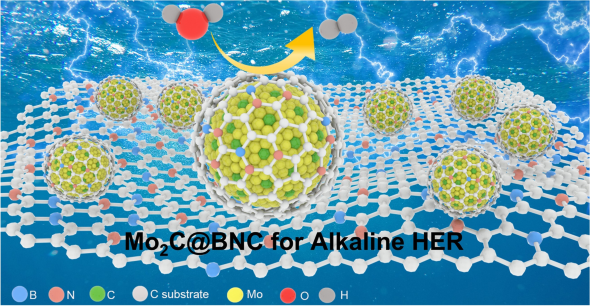
Synergistic Effect of Dual-Doped Carbon on Mo2C Nanocrystals Facilitates Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution
Corresponding Author: Yagang Zhang
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 15 (2023), Article Number: 166
Abstract
Molybdenum carbide (Mo2C) materials are promising electrocatalysts with potential applications in hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) due to low cost and Pt-like electronic structures. Nevertheless, their HER activity is usually hindered by the strong hydrogen binding energy. Moreover, the lack of water-cleaving sites makes it difficult for the catalysts to work in alkaline solutions. Here, we designed and synthesized a B and N dual-doped carbon layer that encapsulated on Mo2C nanocrystals (Mo2C@BNC) for accelerating HER under alkaline condition. The electronic interactions between the Mo2C nanocrystals and the multiple-doped carbon layer endow a near-zero H adsorption Gibbs free energy on the defective C atoms over the carbon shell. Meanwhile, the introduced B atoms afford optimal H2O adsorption sites for the water-cleaving step. Accordingly, the dual-doped Mo2C catalyst with synergistic effect of non-metal sites delivers superior HER performances of a low overpotential (99 mV@10 mA cm−2) and a small Tafel slope (58.1 mV dec−1) in 1 M KOH solution. Furthermore, it presents a remarkable activity that outperforming the commercial 10% Pt/C catalyst at large current density, demonstrating its applicability in industrial water splitting. This study provides a reasonable design strategy towards noble-metal-free HER catalysts with high activity.
Highlights:
1 The B and N dual-doped carbon layer that encapsulated on Mo2C nanocrystals (Mo2C@BNC) were fabricated for accelerating HER under alkaline condition.
2 Theoretical calculations reveal that the H2O could be decomposed spontaneously over the introduced B sites, and the defective C atoms in the dual-doped carbon layer provide the best H binding sites.
3 The optimized dual doped Mo2C catalyst with synergistic effect of non-metal sites delivers superior HER performances.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- C. Li, N. Clament Sagaya Selvam, J. Fang, Shape-controlled synthesis of platinum-based nanocrystals and their electrocatalytic applications in fuel cells. Nano-Micro Lett. 15, 83 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01060-2
- B. Jiang, D. Tian, Y. Qiu, X. Song, Y. Zhang et al., High-index faceted nanocrystals as highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00769-2
- Y. Yang, Y. Yu, J. Li, Q. Chen, Y. Du et al., Engineering ruthenium-based electrocatalysts for effective hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 160 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00679-3
- R. Li, H. Xu, P. Yang, D. Wang, Y. Li et al., Synergistic interfacial and doping engineering of heterostructured NiCo(OH)x-CoyW as an efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 120 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00639-x
- B. Guo, Y. Ding, H. Huo, X. Wen, X. Ren et al., Recent advances of transition metal basic salts for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction and overall water electrolysis. Nano-Micro Lett. 15, 57 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01038-0
- Z. Chen, X. Duan, W. Wei, S. Wang, B.J. Ni, Iridium-based nanomaterials for electrochemical water splitting. Nano Energy 78, 105270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105270
- Q. Yin, C.L. Hill, Water splitting: passing the acid test. Nat. Chem. 10(1), 6–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2921
- F. Lu, M. Zhou, Y. Zhou, X. Zeng, First-row transition metal based catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction under alkaline conditions: basic principles and recent advances. Small 13(45), 1701931 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.20170193
- J.N. Tiwari, S. Sultan, C.W. Myung, T. Yoon, N. Li et al., Multicomponent electrocatalyst with ultralow Pt loading and high hydrogen evolution activity. Nat. Energy 3(9), 773–782 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-018-0209-x
- C. Xie, W. Chen, S. Du, D. Yan, Y. Zhang et al., In-situ phase transition of WO3 boosting electron and hydrogen transfer for enhancing hydrogen evolution on Pt. Nano Energy 71, 104653 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104653
- J. Chen, Y. Ha, R. Wang, Y. Liu, H. Xu et al., Inner Co synergizing outer ru supported on carbon nanotubes for efficient pH-universal hydrogen evolution catalysis. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 186 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00933-2
- Q. Cheng, C. Hu, G. Wang, Z. Zou, H. Yang et al., Carbon-defect-driven electroless deposition of Pt atomic clusters for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142(12), 5594–5601 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b11524
- J. Zhang, E. Wang, S. Cui, S. Yang, X. Zou et al., Single-Atom Pt anchored on oxygen vacancy of monolayer Ti3C2Tx for superior hydrogen evolution. Nano Lett. 22(3), 1398–1405 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c04809
- M. Zhou, H. Li, A. Long, B. Zhou, F. Lu et al., Modulating 3d orbitals of Ni atoms on Ni-Pt edge sites enables highly-efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 11(36), 2101789 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202101789
- B. Šljukić, M. Vujković, L. Amaral, D.M.F. Santos, R.P. Rocha et al., Carbon-supported Mo2C electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(30), 15505–15512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta02346g
- Y. Qiu, Z. Wen, C. Jiang, X. Wu, R. Si et al., Rational design of atomic layers of Pt anchored on Mo2C nanorods for efficient hydrogen evolution over a wide pH range. Small 15(14), e1900014 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201900014
- W. Fu, Y. Wang, W. Tian, H. Zhang, J. Li et al., Non-metal single-phosphorus-atom catalysis of hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59(52), 23791–23799 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202011358
- H. Vrubel, X. Hu, Molybdenum boride and carbide catalyze hydrogen evolution in both acidic and basic solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51(51), 12703–12706 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201207111
- X. Yang, J. Cheng, X. Yang, Y. Xu, W. Sun et al., Facet-tunable coral-like Mo2C catalyst for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 451(4), 138977 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138977
- Y. Shi, B. Zhang, Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45(6), 1529–1541 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00434a
- J. Greeley, T.F. Jaramillo, J. Bonde, I.B. Chorkendorff, J.K. Norskov, Computational high-throughput screening of electrocatalytic materials for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Mater. 5(11), 909–913 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1752
- F. Yu, Y. Gao, Z. Lang, Y. Ma, L. Yin, Electrocatalytic performance of ultrasmall Mo2C affected by different transition metal dopants in hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 10(13), 6080–6087 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr00908b
- C. Wan, B.M. Leonard, Iron-doped molybdenum carbide catalyst with high activity and stability for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Mater. 27(12), 4281–4288 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b0062
- H. Wei, J. Wang, Q. Lin, Y. Zou, X. Chen et al., Incorporating ultra-small N-doped Mo2C nanops onto 3D N-doped flower-like carbon nanospheres for robust electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 86, 106047 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106047
- Y. Lu, C. Yue, Y. Li, W. Bao, X. Guo et al., Atomically dispersed Ni on Mo2C embedded in N, P co-doped carbon derived from polyoxometalate supramolecule for high-efficiency hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 296, 120336 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120336
- D. Wang, T. Liu, J. Wang, Z. Wu, N, P(S) Co-doped Mo2C/C hybrid electrocatalysts for improved hydrogen generation. Carbon 139, 845–852 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.07.043
- Y. Liu, G. Yu, G.D. Li, Y. Sun, T. Asefa et al., Coupling Mo2C with nitrogen-rich nanocarbon leads to efficient hydrogen-evolution electrocatalytic sites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 127(37), 10902–10907 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201504376
- T.T. Yang, W.A. Saidi, Graphene activation explains the enhanced hydrogen evolution on graphene-coated molybdenum carbide electrocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11(7), 2759–2764 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c00615
- G. Chen, T. Wang, J. Zhang, P. Liu, H. Sun et al., Accelerated hydrogen evolution kinetics on NiFe-layered double hydroxide electrocatalysts by tailoring water dissociation active sites. Adv. Mater. 30(10), 1706279 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706279
- S. Ye, F. Luo, T. Xu, P. Zhang, H. Shi et al., Boosting the alkaline hydrogen evolution of Ru nanoclusters anchored on B/N–doped graphene by accelerating water dissociation. Nano Energy 68, 104301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104301
- D.S. Baek, J. Lee, J. Kim, S.H. Joo, Metastable phase-controlled synthesis of mesoporous molybdenum carbides for efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. ACS Catal. 12(12), 7415–7426 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.2c01772
- Y. Lin, M. Zhou, X. Tai, H. Li, X. Han et al., Analytical transmission electron microscopy for emerging advanced materials. Matter 4(7), 2309–2339 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2021.05.005
- H. Jiang, L. Yan, S. Zhang, Y. Zhao, X. Yang et al., Electrochemical surface restructuring of phosphorus-doped carbon@ MoP electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 215 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00737-w
- Y. Huang, Q. Gong, X. Song, K. Feng, K. Nie et al., Mo2C nanops dispersed on hierarchical carbon microflowers for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 10(12), 11337–11343 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b0658
- G. Qian, J. Chen, T. Yu, J. Liu, L. Luo et al., Three-phase heterojunction NiMo-based nano-needle for water splitting at industrial alkaline condition. Nano-Micro Lett. 14(1), 20 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00744-x
- T. Zhang, G. Wen, X. Huang, B. Zhong, H. Yu, Preparation of high purity BCN hollow spheres by pyrolyzing a simple polymeric precursor. CrystEngComm 12(11), 3506–3510 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/c003714a
- X. Yu, P. Han, Z. Wei, L. Huang, Z. Gu et al., Boron-doped graphene for electrocatalytic N2 reduction. Joule 2(8), 1610–1622 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.06.007
- A. Dogra, I. Barlocco, A. Singh, F. Somodi, A. Villa et al., Metal free alkene hydrogenation by B-doped graphitic carbon nitride. Catal. Sci. Technol. 10(9), 3024–3028 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cy00488j
- R. Ma, Y. Zhou, Y. Chen, P. Li, Q. Liu et al., Ultrafine molybdenum carbide nanops composited with carbon as a highly active hydrogen-evolution electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 127(49), 14936–14940 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201506727
- H. Li, F. Yu, X. Ling, H. Wan, M. Zhang et al., Dual-cation-doped MoS2 nanosheets accelerating tandem alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanotechnology 32(44), 445703 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ac17c5
- J.S. Li, Y. Wang, C.H. Liu, S.L. Li, Y.G. Wang et al., Coupled molybdenum carbide and reduced graphene oxide electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 7(1), 11204 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11204
- H. Tabassum, R. Zou, A. Mahmood, Z. Liang, S. Guo, A catalyst-free synthesis of B, N co-doped graphene nanostructures with tunable dimensions as highly efficient metal free dual electrocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 4(42), 16469–16475 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta07214c
- H. Zhang, Z. Ma, J. Duan, H. Liu, G. Liu et al., Active sites implanted carbon cages in core-shell architecture: highly active and durable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 10(1), 684–694 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b05728
- H. Xu, H. Jia, B. Fei, Y. Ha, H. Li et al., Charge transfer engineering via multiple heteroatom doping in dual carbon-coupled cobalt phosphides for highly efficient overall water splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 268, 118404 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118404
- X. Wang, Y. Zheng, W. Sheng, Z.J. Xu, M. Jaroniec et al., Strategies for design of electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution under alkaline conditions. Mater. Today 36, 125–138 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2019.12.003
- T. Shinagawa, A. Garcia-Esparza, K. Takanabe, Insight on Tafel slopes from a microkinetic analysis of aqueous electrocatalysis for energy conversion. Sci. Rep. 5, 13801 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13801
- M.A.R. Anjum, M.H. Lee, J.S. Lee, Boron- and nitrogen-codoped molybdenum carbide nanops imbedded in a BCN network as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. ACS Catal. 8(9), 8296–8305 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b01794
References
C. Li, N. Clament Sagaya Selvam, J. Fang, Shape-controlled synthesis of platinum-based nanocrystals and their electrocatalytic applications in fuel cells. Nano-Micro Lett. 15, 83 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01060-2
B. Jiang, D. Tian, Y. Qiu, X. Song, Y. Zhang et al., High-index faceted nanocrystals as highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00769-2
Y. Yang, Y. Yu, J. Li, Q. Chen, Y. Du et al., Engineering ruthenium-based electrocatalysts for effective hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 160 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00679-3
R. Li, H. Xu, P. Yang, D. Wang, Y. Li et al., Synergistic interfacial and doping engineering of heterostructured NiCo(OH)x-CoyW as an efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 120 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00639-x
B. Guo, Y. Ding, H. Huo, X. Wen, X. Ren et al., Recent advances of transition metal basic salts for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction and overall water electrolysis. Nano-Micro Lett. 15, 57 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01038-0
Z. Chen, X. Duan, W. Wei, S. Wang, B.J. Ni, Iridium-based nanomaterials for electrochemical water splitting. Nano Energy 78, 105270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105270
Q. Yin, C.L. Hill, Water splitting: passing the acid test. Nat. Chem. 10(1), 6–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2921
F. Lu, M. Zhou, Y. Zhou, X. Zeng, First-row transition metal based catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction under alkaline conditions: basic principles and recent advances. Small 13(45), 1701931 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.20170193
J.N. Tiwari, S. Sultan, C.W. Myung, T. Yoon, N. Li et al., Multicomponent electrocatalyst with ultralow Pt loading and high hydrogen evolution activity. Nat. Energy 3(9), 773–782 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-018-0209-x
C. Xie, W. Chen, S. Du, D. Yan, Y. Zhang et al., In-situ phase transition of WO3 boosting electron and hydrogen transfer for enhancing hydrogen evolution on Pt. Nano Energy 71, 104653 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104653
J. Chen, Y. Ha, R. Wang, Y. Liu, H. Xu et al., Inner Co synergizing outer ru supported on carbon nanotubes for efficient pH-universal hydrogen evolution catalysis. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 186 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00933-2
Q. Cheng, C. Hu, G. Wang, Z. Zou, H. Yang et al., Carbon-defect-driven electroless deposition of Pt atomic clusters for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142(12), 5594–5601 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b11524
J. Zhang, E. Wang, S. Cui, S. Yang, X. Zou et al., Single-Atom Pt anchored on oxygen vacancy of monolayer Ti3C2Tx for superior hydrogen evolution. Nano Lett. 22(3), 1398–1405 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c04809
M. Zhou, H. Li, A. Long, B. Zhou, F. Lu et al., Modulating 3d orbitals of Ni atoms on Ni-Pt edge sites enables highly-efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 11(36), 2101789 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202101789
B. Šljukić, M. Vujković, L. Amaral, D.M.F. Santos, R.P. Rocha et al., Carbon-supported Mo2C electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(30), 15505–15512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta02346g
Y. Qiu, Z. Wen, C. Jiang, X. Wu, R. Si et al., Rational design of atomic layers of Pt anchored on Mo2C nanorods for efficient hydrogen evolution over a wide pH range. Small 15(14), e1900014 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201900014
W. Fu, Y. Wang, W. Tian, H. Zhang, J. Li et al., Non-metal single-phosphorus-atom catalysis of hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59(52), 23791–23799 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202011358
H. Vrubel, X. Hu, Molybdenum boride and carbide catalyze hydrogen evolution in both acidic and basic solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51(51), 12703–12706 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201207111
X. Yang, J. Cheng, X. Yang, Y. Xu, W. Sun et al., Facet-tunable coral-like Mo2C catalyst for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 451(4), 138977 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138977
Y. Shi, B. Zhang, Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45(6), 1529–1541 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00434a
J. Greeley, T.F. Jaramillo, J. Bonde, I.B. Chorkendorff, J.K. Norskov, Computational high-throughput screening of electrocatalytic materials for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Mater. 5(11), 909–913 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1752
F. Yu, Y. Gao, Z. Lang, Y. Ma, L. Yin, Electrocatalytic performance of ultrasmall Mo2C affected by different transition metal dopants in hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 10(13), 6080–6087 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr00908b
C. Wan, B.M. Leonard, Iron-doped molybdenum carbide catalyst with high activity and stability for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Mater. 27(12), 4281–4288 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b0062
H. Wei, J. Wang, Q. Lin, Y. Zou, X. Chen et al., Incorporating ultra-small N-doped Mo2C nanops onto 3D N-doped flower-like carbon nanospheres for robust electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 86, 106047 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106047
Y. Lu, C. Yue, Y. Li, W. Bao, X. Guo et al., Atomically dispersed Ni on Mo2C embedded in N, P co-doped carbon derived from polyoxometalate supramolecule for high-efficiency hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 296, 120336 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120336
D. Wang, T. Liu, J. Wang, Z. Wu, N, P(S) Co-doped Mo2C/C hybrid electrocatalysts for improved hydrogen generation. Carbon 139, 845–852 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.07.043
Y. Liu, G. Yu, G.D. Li, Y. Sun, T. Asefa et al., Coupling Mo2C with nitrogen-rich nanocarbon leads to efficient hydrogen-evolution electrocatalytic sites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 127(37), 10902–10907 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201504376
T.T. Yang, W.A. Saidi, Graphene activation explains the enhanced hydrogen evolution on graphene-coated molybdenum carbide electrocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11(7), 2759–2764 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c00615
G. Chen, T. Wang, J. Zhang, P. Liu, H. Sun et al., Accelerated hydrogen evolution kinetics on NiFe-layered double hydroxide electrocatalysts by tailoring water dissociation active sites. Adv. Mater. 30(10), 1706279 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706279
S. Ye, F. Luo, T. Xu, P. Zhang, H. Shi et al., Boosting the alkaline hydrogen evolution of Ru nanoclusters anchored on B/N–doped graphene by accelerating water dissociation. Nano Energy 68, 104301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104301
D.S. Baek, J. Lee, J. Kim, S.H. Joo, Metastable phase-controlled synthesis of mesoporous molybdenum carbides for efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. ACS Catal. 12(12), 7415–7426 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.2c01772
Y. Lin, M. Zhou, X. Tai, H. Li, X. Han et al., Analytical transmission electron microscopy for emerging advanced materials. Matter 4(7), 2309–2339 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2021.05.005
H. Jiang, L. Yan, S. Zhang, Y. Zhao, X. Yang et al., Electrochemical surface restructuring of phosphorus-doped carbon@ MoP electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 215 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00737-w
Y. Huang, Q. Gong, X. Song, K. Feng, K. Nie et al., Mo2C nanops dispersed on hierarchical carbon microflowers for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 10(12), 11337–11343 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b0658
G. Qian, J. Chen, T. Yu, J. Liu, L. Luo et al., Three-phase heterojunction NiMo-based nano-needle for water splitting at industrial alkaline condition. Nano-Micro Lett. 14(1), 20 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00744-x
T. Zhang, G. Wen, X. Huang, B. Zhong, H. Yu, Preparation of high purity BCN hollow spheres by pyrolyzing a simple polymeric precursor. CrystEngComm 12(11), 3506–3510 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/c003714a
X. Yu, P. Han, Z. Wei, L. Huang, Z. Gu et al., Boron-doped graphene for electrocatalytic N2 reduction. Joule 2(8), 1610–1622 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.06.007
A. Dogra, I. Barlocco, A. Singh, F. Somodi, A. Villa et al., Metal free alkene hydrogenation by B-doped graphitic carbon nitride. Catal. Sci. Technol. 10(9), 3024–3028 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cy00488j
R. Ma, Y. Zhou, Y. Chen, P. Li, Q. Liu et al., Ultrafine molybdenum carbide nanops composited with carbon as a highly active hydrogen-evolution electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 127(49), 14936–14940 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201506727
H. Li, F. Yu, X. Ling, H. Wan, M. Zhang et al., Dual-cation-doped MoS2 nanosheets accelerating tandem alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanotechnology 32(44), 445703 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ac17c5
J.S. Li, Y. Wang, C.H. Liu, S.L. Li, Y.G. Wang et al., Coupled molybdenum carbide and reduced graphene oxide electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 7(1), 11204 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11204
H. Tabassum, R. Zou, A. Mahmood, Z. Liang, S. Guo, A catalyst-free synthesis of B, N co-doped graphene nanostructures with tunable dimensions as highly efficient metal free dual electrocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 4(42), 16469–16475 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta07214c
H. Zhang, Z. Ma, J. Duan, H. Liu, G. Liu et al., Active sites implanted carbon cages in core-shell architecture: highly active and durable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 10(1), 684–694 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b05728
H. Xu, H. Jia, B. Fei, Y. Ha, H. Li et al., Charge transfer engineering via multiple heteroatom doping in dual carbon-coupled cobalt phosphides for highly efficient overall water splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 268, 118404 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118404
X. Wang, Y. Zheng, W. Sheng, Z.J. Xu, M. Jaroniec et al., Strategies for design of electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution under alkaline conditions. Mater. Today 36, 125–138 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2019.12.003
T. Shinagawa, A. Garcia-Esparza, K. Takanabe, Insight on Tafel slopes from a microkinetic analysis of aqueous electrocatalysis for energy conversion. Sci. Rep. 5, 13801 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13801
M.A.R. Anjum, M.H. Lee, J.S. Lee, Boron- and nitrogen-codoped molybdenum carbide nanops imbedded in a BCN network as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. ACS Catal. 8(9), 8296–8305 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b01794