Angle-Resolved Plasmonic Properties of Single Gold Nanorod Dimers
Corresponding Author: Weihai Ni
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 6 No. 4 (2014), Article Number: 372-380
Abstract
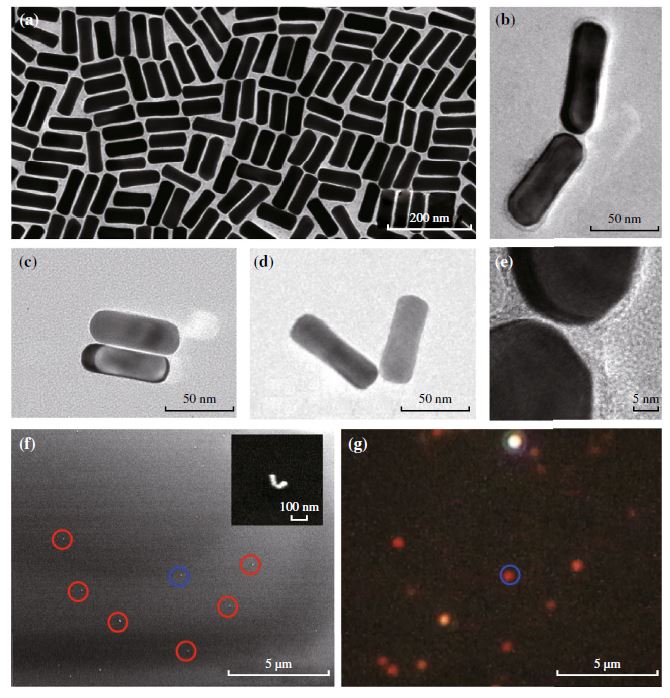
Through wet-chemical assembly methods, gold nanorods were placed close to each other and formed a dimer with a gap distance ~1 nm, and hence degenerated plasmonic dipole modes of individual nanorods coupled together to produce hybridized bonding and antibonding resonance modes. Previous studies using a condenser for illumination result in averaged signals over all excitation angles. By exciting an individual dimer obliquely at different angles, we demonstrate that these two new resonance modes are highly tunable and sensitive to the angle between the excitation polarization and the dimer orientation, which follows cos2φ dependence. Moreover, for dimer structures with various structure angles, the resonance wavelengths as well as the refractive index sensitivities were found independent of the structure angle. Calculated angle-resolved plasmonic properties are in good agreement with the measurements. The assembled nanostructures investigated here are important for fundamental researches as well as potential applications when they are used as building blocks in plasmon-based optical and optoelectronic devices.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- S. Link, M.A. El-Sayed, Optical properties and ultrafast dynamics of metallic nanocrystals. Annu. Rev. Phys. 54(1), 331–366 (2003). doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.54.011002.103759
- S. Biswas, J. Duan, D. Nepal, R. Pachter, R. Vaia, Plasmonic resonances in self-assembled reduced symmetry gold nanorod structures. Nano Lett. 13(5), 2220–2225 (2013). doi:10.1021/nl4007358
- B. Luk’yanchuk, N.I. Zheludev, S.A. Maier, N.J. Halas, P. Nordlander, H. Giessen, C.T. Chong, The fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 9(9), 707–715 (2010). doi:10.1038/nmat2810
- L. Shao, K.C. Woo, H. Chen, Z. Jin, J. Wang, H.Q. Lin, Angle- and energy-resolved plasmon coupling in gold nanorod dimers. ACS Nano 4(6), 3053–3062 (2010). doi:10.1021/nn100180d
- R. Iovine, L.L. Spada, L. Vegni, Optical properties of modified nanorod particles for biomedical sensing. Magn. IEEE Trans. 50(2), 169–172 (2014). doi:10.1109/TMAG.2013.2284552
- H. Chen, L. Shao, Q. Li, J. Wang, Gold nanorods and their plasmonic properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(7), 2679–2724 (2013). doi:10.1039/C2CS35367A
- G. Baffou, R. Quidant, Nanoplasmonics for chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43(11), 3898–3907 (2014). doi:10.1039/C3CS60364D
- D. Gomez, T. Davis, A. Funston, Plasmonics by design: design principles to structure–function relationships with assemblies of metal nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2(17), 3077–3087 (2014). doi:10.1039/C3TC32041C
- J.N. Li, T.Z. Liu, H.R. Zheng, F. Gao, J. Dong, Z.L. Zhang, Z.Y. Zhang, Plasmon resonances and strong electric field enhancements in side-by-side tangent nanospheroid homodimers. Opt. Express 21(14), 17176–17185 (2013). doi:10.1364/OE.21.017176
- R. Fernández-García, Y. Sonnefraud, A.I. Fernández-Domínguez, V. Giannini, S.A. Maier, Design considerations for near-field enhancement in optical antennas. Contemp. Phys. 55(1), 1–11 (2014). doi:10.1080/00107514.2013.850788
- P.K. Jain, S. Eustis, M.A. El-Sayed, Plasmon coupling in nanorod assemblies: optical absorption, discrete dipole approximation simulation, and exciton-coupling model. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(37), 18243–18253 (2006). doi:10.1021/jp063879z
- J. Kumar, X. Wei, S. Barrow, A.M. Funston, K.G. Thomas, P. Mulvaney, Surface plasmon coupling in end-to-end linked gold nanorod dimers and trimers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15(12), 4258–4264 (2013). doi:10.1039/C3CP44657C
- S. Biswas, J. Duan, D. Nepal, K. Park, R. Pachter, R.A. Vaia, Plasmon induced transparency in the visible via self-assembled gold nanorod heterodimers. Nano Lett. 13(12), 6287–6291 (2013). doi:10.1021/nl403911z
- L.V. Brown, H. Sobhani, J.B. Lassiter, P. Nordlander, N.J. Halas, Heterodimers: plasmonic properties of mismatched nanoparticle pairs. ACS Nano 4(2), 819–832 (2010). doi:10.1021/nn9017312
- C. Tabor, D. Van Haute, M.A. El-Sayed, Effect of orientation on plasmonic coupling between gold nanorods. ACS Nano 3(11), 3670–3678 (2009). doi:10.1021/nn900779f
- M.W. Chu, V. Myroshnychenko, C.H. Chen, J.P. Deng, C.Y. Mou, F.J. García de Abajo, Probing bright and dark surface-plasmon modes in individual and coupled noble metal nanoparticles using an electron beam. Nano Lett. 9(1), 399–404 (2009). doi:10.1021/nl803270x
- M.S.M. Saifullah, T. Ondarçuhu, D.K. Koltsov, C. Joachim, M.E. Welland, A reliable scheme for fabricating sub-5 nm co-planar junctions for single-molecule electronics. Nanotechnology 13(5), 659 (2002). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/13/5/323
- L.S. Slaughter, Y. Wu, B.A. Willingham, P. Nordlander, S. Link, Effects of symmetry breaking and conductive contact on the plasmon coupling in gold nanorod dimers. ACS Nano 4(8), 4657–4666 (2010). doi:10.1021/nn1011144
- S. Panaro, A. Nazir, C. Liberale, G. Das, H. Wang, F. De Angelis, R.P. Zaccaria, E. Di Fabrizio, A. Toma, Dark to bright mode conversion on dipolar nanoantennas: a symmetry-breaking approach. ACS Photonics 1(4), 310–314 (2014). doi:10.1021/ph500044w
- W.S. Chang, J.W. Ha, L.S. Slaughter, S. Link, Plasmonic nanorod absorbers as orientation sensors. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107(7), 2781–2786 (2010). doi:10.1073/pnas.0910127107
- C. Sönnichsen, A.P. Alivisatos, Gold nanorods as novel nonbleaching plasmon-based orientation sensors for polarized single-particle microscopy. Nano Lett. 5(2), 301–304 (2004). doi:10.1021/nl048089k
- W.H. Ni, H.J. Chen, J. Su, Z.H. Sun, J.F. Wang, H.K. Wu, Effects of dyes, gold nanocrystals, pH, and metal ions on plasmonic and molecular resonance coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(13), 4806–4814 (2010). doi:10.1021/ja910239b
- W.H. Ni, R.A. Mosquera, J. Perez-Juste, L.M. Liz-Marzan, Evidence for hydrogen-bonding-directed assembly of gold nanorods in aqueous solution. J. Phy. Chem. Lett. 1(8), 1181–1185 (2010). doi:10.1021/jz1002154
- P. Pramod, K.G. Thomas, Plasmon coupling in dimers of Au nanorods. Adv. Mater. 20(22), 4300–4305 (2008). doi:10.1002/adma.200703057
- J. Kern, S. Grossmann, N.V. Tarakina, T. Hackel, M. Emmerling, M. Kamp, J.S. Huang, P. Biagioni, J.C. Prangsma, B. Hecht, Atomic-scale confinement of resonant optical fields. Nano Lett. 12(11), 5504–5509 (2012). doi:10.1021/nl302315g
- W. Ni, X. Kou, Z. Yang, J. Wang, Tailoring longitudinal surface plasmon wavelengths, scattering and absorption cross sections of gold nanorods. ACS Nano 2(4), 677–686 (2008). doi:10.1021/nn7003603
- Y. Wu, P. Nordlander, Finite-difference time-domain modeling of the optical properties of nanoparticles near dielectric substrates. J. Phy. Chem. C 114(16), 7302–7307 (2010). doi:10.1021/jp908980d
- P. Yang, K.N. Liou, Finite-difference time domain method for light scattering by small ice crystals in three-dimensional space. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 13(10), 2072–2085 (1996). doi:10.1364/JOSAA.13.002072
- E. Prodan, C. Radloff, N.J. Halas, P. Nordlander, A hybridization model for the plasmon response of complex nanostructures. Science 302(5644), 419–422 (2003). doi:10.1126/science.1089171
- H.C. van de Hulst, Light scattering by small particles (Dover Publications, New York, 1957)
- R. Gans, The state of ultramicroscopic silver particles. Ann. Phys-Berlin 47(10), 270–284 (1915). doi:10.1002/andp.19153521006
- P.B. Johnson, R.W. Christy, Optical constants of noble metals. Phy. Rev. B 6(12), 4370–4379 (1972). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.6.4370
- B.T. Draine, The discrete-dipole approximation and its application to interstellar graphite grains. Astro Phys. J. 333(2), 848–872 (1988). doi:10.1086/166795
- K. Liu, A. Ahmed, S. Chung, K. Sugikawa, G. Wu, Z. Nie, R. Gordon, E. Kumacheva, In situ plasmonic counter for polymerization of chains of gold nanorods in solution. ACS Nano 7(7), 5901–5910 (2013). doi:10.1021/nn402363p
- Z. Sun, W. Ni, Z. Yang, X. Kou, L. Li, J. Wang, pH-controlled reversible assembly and disassembly of gold nanorods. Small 4(9), 1287–1292 (2008). doi:10.1002/smll.200800099
References
S. Link, M.A. El-Sayed, Optical properties and ultrafast dynamics of metallic nanocrystals. Annu. Rev. Phys. 54(1), 331–366 (2003). doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.54.011002.103759
S. Biswas, J. Duan, D. Nepal, R. Pachter, R. Vaia, Plasmonic resonances in self-assembled reduced symmetry gold nanorod structures. Nano Lett. 13(5), 2220–2225 (2013). doi:10.1021/nl4007358
B. Luk’yanchuk, N.I. Zheludev, S.A. Maier, N.J. Halas, P. Nordlander, H. Giessen, C.T. Chong, The fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 9(9), 707–715 (2010). doi:10.1038/nmat2810
L. Shao, K.C. Woo, H. Chen, Z. Jin, J. Wang, H.Q. Lin, Angle- and energy-resolved plasmon coupling in gold nanorod dimers. ACS Nano 4(6), 3053–3062 (2010). doi:10.1021/nn100180d
R. Iovine, L.L. Spada, L. Vegni, Optical properties of modified nanorod particles for biomedical sensing. Magn. IEEE Trans. 50(2), 169–172 (2014). doi:10.1109/TMAG.2013.2284552
H. Chen, L. Shao, Q. Li, J. Wang, Gold nanorods and their plasmonic properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(7), 2679–2724 (2013). doi:10.1039/C2CS35367A
G. Baffou, R. Quidant, Nanoplasmonics for chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43(11), 3898–3907 (2014). doi:10.1039/C3CS60364D
D. Gomez, T. Davis, A. Funston, Plasmonics by design: design principles to structure–function relationships with assemblies of metal nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2(17), 3077–3087 (2014). doi:10.1039/C3TC32041C
J.N. Li, T.Z. Liu, H.R. Zheng, F. Gao, J. Dong, Z.L. Zhang, Z.Y. Zhang, Plasmon resonances and strong electric field enhancements in side-by-side tangent nanospheroid homodimers. Opt. Express 21(14), 17176–17185 (2013). doi:10.1364/OE.21.017176
R. Fernández-García, Y. Sonnefraud, A.I. Fernández-Domínguez, V. Giannini, S.A. Maier, Design considerations for near-field enhancement in optical antennas. Contemp. Phys. 55(1), 1–11 (2014). doi:10.1080/00107514.2013.850788
P.K. Jain, S. Eustis, M.A. El-Sayed, Plasmon coupling in nanorod assemblies: optical absorption, discrete dipole approximation simulation, and exciton-coupling model. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(37), 18243–18253 (2006). doi:10.1021/jp063879z
J. Kumar, X. Wei, S. Barrow, A.M. Funston, K.G. Thomas, P. Mulvaney, Surface plasmon coupling in end-to-end linked gold nanorod dimers and trimers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15(12), 4258–4264 (2013). doi:10.1039/C3CP44657C
S. Biswas, J. Duan, D. Nepal, K. Park, R. Pachter, R.A. Vaia, Plasmon induced transparency in the visible via self-assembled gold nanorod heterodimers. Nano Lett. 13(12), 6287–6291 (2013). doi:10.1021/nl403911z
L.V. Brown, H. Sobhani, J.B. Lassiter, P. Nordlander, N.J. Halas, Heterodimers: plasmonic properties of mismatched nanoparticle pairs. ACS Nano 4(2), 819–832 (2010). doi:10.1021/nn9017312
C. Tabor, D. Van Haute, M.A. El-Sayed, Effect of orientation on plasmonic coupling between gold nanorods. ACS Nano 3(11), 3670–3678 (2009). doi:10.1021/nn900779f
M.W. Chu, V. Myroshnychenko, C.H. Chen, J.P. Deng, C.Y. Mou, F.J. García de Abajo, Probing bright and dark surface-plasmon modes in individual and coupled noble metal nanoparticles using an electron beam. Nano Lett. 9(1), 399–404 (2009). doi:10.1021/nl803270x
M.S.M. Saifullah, T. Ondarçuhu, D.K. Koltsov, C. Joachim, M.E. Welland, A reliable scheme for fabricating sub-5 nm co-planar junctions for single-molecule electronics. Nanotechnology 13(5), 659 (2002). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/13/5/323
L.S. Slaughter, Y. Wu, B.A. Willingham, P. Nordlander, S. Link, Effects of symmetry breaking and conductive contact on the plasmon coupling in gold nanorod dimers. ACS Nano 4(8), 4657–4666 (2010). doi:10.1021/nn1011144
S. Panaro, A. Nazir, C. Liberale, G. Das, H. Wang, F. De Angelis, R.P. Zaccaria, E. Di Fabrizio, A. Toma, Dark to bright mode conversion on dipolar nanoantennas: a symmetry-breaking approach. ACS Photonics 1(4), 310–314 (2014). doi:10.1021/ph500044w
W.S. Chang, J.W. Ha, L.S. Slaughter, S. Link, Plasmonic nanorod absorbers as orientation sensors. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107(7), 2781–2786 (2010). doi:10.1073/pnas.0910127107
C. Sönnichsen, A.P. Alivisatos, Gold nanorods as novel nonbleaching plasmon-based orientation sensors for polarized single-particle microscopy. Nano Lett. 5(2), 301–304 (2004). doi:10.1021/nl048089k
W.H. Ni, H.J. Chen, J. Su, Z.H. Sun, J.F. Wang, H.K. Wu, Effects of dyes, gold nanocrystals, pH, and metal ions on plasmonic and molecular resonance coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(13), 4806–4814 (2010). doi:10.1021/ja910239b
W.H. Ni, R.A. Mosquera, J. Perez-Juste, L.M. Liz-Marzan, Evidence for hydrogen-bonding-directed assembly of gold nanorods in aqueous solution. J. Phy. Chem. Lett. 1(8), 1181–1185 (2010). doi:10.1021/jz1002154
P. Pramod, K.G. Thomas, Plasmon coupling in dimers of Au nanorods. Adv. Mater. 20(22), 4300–4305 (2008). doi:10.1002/adma.200703057
J. Kern, S. Grossmann, N.V. Tarakina, T. Hackel, M. Emmerling, M. Kamp, J.S. Huang, P. Biagioni, J.C. Prangsma, B. Hecht, Atomic-scale confinement of resonant optical fields. Nano Lett. 12(11), 5504–5509 (2012). doi:10.1021/nl302315g
W. Ni, X. Kou, Z. Yang, J. Wang, Tailoring longitudinal surface plasmon wavelengths, scattering and absorption cross sections of gold nanorods. ACS Nano 2(4), 677–686 (2008). doi:10.1021/nn7003603
Y. Wu, P. Nordlander, Finite-difference time-domain modeling of the optical properties of nanoparticles near dielectric substrates. J. Phy. Chem. C 114(16), 7302–7307 (2010). doi:10.1021/jp908980d
P. Yang, K.N. Liou, Finite-difference time domain method for light scattering by small ice crystals in three-dimensional space. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 13(10), 2072–2085 (1996). doi:10.1364/JOSAA.13.002072
E. Prodan, C. Radloff, N.J. Halas, P. Nordlander, A hybridization model for the plasmon response of complex nanostructures. Science 302(5644), 419–422 (2003). doi:10.1126/science.1089171
H.C. van de Hulst, Light scattering by small particles (Dover Publications, New York, 1957)
R. Gans, The state of ultramicroscopic silver particles. Ann. Phys-Berlin 47(10), 270–284 (1915). doi:10.1002/andp.19153521006
P.B. Johnson, R.W. Christy, Optical constants of noble metals. Phy. Rev. B 6(12), 4370–4379 (1972). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.6.4370
B.T. Draine, The discrete-dipole approximation and its application to interstellar graphite grains. Astro Phys. J. 333(2), 848–872 (1988). doi:10.1086/166795
K. Liu, A. Ahmed, S. Chung, K. Sugikawa, G. Wu, Z. Nie, R. Gordon, E. Kumacheva, In situ plasmonic counter for polymerization of chains of gold nanorods in solution. ACS Nano 7(7), 5901–5910 (2013). doi:10.1021/nn402363p
Z. Sun, W. Ni, Z. Yang, X. Kou, L. Li, J. Wang, pH-controlled reversible assembly and disassembly of gold nanorods. Small 4(9), 1287–1292 (2008). doi:10.1002/smll.200800099