, Adv. Mater. 22(20), E156–E159 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adma.200904155
- X. Xin, M. He, W. Han, J. Jung and Z. Lin, “Low-cost copper zinc tin sulfide counter electrodes for high-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50(49), 11739–11742 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201104786
- Y. F. Du, J. Q. Fan, W. H. Zhou, Z. J. Zhou, J. Jiao and S. X. Wu, “One-step synthesis of stoichiometric Cu2ZnSnSe4 as counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells”, ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 4(3), 1796–1802 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/am3000616
- J. Shi, Z. Li, D. Zhang, Q. Liu, Z. Sun and S. Huang, “Fabrication of Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin films by sputtering from a single quaternary chalcogenide target”, Prog. Photovoltaics. 19(2), 160–164 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pip.1001
- X. Li, D. Zhang, S. Chen, H. Zhang, Z. Sun, S. Huang and X. Yin, “Dye-sensitized solar cells with higher Jsc by using polyvinylidene fluoride membrane counter electrodes”, Nano-Micro Lett. 3(3), 195–199 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.3786/nml.v3i3.p195-199
- H. Yoo and J. Kim, “Comparative study of Cu2ZnSnS4 film growth”, Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. C 95(1), 239–244 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2010.04.060
- S. Han, M. Kong, Y. Guo and M. Wang, “Synthesis of copper indium sulfide nanoparticles by solvothermal method”, Mater. Lett. 63(13), 1192–1194 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.02.032
- C. Zou, L. Zhang, D. Lin, Y. Yang, Q. Li, X. Xu, X. Chen and S. Huang, “Facile synthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals”, Cryst. Eng. Comm. 13(10), 3310–3313 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c0ce00631a
- J. He, L. Sun, S. Chen, Y. Chen, P. Yang and J. Chu, “Composition dependence of structure and optical properties of Cu2ZnSn (S, Se)4 solid solutions: An experimental study”, J. Alloy Compd. 511(1), 129–132 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.08.099
- C. Jiang, J. S. Lee and D. V. Talapin, “Soluble precursors for CuInSe2, CuIn1t−x GaxSe2, and Cu2ZnSn (S, Se)4 based on colloidal nanocrystals and molecular metal chalcogenide surface ligands”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(11), 5010–5013 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja2105812
- D. Zhang, X. Li, S. Chen, F. Tao, Z. Sun, X. Yin and S. Huang, “Fabrication of double-walled carbon nanotube counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Solid State Electrochem. 14(9), 1541–1546 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10008-009-0982-3
- J. Bisquert, “Theory of the impedance of electron diffusion and recombination in a thin layer”, J. Phys. Chem. B 106(2), 325–333 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp011941g
- A. Fillinger, D. Soltz and B. Parkinson, “Dye sensitization of natural anatase crystals with a ruthenium-based dye”, J. Solid State Electrochem. 149(9), A1146–A1156 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1149/1.1495497
- Q. Wang, J. E. Moser and M. Grätzel, “Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic analysis of dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Phys. Chem. B 109(31), 14945–14953 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp052768h
- T. Hoshikawa, M. Yamada, R. Kikuchi and K. Eguchi, “Impedance analysis of internal resistance affecting the photoelectrochemical performance of dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Solid State Electrochem. 152(2), E68–E73 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1149/1.184776
- C. Longo, J. Freitas and M. A. De Paoli, “Performance and stability of TiO2 dye solar cells assembled with flexible electrodes and a polymer electrolyte”, J. Photoch. Photobio. A 159(1), 33–39 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(03)00106-0
- M. Bernard, H. Cachet, P. Falaras, A. Hugot-Le Goff, M. Kalbac, I. Lukes, N. Oanh, T. Stergiopoulos and I. Arabatzis, “Sensitization of TiO2 by Polypyridine Dyes Role of the Electron Donor”, J. Solid State Electr. 150(3), E155–E164 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1149/1.1543951
- G. Zhu, L. Pan, T. Lu, T. Xu and Z. Sun, “Electrophoretic deposition of reduced graphene-carbon nanotubes composite films as counter electrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Mater. Chem. 21(38), 14869–14875 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c1jm12433a
- L. Han, N. Koide, Y. Chiba, A. Islam, R. Komiya, N. Fuke, A. Fukui and R. Yamanaka, “Improvement of efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells by reduction of internal resistance”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86(21), 213501-213501-3 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1925773
- E. Ramasamy, W. J. Lee, D. Y. Lee and J. S. Song, “Nanocarbon counterelectrode for dye sensitized solar cells”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(17), 173103 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2731495
- A. R. Ko, J. K. Oh, Y. W. Lee, S. B. Han and K. W. Park, “Characterizations of tungsten carbide as a non-Pt counter electrode in dye-sensitized solar cells”, Mater. Lett. 65(14), 2220–2223 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.04.062
References
B. O’Regan and M. Grfitzeli, “A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films”, nature 353(6346), 737–740 (1991). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/353737a0
M. Nazeeruddin, A. Kay, I. Rodicio, R. Humphry-Baker, E. Mueller, P. Liska, N. Vlachopoulos and M. Graetzel, “Conversion of light to electricity by cis-X2bis (2, 2′-bipyridyl-4, 4′-dicarboxylate) ruthenium (II) charge-transfer sensitizers (X= Cl-, Br-, I-, CN-, and SCN-) on nanocrystalline titanium dioxide electrodes”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115(14), 6382–6390 (1993). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja00067a063
M. Malekshahi Byranvand, Ali Nemati Kharat and Mohammad Hossein Bazargan, “Titania nanostructures for Dye-sensitized solar cells”, Nano-Micro Lett. 4(4), 253–266 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.3786/nml.v4n4.p253-266
Yafei Zhang, Huijuan Geng, Zhihua Zhou, Jiang Wu, Zhiming Wang, Yaozhong Zhang, Zhongli Li, Liying Zhang, Zhi Yang and Hueyliang Hwang, “Development of inorganic solar cells by nanotechnology”, Nano-Micro Lett. 4(2), 124–134 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.3786/nml.v4i2.p124-134
T. Ma, X. Fang, M. Akiyama, K. Inoue, H. Noma and E. Abe, “Properties of several types of novel counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Electroanal. Chem. 574(1), 77–83 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2004.08.002
P. Li, J. Wu, J. Lin, M. Huang, Z. Lan and Q. Li, “Improvement of performance of dye-sensitized solar cells based on electrodeposited-platinum counter electrode”, Electrochim. Acta 53(12), 4161–4166 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.12.073
G. Calogero, P. Calandra, A. Irrera, A. Sinopoli, I. Citro and G. Di Marco, “A new type of transparent and low cost counter-electrode based on platinum nanoparticles for dye-sensitized solar cells”, Energy Environ. Sci. 4(5), 1838–1844 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c0ee00463d
A. Kay and M. Grätzel, “Low cost photovoltaic modules based on dye sensitized nanocrystalline titanium dioxide and carbon powder”, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 44(1), 99–117 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0927-0248(96)00063-3
J. Roy-Mayhew, D. Bozym, C. Punckt and I. Aksay, “Functionalized graphene as a catalytic counter electrode in dye-sensitized solar cells”, ACS Nano 4(10), 6203–6211 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn1016428
Q. Tai, B. Chen, F. Guo, S. Xu, H. Hu, B. Sebo and X. Z. Zhao, “In situ prepared transparent polyaniline electrode and its application in bifacial dye-sensitized solar cells”, ACS Nano 5(5), 3795–3799 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn200133g
K. M. Lee, C. Y. Hsu, P. Y. Chen, M. Ikegami, T. Miyasaka and K. C. Ho, “Highly porous PProDOT-Et2 film as counter electrode for plastic dye-sensitized solar cells”, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11(18), 3375–3379 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b823011k
D. Zhang, X. Li, H. Li, S. Chen, Z. Sun, X. Yin and S. Huang, “Graphene-based counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells”, Carbon 49(15), 5382–5388 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2011.08.005
Q. Jiang, G. Li, S. Liu and X. Gao, “Surface-nitrided nickel with bifunctional structure as low-cost counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Phys. Chem. C 114(31), 13397–13401 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp1035184
M. Wang, A. M. Anghel, B. Marsan, N. L. Cevey Ha, N. Pootrakulchote, S. M. Zakeeruddin and M. Grätzel, “CoS supersedes Pt as efficient electrocatalyst for triiodide reduction in dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(44), 15976–15977 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja905970y
H. Sun, D. Qin, S. Huang, X. Guo, D. Li, Y. Luo and Q. Meng, “Dye-sensitized solar cells with NiS counter electrodes electrodeposited by a potential reversal technique”, Energy Environ. Sci. 4(8), 2630–2637 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c0ee00791a
M. Wu, X. Lin, A. Hagfeldt and T. Ma, “Low-cost molybdenum carbide and tungsten carbide counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50(15), 3520–3524 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201006635
H. Katagiri, K. Jimbo, W. S. Maw, K. Oishi, M. Yamazaki, H. Araki and A. Takeuchi, “Development of CZTS-based thin film solar cells”, Thin Solid Films 517(7), 2455–2460 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2008.11.002
G. Zoppi, I. Forbes, R. Miles, P. J. Dale, J. J. Scragg and L. M. Peter, “Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin film solar cells produced by selenisation of magnetron sputtered precursors”, Prog. Photovoltaics 17(5), 315–319 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pip.886
T. K. Todorov, K. B. Reuter and D. B. Mitzi, “High-efficiency solar cell with earth-abundant liquid-processed absorber”, Adv. Mater. 22(20), E156–E159 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adma.200904155
X. Xin, M. He, W. Han, J. Jung and Z. Lin, “Low-cost copper zinc tin sulfide counter electrodes for high-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50(49), 11739–11742 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201104786
Y. F. Du, J. Q. Fan, W. H. Zhou, Z. J. Zhou, J. Jiao and S. X. Wu, “One-step synthesis of stoichiometric Cu2ZnSnSe4 as counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells”, ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 4(3), 1796–1802 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/am3000616
J. Shi, Z. Li, D. Zhang, Q. Liu, Z. Sun and S. Huang, “Fabrication of Cu (In, Ga) Se2 thin films by sputtering from a single quaternary chalcogenide target”, Prog. Photovoltaics. 19(2), 160–164 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pip.1001
X. Li, D. Zhang, S. Chen, H. Zhang, Z. Sun, S. Huang and X. Yin, “Dye-sensitized solar cells with higher Jsc by using polyvinylidene fluoride membrane counter electrodes”, Nano-Micro Lett. 3(3), 195–199 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.3786/nml.v3i3.p195-199
H. Yoo and J. Kim, “Comparative study of Cu2ZnSnS4 film growth”, Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. C 95(1), 239–244 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2010.04.060
S. Han, M. Kong, Y. Guo and M. Wang, “Synthesis of copper indium sulfide nanoparticles by solvothermal method”, Mater. Lett. 63(13), 1192–1194 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.02.032
C. Zou, L. Zhang, D. Lin, Y. Yang, Q. Li, X. Xu, X. Chen and S. Huang, “Facile synthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals”, Cryst. Eng. Comm. 13(10), 3310–3313 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c0ce00631a
J. He, L. Sun, S. Chen, Y. Chen, P. Yang and J. Chu, “Composition dependence of structure and optical properties of Cu2ZnSn (S, Se)4 solid solutions: An experimental study”, J. Alloy Compd. 511(1), 129–132 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.08.099
C. Jiang, J. S. Lee and D. V. Talapin, “Soluble precursors for CuInSe2, CuIn1t−x GaxSe2, and Cu2ZnSn (S, Se)4 based on colloidal nanocrystals and molecular metal chalcogenide surface ligands”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(11), 5010–5013 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja2105812
D. Zhang, X. Li, S. Chen, F. Tao, Z. Sun, X. Yin and S. Huang, “Fabrication of double-walled carbon nanotube counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Solid State Electrochem. 14(9), 1541–1546 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10008-009-0982-3
J. Bisquert, “Theory of the impedance of electron diffusion and recombination in a thin layer”, J. Phys. Chem. B 106(2), 325–333 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp011941g
A. Fillinger, D. Soltz and B. Parkinson, “Dye sensitization of natural anatase crystals with a ruthenium-based dye”, J. Solid State Electrochem. 149(9), A1146–A1156 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1149/1.1495497
Q. Wang, J. E. Moser and M. Grätzel, “Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic analysis of dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Phys. Chem. B 109(31), 14945–14953 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp052768h
T. Hoshikawa, M. Yamada, R. Kikuchi and K. Eguchi, “Impedance analysis of internal resistance affecting the photoelectrochemical performance of dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Solid State Electrochem. 152(2), E68–E73 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1149/1.184776
C. Longo, J. Freitas and M. A. De Paoli, “Performance and stability of TiO2 dye solar cells assembled with flexible electrodes and a polymer electrolyte”, J. Photoch. Photobio. A 159(1), 33–39 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(03)00106-0
M. Bernard, H. Cachet, P. Falaras, A. Hugot-Le Goff, M. Kalbac, I. Lukes, N. Oanh, T. Stergiopoulos and I. Arabatzis, “Sensitization of TiO2 by Polypyridine Dyes Role of the Electron Donor”, J. Solid State Electr. 150(3), E155–E164 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1149/1.1543951
G. Zhu, L. Pan, T. Lu, T. Xu and Z. Sun, “Electrophoretic deposition of reduced graphene-carbon nanotubes composite films as counter electrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells”, J. Mater. Chem. 21(38), 14869–14875 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c1jm12433a
L. Han, N. Koide, Y. Chiba, A. Islam, R. Komiya, N. Fuke, A. Fukui and R. Yamanaka, “Improvement of efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells by reduction of internal resistance”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86(21), 213501-213501-3 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1925773
E. Ramasamy, W. J. Lee, D. Y. Lee and J. S. Song, “Nanocarbon counterelectrode for dye sensitized solar cells”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(17), 173103 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2731495
A. R. Ko, J. K. Oh, Y. W. Lee, S. B. Han and K. W. Park, “Characterizations of tungsten carbide as a non-Pt counter electrode in dye-sensitized solar cells”, Mater. Lett. 65(14), 2220–2223 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.04.062