Dual-Fuel-Driven Bactericidal Micromotor
Corresponding Author: Bin Dong
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 8 No. 2 (2016), Article Number: 157-164
Abstract
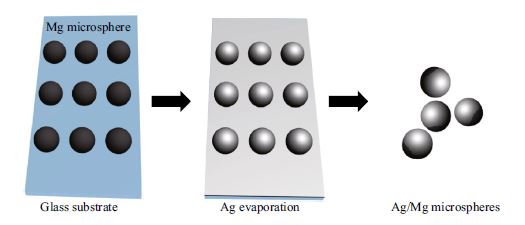
In this paper, we report fabrication of the bimetallic Janus microsphere, a magnesium microsphere with a silver surface coating, through thermal evaporation technique. Because of the Janus structure, this micromotor can be propelled in two different directions by the surface silver or magnesium ‘engine’ and hydrogen peroxide or water fuel. In addition, due to the bactericidal property of silver, this autonomous micromotor is capable of killing bacteria in solution. As compared to the static one, the micromotor is able to kill the bacteria at a much faster rate (about nine times of that of the static one), demonstrating the superiority of the motion one. We thus believe that the micromotor shown in the current study is potentially attractive for the environmental hygiene applications.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- R.F. Ismagilov, A. Schwartz, N. Bowden, G.M. Whitesides, Autonomous movement and self-assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41(4), 652–654 (2002). doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20020215)41:4<652:AID-ANIE652>3.0.CO;2-U
- M. Guix, C.C. Mayorga-Martinez, A. Merkoci, Nano/micromotors in (bio)chemical science applications. Chem. Rev. 114(12), 6285–6322 (2014). doi:10.1021/cr400273r
- S. Sanchez, L. Soler, J. Katuri, Chemically powered micro- and nanomotors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54(5), 1414–1444 (2015). doi:10.1002/anie.201406096
- S. Sengupta, M.E. Ibele, A. Sen, Fantastic voyage: designing self-powered nanorobots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51(34), 8434–8445 (2012). doi:10.1002/anie.201202044
- J. Wang, Can man-made nanomachines compete with nature biomotors? ACS Nano 3(1), 4–9 (2009). doi:10.1021/nn800829k
- J. Wang, W. Gao, Nano/microscale motors: biomedical opportunities and challenges. ACS Nano 6(7), 5745–5751 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn3028997
- S. Campuzano, J. Orozco, D. Kagan, M. Guix, W. Gao, S. Sattayasamitsathit, J.C. Claussen, A. Merkoci, J. Wang, Bacterial isolation by lectin-modified microengines. Nano Lett. 12(1), 396–401 (2012). doi:10.1021/nl203717q
- J. Burdick, R. Laocharoensuk, P.M. Wheat, J.D. Posner, J. Wang, Synthetic nanomotors in microchannel networks: directional microchip motion and controlled manipulation of cargo. JACS 130(26), 8164–9165 (2008). doi:10.1021/ja803529u
- W. Gao, D. Kagan, O.S. Pak, C. Clawson, S. Campuzano et al., Cargo-towing fuel-free magnetic nanoswimmers for targeted drug delivery. Small 8(3), 460–467 (2012). doi:10.1002/smll.201101909
- J.X. Li, V.V. Singh, S. Sattayasamitsathit, J. Orozco, K. Kaufmann, R.F. Dong, W. Gao, B. Jurado-Sanchez, Y. Fedorak, J. Wang, Water-driven micromotors for rapid photocatalytic degradation of biological and chemical warfare agents. ACS Nano 8(11), 11118–11125 (2014). doi:10.1021/nn505029k
- D. Patra, S. Sengupta, W.T. Duan, H. Zhang, R. Pavlick, A. Sen, Intelligent, self-powered, drug delivery systems. Nanoscale 5(4), 1273–1283 (2013). doi:10.1039/C2NR32600K
- M. Guix, J. Orozco, M. Garcia, W. Gao, S. Sattayasamitsathit, A. Merkoci, A. Escarpa, J. Wang, Superhydrophobic alkanethiol-coated microsubmarines for effective removal of oil. ACS Nano 6(5), 4445–4451 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn301175b
- J. Orozco, G.Z. Cheng, D. Vilela, S. Sattayasamitsathit, R. Vazquez-Duhalt et al., Micromotor-based high-yielding fast oxidative detoxification of chemical threats. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52(50), 13276–13279 (2013). doi:10.1002/anie.201308072
- W. Gao, A. Uygun, J. Wang, Hydrogen-bubble-propelled zinc-based microrockets in strongly acidic media. JACS 134(2), 897–900 (2012). doi:10.1021/ja210874s
- R. Golestanian, T. Liverpool, A. Ajdari, Propulsion of a molecular machine by asymmetric distribution of reaction products. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(22), 220801 (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.220801
- W.F. Paxton, K.C. Kistler, C.C. Olmeda, A. Sen, S.K. St Angelo, Y.Y. Cao, T.E. Mallouk, P.E. Lammert, V.H. Crespi, Catalytic nanomotors: autonomous movement of striped nanorods. JACS 126(41), 13424–13431 (2004). doi:10.1021/ja047697z
- S. Tottori, L. Zhang, F.M. Qiu, K.K. Krawczyk, A. Franco-Obregon, B.J. Nelson, Magnetic helical micromachines: fabrication, controlled swimming, and cargo transport. Adv. Mater. 24(6), 811–816 (2012). doi:10.1002/adma.201103818
- W. Wang, L.A. Castro, M. Hoyos, T.E. Mallouk, Autonomous motion of metallic microrods propelled by ultrasound. ACS Nano 6(7), 6122–6132 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn301312z
- L.M. Liu, M. Liu, Y.J. Su, Y.G. Dong, W. Zhou, L.N. Zhang, H. Zhang, B. Dong, L.F. Chi, Tadpole-like artificial micromotor. Nanoscale 7(6), 2276–2280 (2015). doi:10.1039/C4NR06621A
- R. Liu, A. Sen, Autonomous nanomotor based on copper-platinum segmented nanobattery. JACS 133(50), 20064–20067 (2011). doi:10.1021/ja2082735
- F.Z. Mou, C.R. Chen, H.R. Ma, Y.X. Yin, Q.Z. Wu, J.G. Guan, Self-propelled micromotors driven by the magnesium-water reaction and their hemolytic properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52(28), 7208–7212 (2013). doi:10.1002/anie.201300913
- W. Gao, X.M. Feng, A. Pei, Y.E. Gu, J.X. Li, J. Wang, Seawater-driven magnesium based janus micromotors for environmental remediation. Nanoscale 5(11), 4696–4700 (2013). doi:10.1039/c3nr01458d
- F.Z. Mou, C.R. Chen, Q. Zhong, Y.X. Yin, H.R. Ma, J.G. Guan, Autonomous motion and temperature-controlled drug delivery of Mg/Pt-poly(n-isopropylacrylamide) janus micromotors driven by simulated body fluid and blood plasma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 6(12), 9897–9903 (2014). doi:10.1021/am502729y
- W. Gao, M. D’Agostino, V. Garcia-Gradilla, J. Orozco, J. Wang, Multi-fuel driven janus micromotors. Small 9(3), 467–471 (2013). doi:10.1002/smll.201201864
- Y.J. Wu, Z.G. Wu, X.K. Lin, Q. He, J.B. Li, Autonomous movement of controllable assembled janus capsule motors. ACS Nano 6(12), 10910–10916 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn304335x
- P.M. Wheat, N.A. Marine, J.L. Moran, J.D. Posner, Rapid fabrication of bimetallic spherical motors. Langmuir 26(16), 13052–13055 (2010). doi:10.1021/la102218w
- T.R. Kline, W.F. Paxton, T.E. Mallouk, A. Sen, Catalytic nanomotors: remote-controlled autonomous movement of striped metallic nanorods. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44(5), 744–746 (2005). doi:10.1002/anie.200461890
- A.A. Solovev, Y.F. Mei, E.B. Urena, G.S. Huang, O.G. Schmidt, Catalytic microtubular jet engines self-propelled by accumulated gas bubbles. Small 5(14), 1688–1692 (2009). doi:10.1002/smll.200900021
- Y.F. Mei, A.A. Solovev, S. Sanchez, O.G. Schmidt, Rolled-up nanotech on polymers: from basic perception to self-propelled catalytic microengines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40(5), 2109–2119 (2011). doi:10.1039/c0cs00078g
- Y.P. He, J.S. Wu, Y.P. Zhao, Designing catalytic nanomotors by dynamic shadowing growth. Nano Lett. 7(5), 1369–1375 (2007). doi:10.1021/nl070461j
- R.W. Raut, N.S. Kolekar, J.R. Lakkakula, V.D. Mendhulkar, S.B. Kashid, Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dried leaves of pongamia pinnata (L) pierre. Nano-Micro Lett. 2(2), 106–113 (2010). doi:10.5101/nml.v2i2.p106-113
- S.A. Masurkar, P.R. Chaudhari, V.B. Shidore, S.P. Kamble, Rapid biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using cymbopogan citratus (lemongrass) and its antimicrobial activity. Nano-Micro Lett. 3(3), 189–194 (2011). doi:10.1007/BF03353671
- Y.J. Jiang, J. Gang, S.Y. Xu, Contact mechanism of the ag-doped trimolybdate nanowire as an antimicrobial agent. Nano-Micro Lett. 4(4), 228–234 (2012). doi:10.1007/BF03353719
- G.J. Zhao, B. Khezri, S. Sanchez, O.G. Schmidt, R.D. Webster, M. Pumera, Corrosion of self-propelled catalytic microengines. Chem. Commun. 49, 9125–9127 (2013). doi:10.1039/c3cc44998j
References
R.F. Ismagilov, A. Schwartz, N. Bowden, G.M. Whitesides, Autonomous movement and self-assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41(4), 652–654 (2002). doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20020215)41:4<652:AID-ANIE652>3.0.CO;2-U
M. Guix, C.C. Mayorga-Martinez, A. Merkoci, Nano/micromotors in (bio)chemical science applications. Chem. Rev. 114(12), 6285–6322 (2014). doi:10.1021/cr400273r
S. Sanchez, L. Soler, J. Katuri, Chemically powered micro- and nanomotors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54(5), 1414–1444 (2015). doi:10.1002/anie.201406096
S. Sengupta, M.E. Ibele, A. Sen, Fantastic voyage: designing self-powered nanorobots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51(34), 8434–8445 (2012). doi:10.1002/anie.201202044
J. Wang, Can man-made nanomachines compete with nature biomotors? ACS Nano 3(1), 4–9 (2009). doi:10.1021/nn800829k
J. Wang, W. Gao, Nano/microscale motors: biomedical opportunities and challenges. ACS Nano 6(7), 5745–5751 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn3028997
S. Campuzano, J. Orozco, D. Kagan, M. Guix, W. Gao, S. Sattayasamitsathit, J.C. Claussen, A. Merkoci, J. Wang, Bacterial isolation by lectin-modified microengines. Nano Lett. 12(1), 396–401 (2012). doi:10.1021/nl203717q
J. Burdick, R. Laocharoensuk, P.M. Wheat, J.D. Posner, J. Wang, Synthetic nanomotors in microchannel networks: directional microchip motion and controlled manipulation of cargo. JACS 130(26), 8164–9165 (2008). doi:10.1021/ja803529u
W. Gao, D. Kagan, O.S. Pak, C. Clawson, S. Campuzano et al., Cargo-towing fuel-free magnetic nanoswimmers for targeted drug delivery. Small 8(3), 460–467 (2012). doi:10.1002/smll.201101909
J.X. Li, V.V. Singh, S. Sattayasamitsathit, J. Orozco, K. Kaufmann, R.F. Dong, W. Gao, B. Jurado-Sanchez, Y. Fedorak, J. Wang, Water-driven micromotors for rapid photocatalytic degradation of biological and chemical warfare agents. ACS Nano 8(11), 11118–11125 (2014). doi:10.1021/nn505029k
D. Patra, S. Sengupta, W.T. Duan, H. Zhang, R. Pavlick, A. Sen, Intelligent, self-powered, drug delivery systems. Nanoscale 5(4), 1273–1283 (2013). doi:10.1039/C2NR32600K
M. Guix, J. Orozco, M. Garcia, W. Gao, S. Sattayasamitsathit, A. Merkoci, A. Escarpa, J. Wang, Superhydrophobic alkanethiol-coated microsubmarines for effective removal of oil. ACS Nano 6(5), 4445–4451 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn301175b
J. Orozco, G.Z. Cheng, D. Vilela, S. Sattayasamitsathit, R. Vazquez-Duhalt et al., Micromotor-based high-yielding fast oxidative detoxification of chemical threats. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52(50), 13276–13279 (2013). doi:10.1002/anie.201308072
W. Gao, A. Uygun, J. Wang, Hydrogen-bubble-propelled zinc-based microrockets in strongly acidic media. JACS 134(2), 897–900 (2012). doi:10.1021/ja210874s
R. Golestanian, T. Liverpool, A. Ajdari, Propulsion of a molecular machine by asymmetric distribution of reaction products. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(22), 220801 (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.220801
W.F. Paxton, K.C. Kistler, C.C. Olmeda, A. Sen, S.K. St Angelo, Y.Y. Cao, T.E. Mallouk, P.E. Lammert, V.H. Crespi, Catalytic nanomotors: autonomous movement of striped nanorods. JACS 126(41), 13424–13431 (2004). doi:10.1021/ja047697z
S. Tottori, L. Zhang, F.M. Qiu, K.K. Krawczyk, A. Franco-Obregon, B.J. Nelson, Magnetic helical micromachines: fabrication, controlled swimming, and cargo transport. Adv. Mater. 24(6), 811–816 (2012). doi:10.1002/adma.201103818
W. Wang, L.A. Castro, M. Hoyos, T.E. Mallouk, Autonomous motion of metallic microrods propelled by ultrasound. ACS Nano 6(7), 6122–6132 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn301312z
L.M. Liu, M. Liu, Y.J. Su, Y.G. Dong, W. Zhou, L.N. Zhang, H. Zhang, B. Dong, L.F. Chi, Tadpole-like artificial micromotor. Nanoscale 7(6), 2276–2280 (2015). doi:10.1039/C4NR06621A
R. Liu, A. Sen, Autonomous nanomotor based on copper-platinum segmented nanobattery. JACS 133(50), 20064–20067 (2011). doi:10.1021/ja2082735
F.Z. Mou, C.R. Chen, H.R. Ma, Y.X. Yin, Q.Z. Wu, J.G. Guan, Self-propelled micromotors driven by the magnesium-water reaction and their hemolytic properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52(28), 7208–7212 (2013). doi:10.1002/anie.201300913
W. Gao, X.M. Feng, A. Pei, Y.E. Gu, J.X. Li, J. Wang, Seawater-driven magnesium based janus micromotors for environmental remediation. Nanoscale 5(11), 4696–4700 (2013). doi:10.1039/c3nr01458d
F.Z. Mou, C.R. Chen, Q. Zhong, Y.X. Yin, H.R. Ma, J.G. Guan, Autonomous motion and temperature-controlled drug delivery of Mg/Pt-poly(n-isopropylacrylamide) janus micromotors driven by simulated body fluid and blood plasma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 6(12), 9897–9903 (2014). doi:10.1021/am502729y
W. Gao, M. D’Agostino, V. Garcia-Gradilla, J. Orozco, J. Wang, Multi-fuel driven janus micromotors. Small 9(3), 467–471 (2013). doi:10.1002/smll.201201864
Y.J. Wu, Z.G. Wu, X.K. Lin, Q. He, J.B. Li, Autonomous movement of controllable assembled janus capsule motors. ACS Nano 6(12), 10910–10916 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn304335x
P.M. Wheat, N.A. Marine, J.L. Moran, J.D. Posner, Rapid fabrication of bimetallic spherical motors. Langmuir 26(16), 13052–13055 (2010). doi:10.1021/la102218w
T.R. Kline, W.F. Paxton, T.E. Mallouk, A. Sen, Catalytic nanomotors: remote-controlled autonomous movement of striped metallic nanorods. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44(5), 744–746 (2005). doi:10.1002/anie.200461890
A.A. Solovev, Y.F. Mei, E.B. Urena, G.S. Huang, O.G. Schmidt, Catalytic microtubular jet engines self-propelled by accumulated gas bubbles. Small 5(14), 1688–1692 (2009). doi:10.1002/smll.200900021
Y.F. Mei, A.A. Solovev, S. Sanchez, O.G. Schmidt, Rolled-up nanotech on polymers: from basic perception to self-propelled catalytic microengines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40(5), 2109–2119 (2011). doi:10.1039/c0cs00078g
Y.P. He, J.S. Wu, Y.P. Zhao, Designing catalytic nanomotors by dynamic shadowing growth. Nano Lett. 7(5), 1369–1375 (2007). doi:10.1021/nl070461j
R.W. Raut, N.S. Kolekar, J.R. Lakkakula, V.D. Mendhulkar, S.B. Kashid, Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dried leaves of pongamia pinnata (L) pierre. Nano-Micro Lett. 2(2), 106–113 (2010). doi:10.5101/nml.v2i2.p106-113
S.A. Masurkar, P.R. Chaudhari, V.B. Shidore, S.P. Kamble, Rapid biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using cymbopogan citratus (lemongrass) and its antimicrobial activity. Nano-Micro Lett. 3(3), 189–194 (2011). doi:10.1007/BF03353671
Y.J. Jiang, J. Gang, S.Y. Xu, Contact mechanism of the ag-doped trimolybdate nanowire as an antimicrobial agent. Nano-Micro Lett. 4(4), 228–234 (2012). doi:10.1007/BF03353719
G.J. Zhao, B. Khezri, S. Sanchez, O.G. Schmidt, R.D. Webster, M. Pumera, Corrosion of self-propelled catalytic microengines. Chem. Commun. 49, 9125–9127 (2013). doi:10.1039/c3cc44998j