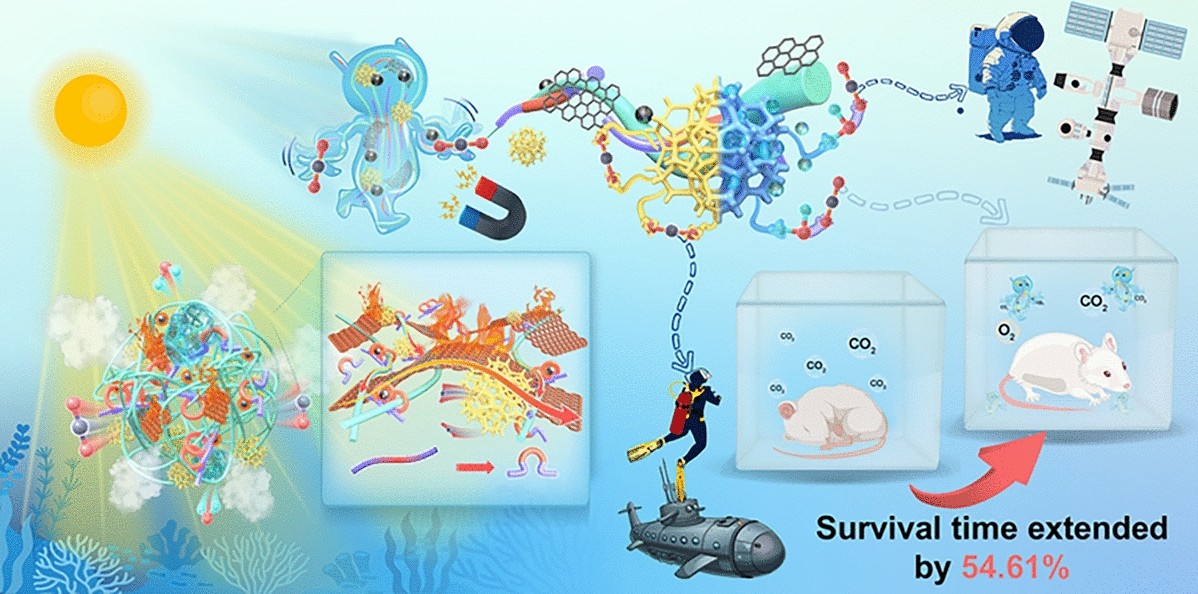
Micro/Nano-Reconfigurable Robots for Intelligent Carbon Management in Confined-Space Life-Support Systems
Corresponding Author: Hui He
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 18 (2026), Article Number: 80
Abstract
Strategically coupling nanoparticle hybrids and internal thermosensitive molecular switches establishes an innovative paradigm for constructing micro/nanoscale-reconfigurable robots, facilitating energy-efficient CO2 management in life-support systems of confined space. Here, a micro/nano-reconfigurable robot is constructed from the CO2 molecular hunters, temperature-sensitive molecular switch, solar photothermal conversion, and magnetically-driven function engines. The molecular hunters within the molecular extension state can capture 6.19 mmol g−1 of CO2 to form carbamic acid and ammonium bicarbonate. Interestingly, the molecular switch of the robot activates a molecular curling state that facilitates CO2 release through nano-reconfiguration, which is mediated by the temperature-sensitive curling of Pluronic F127 molecular chains during the photothermal desorption. Nano-reconfiguration of robot alters the amino microenvironment, including increasing surface electrostatic potential of the amino group and decreasing overall lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy level. This weakened the nucleophilic attack ability of the amino group toward the adsorption product derivatives, thereby inhibiting the side reactions that generate hard-to-decompose urea structures, achieving the lowest regeneration temperature of 55 °C reported to date. The engine of the robot possesses non-contact magnetically-driven micro-reconfiguration capability to achieve efficient photothermal regeneration while avoiding local overheating. Notably, the robot successfully prolonged the survival time of mice in the sealed container by up to 54.61%, effectively addressing the issue of carbon suffocation in confined spaces. This work significantly enhances life-support systems for deep-space exploration, while stimulating innovations in sustainable carbon management technologies for terrestrial extreme environments.
Highlights:
1 The micro/nano-reconfigurable robots for life-support systems were fabricated by CO₂-capturing molecular hunters, temperature-sensitive molecular switches, and solar photothermal conversion/magnetically-driven dual function engines.
2 The ultralow regeneration temperature (55 °C) and non-contact heat management of robots were achieved through nano-reconfiguration of internal temperature-responsive molecules and micro-reconfiguration of magnetic/photothermal synergy of Fe3O4 nanoparticles.
3 Exceptional dynamic carbon management of robots extended the survival time of mice in confined spaces by 54.61%.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- B.F. Palmer, D.J. Clegg, Respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis: core curriculum 2023. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 82(3), 347–359 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.02.004
- T.A. Jacobson, J.S. Kler, M.T. Hernke, R.K. Braun, K.C. Meyer et al., Direct human health risks of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide. Nat. Sustain. 2(8), 691–701 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0323-1
- S. Jeong, J. Shin, J. Kim, H. Kim, J.G. Lee et al., Human circulatory/respiratory-inspired comprehensive air purification system. Adv. Mater. 36(41), e2405568 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202405568
- R. Castro-Amoedo, J. Granacher, M. Abou Daher, F. Maréchal, On the role of system integration of carbon capture and mineralization in achieving net-negative emissions in industrial sectors. Energy Environ. Sci. 16(10), 4356–4372 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ee01803b
- M. Zhao, L. Huang, Y. Gao, Z. Wang, S. Liang et al., Design of ultra-stable solid amine adsorbents and mechanisms of hydroxyl group-dependent deactivation for reversible CO2 capture from flue gas. Nano-Micro Lett. 17, 170 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-025-01664-w
- J. Oh, D. Kim, S. Roussanaly, R. Anantharaman, Y. Lim, Optimal capacity design of amine-based onboard CO2 capture systems under variable marine engine loads. Chem. Eng. J. 483, 149136 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.149136
- F. Meng, Y. Meng, T. Ju, S. Han, L. Lin et al., Research progress of aqueous amine solution for CO2 capture: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 168, 112902 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2022.112902
- M. Hou, L. Li, R. Xu, Y. Lu, J. Song et al., Precursor-chemistry engineering toward ultrapermeable carbon molecular sieve membrane for CO2 capture. J. Energy Chem. 102, 421–430 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2024.11.006
- M. Shen, F. Kong, W. Guo, Z. Zuo, C. Guo et al., Enhanced direct air carbon capture on NaX zeolite by electric-field enhanced physical adsorption and in situ CO2 synergistic effects of cold plasma. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(49), 2408922 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202408922
- C. Cleeton, F.L. de Oliveira, R.F. Neumann, A.H. Farmahini, B. Luan et al., A process-level perspective of the impact of molecular force fields on the computational screening of MOFs for carbon capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 16(9), 3899–3918 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ee00858d
- P.G. Boyd, A. Chidambaram, E. García-Díez, C.P. Ireland, T.D. Daff et al., Data-driven design of metal-organic frameworks for wet flue gas CO2 capture. Nature 576(7786), 253–256 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1798-7
- X. Wang, M. Alzayer, A.J. Shih, S. Bose, H. Xie et al., Tailoring hydrophobicity and pore environment in physisorbents for improved carbon dioxide capture under high humidity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146(6), 3943–3954 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c11671
- H.J. Moon, J.M.Y. Carrillo, C.W. Jones, Distribution and mobility of amines confined in porous silica supports assessed via neutron scattering, NMR, and MD simulations: impacts on CO2 sorption kinetics and capacities. Acc. Chem. Res. 56(19), 2620–2630 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00363
- Z. Zheng, Y.-S. Wang, M. Wang, G.-H. Zhao, G.-P. Hao et al., Anomalous enhancement of humid CO2 capture by local surface bound water in polar carbon nanopores. Nat. Commun. 15(1), 8919 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53367-2
- B. Singh, Z.E. Gorji, R. Singh, V. Sharma, T. Repo, Silica gel supported solid amine sorbents for CO2 capture. Energy Environ. Mater. 8, e12832 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12832
- X. Sun, X. Shen, H. Wang, F. Yan, J. Hua et al., Atom-level interaction design between amines and support for achieving efficient and stable CO2 capture. Nat. Commun. 15, 5068 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48994-8
- R. Navik, E. Wang, X. Ding, K. Qiu, J. Li, Atmospheric carbon dioxide capture by adsorption on amine-functionalized silica composites: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 22(4), 1791–1830 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-024-01737-z
- Y. Hoshino, K. Imamura, M. Yue, G. Inoue, Y. Miura, Reversible absorption of CO2 triggered by phase transition of amine-containing micro- and nanogel ps. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(44), 18177–18180 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3080192
- J. Lin, W. Lu, X. Shi, Q. Lu, L. Wang et al., Design of an intelligent nanofiber-based solid amine adsorbent with high CO2 capture capacity and an ultralow regeneration temperature. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 9(30), 10184–10195 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c02387
- W. Lu, X. Shi, H. Zhou, W. Luo, L. Wang et al., Tailoring and properties of a novel solar energy-triggered regenerative bionic fiber adsorbent for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 449, 137885 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137885
- W. Luo, W. Lu, Q. Xiang, L. Zhan, X. Yang et al., Engineering a photothermal responsive cellulose carbon capture material for solar-driven CO2 desorption. Chem. Eng. J. 489, 151144 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.151144
- X. Shi, W. Lu, Y. Xue, H. Zhou, F. Xue et al., Design of thermo-responsive hyperbranched nanofibre-based adsorbent with high CO2 adsorption capacity and analysis of its ultra-low temperature regeneration mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 424, 130362 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130362
- J. Gallagher, Lighting the way. Nat. Energy 9(1), 8 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-024-01455-4
- T. Kataoka, Y. Orita, Y. Shimoyama, Photothermal release of CO2 using carbon/silica composite toward direct air capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 62(40), 16383–16389 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.3c01721
- J. Gao, X. Song, J. Yan, J. Yuan, L. Cao et al., Photoinduced phase transitions in nanogel ps for reversible CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 455, 140621 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140621
- T. Guo, D. Zhu, C. Zhao, Y. Xu, J. Wang et al., Efficient solar-driven carbon dioxide capture system for greenhouse using graphene-contained deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 332, 125754 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125754
- H. Li, M.R. Hill, C. Doblin, S. Lim, A.J. Hill et al., Visible light triggered CO2 liberation from silver nanocrystals incorporated metal–organic frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26(27), 4815–4821 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201600827
- R. Xu, H. Cui, N. Wei, Y. Yu, L. Dai et al., Biomimetic micro-nanostructured evaporator with dual-transition-metal MXene for efficient solar steam generation and multifunctional salt harvesting. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 102 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01612-0
- M.T. Dunstan, F. Donat, A.H. Bork, C.P. Grey, C.R. Müller, CO2 capture at medium to high temperature using solid oxide-based sorbents: fundamental aspects, mechanistic insights, and recent advances. Chem. Rev. 121(20), 12681–12745 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00100
- S. Li, Y. Guta, M.F. Calegari Andrade, E. Hunter-Sellars, A. Maiti et al., Competing kinetic consequences of CO2 on the oxidative degradation of branched poly(ethylenimine). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146(41), 28201–28213 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c08126
- M. Chen, J. Zhu, K. Zhang, H. Zhou, Y. Gao et al., Carbon nanofiber/polyaniline composite aerogel with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding, low thermal conductivity, and extremely low heat release. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 80 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01583-2
- M. He, L. Zhang, K. Ruan, J. Zhang, H. Zhang et al., Functionalized aluminum nitride for improving hydrolysis resistances of highly thermally conductive polysiloxane composites. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 134 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-025-01669-5
- Y. Hu, H. Ma, M. Wu, T. Lin, H. Yao et al., A reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly for dynamic solar steam generation. Nat. Commun. 13, 4335 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32051-3
- L. Li, Z. Yu, J. Liu, M. Yang, G. Shi et al., Swarming responsive photonic nanorobots for motile-targeting microenvironmental mapping and mapping-guided photothermal treatment. Nano-Micro Lett. 15(1), 141 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01095-5
- G. Xu, Y.Q. Gao, Y.X. Gao, G. Wu, J.Y. Zhang et al., An improved formula for standard hypoxia tolerance time (STT) to evaluate hypoxic tolerance in mice. Mil. Med. Res. 5, 33 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-018-0180-7
- P. Singla, S. Garg, J. McClements, O. Jamieson, M. Peeters et al., Advances in the therapeutic delivery and applications of functionalized Pluronics: a critical review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 299, 102563 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102563
- R. Ben Said, J.M. Kolle, K. Essalah, B. Tangour, A. Sayari, A unified approach to CO2–amine reaction mechanisms. ACS Omega 5(40), 26125–26133 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c03727
- A. Sayari, A. Heydari-Gorji, Y. Yang, CO2-induced degradation of amine-containing adsorbents: reaction products and pathways. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(33), 13834–13842 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja304888a
- C. Li, X. Cao, G. Liu, L. Huang, M. Chu et al., Optimizing CO2 adsorption/desorption via the coupling of imidazole and carbon nanotubes paper for spontaneous CO2 uptake from ambient air and solar-driven release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(33), 2400423 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202400423
- H. Lei, Z. Chen, J. Zhang, W. Yu, Ti3C2Tx MXene-assisted solar-driven CO2 adsorption and photothermal regeneration over mesoporous SiO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 347, 127537 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.127537
- H. Wang, Y. Xuan, Solar-driven high-performance biomass porous carbon for efficient CO2 capture. Fuel 372, 132246 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2024.132246
- J. Gao, J. Yuan, C. Chen, S. Wu, Q. Long et al., Solar induced low-temperature phase separation in thermomorphic solvents for CO2 capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 348, 127783 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.127783
References
B.F. Palmer, D.J. Clegg, Respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis: core curriculum 2023. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 82(3), 347–359 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.02.004
T.A. Jacobson, J.S. Kler, M.T. Hernke, R.K. Braun, K.C. Meyer et al., Direct human health risks of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide. Nat. Sustain. 2(8), 691–701 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0323-1
S. Jeong, J. Shin, J. Kim, H. Kim, J.G. Lee et al., Human circulatory/respiratory-inspired comprehensive air purification system. Adv. Mater. 36(41), e2405568 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202405568
R. Castro-Amoedo, J. Granacher, M. Abou Daher, F. Maréchal, On the role of system integration of carbon capture and mineralization in achieving net-negative emissions in industrial sectors. Energy Environ. Sci. 16(10), 4356–4372 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ee01803b
M. Zhao, L. Huang, Y. Gao, Z. Wang, S. Liang et al., Design of ultra-stable solid amine adsorbents and mechanisms of hydroxyl group-dependent deactivation for reversible CO2 capture from flue gas. Nano-Micro Lett. 17, 170 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-025-01664-w
J. Oh, D. Kim, S. Roussanaly, R. Anantharaman, Y. Lim, Optimal capacity design of amine-based onboard CO2 capture systems under variable marine engine loads. Chem. Eng. J. 483, 149136 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.149136
F. Meng, Y. Meng, T. Ju, S. Han, L. Lin et al., Research progress of aqueous amine solution for CO2 capture: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 168, 112902 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2022.112902
M. Hou, L. Li, R. Xu, Y. Lu, J. Song et al., Precursor-chemistry engineering toward ultrapermeable carbon molecular sieve membrane for CO2 capture. J. Energy Chem. 102, 421–430 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2024.11.006
M. Shen, F. Kong, W. Guo, Z. Zuo, C. Guo et al., Enhanced direct air carbon capture on NaX zeolite by electric-field enhanced physical adsorption and in situ CO2 synergistic effects of cold plasma. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(49), 2408922 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202408922
C. Cleeton, F.L. de Oliveira, R.F. Neumann, A.H. Farmahini, B. Luan et al., A process-level perspective of the impact of molecular force fields on the computational screening of MOFs for carbon capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 16(9), 3899–3918 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ee00858d
P.G. Boyd, A. Chidambaram, E. García-Díez, C.P. Ireland, T.D. Daff et al., Data-driven design of metal-organic frameworks for wet flue gas CO2 capture. Nature 576(7786), 253–256 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1798-7
X. Wang, M. Alzayer, A.J. Shih, S. Bose, H. Xie et al., Tailoring hydrophobicity and pore environment in physisorbents for improved carbon dioxide capture under high humidity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146(6), 3943–3954 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c11671
H.J. Moon, J.M.Y. Carrillo, C.W. Jones, Distribution and mobility of amines confined in porous silica supports assessed via neutron scattering, NMR, and MD simulations: impacts on CO2 sorption kinetics and capacities. Acc. Chem. Res. 56(19), 2620–2630 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00363
Z. Zheng, Y.-S. Wang, M. Wang, G.-H. Zhao, G.-P. Hao et al., Anomalous enhancement of humid CO2 capture by local surface bound water in polar carbon nanopores. Nat. Commun. 15(1), 8919 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53367-2
B. Singh, Z.E. Gorji, R. Singh, V. Sharma, T. Repo, Silica gel supported solid amine sorbents for CO2 capture. Energy Environ. Mater. 8, e12832 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12832
X. Sun, X. Shen, H. Wang, F. Yan, J. Hua et al., Atom-level interaction design between amines and support for achieving efficient and stable CO2 capture. Nat. Commun. 15, 5068 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48994-8
R. Navik, E. Wang, X. Ding, K. Qiu, J. Li, Atmospheric carbon dioxide capture by adsorption on amine-functionalized silica composites: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 22(4), 1791–1830 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-024-01737-z
Y. Hoshino, K. Imamura, M. Yue, G. Inoue, Y. Miura, Reversible absorption of CO2 triggered by phase transition of amine-containing micro- and nanogel ps. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(44), 18177–18180 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3080192
J. Lin, W. Lu, X. Shi, Q. Lu, L. Wang et al., Design of an intelligent nanofiber-based solid amine adsorbent with high CO2 capture capacity and an ultralow regeneration temperature. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 9(30), 10184–10195 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c02387
W. Lu, X. Shi, H. Zhou, W. Luo, L. Wang et al., Tailoring and properties of a novel solar energy-triggered regenerative bionic fiber adsorbent for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 449, 137885 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137885
W. Luo, W. Lu, Q. Xiang, L. Zhan, X. Yang et al., Engineering a photothermal responsive cellulose carbon capture material for solar-driven CO2 desorption. Chem. Eng. J. 489, 151144 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.151144
X. Shi, W. Lu, Y. Xue, H. Zhou, F. Xue et al., Design of thermo-responsive hyperbranched nanofibre-based adsorbent with high CO2 adsorption capacity and analysis of its ultra-low temperature regeneration mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 424, 130362 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130362
J. Gallagher, Lighting the way. Nat. Energy 9(1), 8 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-024-01455-4
T. Kataoka, Y. Orita, Y. Shimoyama, Photothermal release of CO2 using carbon/silica composite toward direct air capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 62(40), 16383–16389 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.3c01721
J. Gao, X. Song, J. Yan, J. Yuan, L. Cao et al., Photoinduced phase transitions in nanogel ps for reversible CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 455, 140621 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140621
T. Guo, D. Zhu, C. Zhao, Y. Xu, J. Wang et al., Efficient solar-driven carbon dioxide capture system for greenhouse using graphene-contained deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 332, 125754 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125754
H. Li, M.R. Hill, C. Doblin, S. Lim, A.J. Hill et al., Visible light triggered CO2 liberation from silver nanocrystals incorporated metal–organic frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26(27), 4815–4821 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201600827
R. Xu, H. Cui, N. Wei, Y. Yu, L. Dai et al., Biomimetic micro-nanostructured evaporator with dual-transition-metal MXene for efficient solar steam generation and multifunctional salt harvesting. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 102 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01612-0
M.T. Dunstan, F. Donat, A.H. Bork, C.P. Grey, C.R. Müller, CO2 capture at medium to high temperature using solid oxide-based sorbents: fundamental aspects, mechanistic insights, and recent advances. Chem. Rev. 121(20), 12681–12745 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00100
S. Li, Y. Guta, M.F. Calegari Andrade, E. Hunter-Sellars, A. Maiti et al., Competing kinetic consequences of CO2 on the oxidative degradation of branched poly(ethylenimine). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146(41), 28201–28213 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c08126
M. Chen, J. Zhu, K. Zhang, H. Zhou, Y. Gao et al., Carbon nanofiber/polyaniline composite aerogel with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding, low thermal conductivity, and extremely low heat release. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 80 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01583-2
M. He, L. Zhang, K. Ruan, J. Zhang, H. Zhang et al., Functionalized aluminum nitride for improving hydrolysis resistances of highly thermally conductive polysiloxane composites. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 134 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-025-01669-5
Y. Hu, H. Ma, M. Wu, T. Lin, H. Yao et al., A reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly for dynamic solar steam generation. Nat. Commun. 13, 4335 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32051-3
L. Li, Z. Yu, J. Liu, M. Yang, G. Shi et al., Swarming responsive photonic nanorobots for motile-targeting microenvironmental mapping and mapping-guided photothermal treatment. Nano-Micro Lett. 15(1), 141 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01095-5
G. Xu, Y.Q. Gao, Y.X. Gao, G. Wu, J.Y. Zhang et al., An improved formula for standard hypoxia tolerance time (STT) to evaluate hypoxic tolerance in mice. Mil. Med. Res. 5, 33 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-018-0180-7
P. Singla, S. Garg, J. McClements, O. Jamieson, M. Peeters et al., Advances in the therapeutic delivery and applications of functionalized Pluronics: a critical review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 299, 102563 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102563
R. Ben Said, J.M. Kolle, K. Essalah, B. Tangour, A. Sayari, A unified approach to CO2–amine reaction mechanisms. ACS Omega 5(40), 26125–26133 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c03727
A. Sayari, A. Heydari-Gorji, Y. Yang, CO2-induced degradation of amine-containing adsorbents: reaction products and pathways. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(33), 13834–13842 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja304888a
C. Li, X. Cao, G. Liu, L. Huang, M. Chu et al., Optimizing CO2 adsorption/desorption via the coupling of imidazole and carbon nanotubes paper for spontaneous CO2 uptake from ambient air and solar-driven release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(33), 2400423 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202400423
H. Lei, Z. Chen, J. Zhang, W. Yu, Ti3C2Tx MXene-assisted solar-driven CO2 adsorption and photothermal regeneration over mesoporous SiO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 347, 127537 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.127537
H. Wang, Y. Xuan, Solar-driven high-performance biomass porous carbon for efficient CO2 capture. Fuel 372, 132246 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2024.132246
J. Gao, J. Yuan, C. Chen, S. Wu, Q. Long et al., Solar induced low-temperature phase separation in thermomorphic solvents for CO2 capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 348, 127783 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.127783